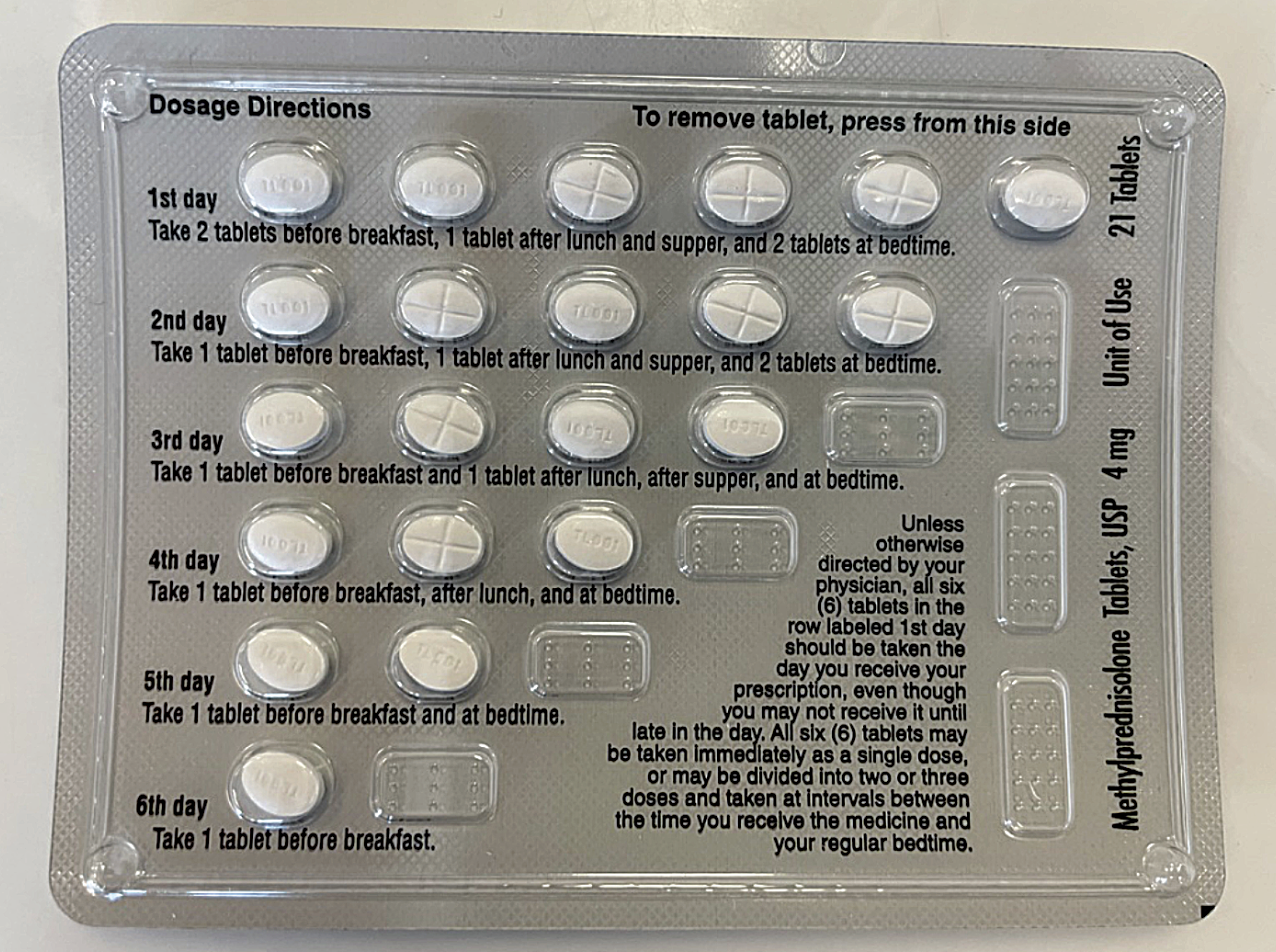
Taking 10mg of prednisone daily requires careful monitoring and understanding. This dosage is commonly prescribed for various inflammatory conditions, but it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution. Your doctor tailored this prescription to your specific needs, considering your health history and the severity of your condition.
Expect potential side effects, including increased appetite, weight gain, mood changes, and insomnia. Regular blood pressure checks are highly recommended due to prednisone’s impact on blood pressure levels. Maintain open communication with your doctor about any symptoms you experience, both expected and unexpected. Early detection and management are key for a positive outcome.
Dietary adjustments may be necessary. Focus on a balanced diet low in sodium and saturated fats to mitigate potential side effects like weight gain and elevated blood pressure. Regular exercise, as advised by your physician, complements medication’s effects and contributes to overall well-being. Remember, prednisone should be taken as directed–never adjust your dosage independently.
Important Note: This information is for educational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your physician or pharmacist before starting, stopping, or changing your prednisone regimen. They can provide personalized guidance based on your unique circumstances.
Specific instructions regarding duration of treatment, potential drug interactions, and alternative options will be provided by your healthcare provider. Be proactive in your health management and schedule regular follow-up appointments.
- 10 mg of Prednisone Daily: A Detailed Guide
- Understanding Prednisone’s Role in Treatment
- Common Conditions Treated with 10mg Prednisone
- Potential Side Effects and How to Manage Them
- Common Side Effects
- Less Common, But Serious Side Effects
- Medication Interactions: What to Avoid
- Tapering Off Prednisone: A Crucial Step
- Understanding Your Tapering Schedule
- Managing Potential Side Effects During Tapering
- Long-Term Effects of Prednisone Use
- Cardiovascular Risks
- Monitoring Your Health While on Prednisone
- When to Consult Your Doctor
10 mg of Prednisone Daily: A Detailed Guide
Always consult your doctor before starting or changing any medication, including prednisone. This dosage is common, but individual needs vary greatly.
Expect to experience some side effects. Common ones include increased appetite, weight gain, mood changes, and trouble sleeping. These are often manageable with lifestyle adjustments. Report any severe or concerning side effects to your doctor immediately.
Your doctor will likely monitor you regularly for potential side effects. Regular blood tests may be required to check your blood pressure and blood sugar levels. These tests help to ensure the medication is working as intended and to detect any potential complications.
Consider these practical tips for managing 10mg of prednisone daily:
| Tip | Details |
|---|---|
| Diet | Eat a balanced diet to mitigate weight gain. Focus on fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins. |
| Exercise | Regular, moderate exercise helps manage weight and improve mood. Consult your doctor before starting a new workout routine. |
| Sleep Hygiene | Prioritize good sleep habits. This includes maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensuring a dark, quiet sleep environment. |
| Medication Timing | Take the medication at the same time each day, as prescribed by your physician. This helps maintain consistent blood levels. |
| Hydration | Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help prevent dehydration, a common side effect. |
Never stop taking prednisone suddenly. Your doctor will provide a tapering schedule to gradually reduce your dosage to minimize withdrawal symptoms. This is crucial for preventing potential health complications.
Your doctor is your best resource for information specific to your health needs and any questions you might have about your medication. Do not hesitate to contact them for clarification or support.
Understanding Prednisone’s Role in Treatment
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, powerfully reduces inflammation and suppresses the immune system. This makes it highly effective for treating various conditions, but understanding its specific role is crucial for safe and successful use.
Doctors prescribe prednisone for:
- Autoimmune diseases: Conditions like lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease benefit from prednisone’s ability to curb immune system overactivity.
- Allergic reactions: Severe allergic reactions, such as anaphylaxis, often require prednisone’s rapid anti-inflammatory action.
- Asthma exacerbations: Prednisone helps control severe asthma attacks by reducing airway inflammation.
- Certain cancers: In some cases, prednisone is part of a cancer treatment plan, often in combination with chemotherapy.
- Organ transplantation: Prednisone helps prevent organ rejection by suppressing the immune response.
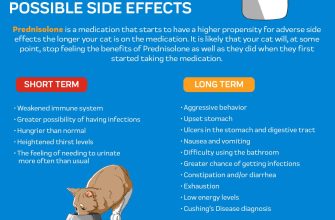
However, prednisone isn’t a long-term solution for most conditions. Prolonged use carries side effects like:
- Increased blood sugar levels
- Weight gain
- Increased risk of infections
- Osteoporosis
- Mood changes
Dosage, duration, and monitoring are therefore tailored to individual needs. Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. They will adjust your dosage and monitor you for potential side effects. Open communication with your physician is key to managing your treatment effectively and safely. Regular check-ups are needed to track progress and minimize risks.
Common Conditions Treated with 10mg Prednisone
Ten milligrams of prednisone daily often treats inflammatory conditions. Autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis frequently benefit from this dosage, reducing joint pain and swelling. Lupus, another autoimmune disease, may also see symptom improvement with this prednisone regimen, managing flares and improving overall well-being.
Severe allergic reactions, such as those causing swelling or breathing difficulties, can be managed with 10mg of prednisone, providing rapid relief. Similarly, certain inflammatory bowel diseases, like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, may utilize this dosage to control inflammation and reduce symptoms like diarrhea and abdominal pain.
Some dermatological conditions, particularly severe eczema or psoriasis, respond well to this dose of prednisone, calming inflammation and improving skin condition. Additionally, certain lung conditions like asthma or sarcoidosis may benefit from 10mg prednisone for inflammation control.
Remember, this information is for general knowledge only. Always consult your doctor before starting or changing any medication, including prednisone. They will assess your individual needs and determine the appropriate dosage and treatment plan.
Potential Side Effects and How to Manage Them
Prednisone, while effective, can cause side effects. Understanding these and how to mitigate them is key to a positive experience.
Common Side Effects
- Increased appetite and weight gain: Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean protein. Portion control is crucial. Regular exercise helps combat weight gain.
- Mood swings: Open communication with your doctor and loved ones is vital. Consider stress-reduction techniques like meditation or yoga.
- Insomnia: Avoid caffeine and alcohol before bed. Establish a relaxing bedtime routine. Talk to your doctor if sleep disturbances persist.
- Increased blood sugar: Monitor your blood sugar regularly, as advised by your doctor. Maintain a healthy diet and discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider. They may recommend adjustments to your medication or lifestyle.
- Increased blood pressure: Regular blood pressure monitoring is necessary. Dietary changes, such as reducing sodium intake, can help. Your doctor might adjust your medications accordingly.
Less Common, But Serious Side Effects
While less frequent, some side effects require immediate medical attention:
- Severe allergic reactions: Symptoms include hives, swelling, difficulty breathing. Seek immediate medical help if you experience these.
- Muscle weakness: Report any unusual muscle weakness or pain to your doctor.
- Bone thinning (osteoporosis): Your doctor may recommend calcium and vitamin D supplements and discuss strategies to prevent bone loss. Regular weight-bearing exercise is beneficial.
- Increased risk of infection: Practice good hygiene and avoid contact with sick individuals. Report any signs of infection to your doctor immediately.
Remember to consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized advice. They can provide tailored recommendations based on your individual health needs and circumstances. Regular check-ups help monitor your progress and address any concerns promptly.
Medication Interactions: What to Avoid
Avoid combining prednisone with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen. This combination increases your risk of stomach ulcers and bleeding.
Don’t take prednisone with blood thinners like warfarin or aspirin without consulting your doctor. Prednisone can alter the effectiveness of these medications, potentially leading to excessive bleeding.
Be cautious when using prednisone with diabetes medications like insulin or oral hypoglycemics. Prednisone can raise your blood sugar levels, requiring adjustments to your diabetes treatment plan.
Avoid combining prednisone with medications that weaken your immune system, such as immunosuppressants. This combination significantly increases your susceptibility to infections.
Some antibiotics can interact with prednisone. Always inform your doctor or pharmacist about all medications you are taking, including antibiotics, to prevent potential interactions.
The following table summarizes potential interactions and recommended actions:
| Medication Class | Specific Examples | Potential Interaction | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| NSAIDs | Ibuprofen, Naproxen | Increased risk of ulcers and bleeding | Avoid concurrent use; discuss alternatives with your doctor. |
| Anticoagulants | Warfarin, Aspirin | Increased bleeding risk | Careful monitoring; potential dose adjustments. |
| Diabetes Medications | Insulin, Metformin | Increased blood sugar | Monitor blood sugar closely; potential dose adjustments. |
| Immunosuppressants | Cyclosporine, Tacrolimus | Increased infection risk | Avoid concurrent use unless medically necessary; close monitoring. |
| Antibiotics | Many | Variable effects | Inform your doctor or pharmacist about all medications. |
Remember to always discuss any new medications or supplements with your doctor or pharmacist before starting them, especially while taking prednisone.
Tapering Off Prednisone: A Crucial Step
Never stop prednisone abruptly. Your doctor will create a personalized tapering schedule, usually decreasing your dose gradually over several weeks or months. This prevents adrenal insufficiency, a serious condition where your body doesn’t produce enough cortisol.
Understanding Your Tapering Schedule
Your doctor will provide specific instructions. A common approach involves reducing your dose by a small amount (e.g., 2.5mg) every few days or weeks. Closely monitor your body’s response. Report any unusual symptoms immediately.
- Follow your prescription exactly. Don’t adjust the dosage without consulting your doctor.
- Keep track of your daily dose. Use a medication log or calendar to stay organized.
- Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments. Your doctor will monitor your progress and adjust the schedule as needed.
Managing Potential Side Effects During Tapering
As your body adjusts, you may experience withdrawal symptoms. These can vary, but commonly include fatigue, muscle weakness, joint pain, and nausea.
- Report any new or worsening symptoms to your physician. They may need to adjust your tapering plan.
- Maintain a healthy diet and lifestyle. Adequate sleep, regular exercise, and a balanced diet can help your body cope with the changes.
- Discuss potential side effect management with your doctor. They may suggest strategies to alleviate discomfort.
Remember, consistent communication with your doctor is key to a safe and successful prednisone taper. Openly discuss any concerns you have.
Long-Term Effects of Prednisone Use
Taking prednisone daily for extended periods carries risks. Bone loss (osteoporosis) is a significant concern. Regular weight-bearing exercise and a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D are crucial countermeasures. Your doctor might recommend bone density scans and discuss medications to protect your bones.
Cardiovascular Risks
Prolonged prednisone use increases blood pressure and cholesterol levels, raising your risk of heart disease and stroke. Regular blood pressure and cholesterol monitoring are essential. Lifestyle changes like a heart-healthy diet and regular physical activity can mitigate these risks. Your physician may prescribe medications to manage blood pressure and cholesterol.
Increased risk of infections is another long-term consequence. Prednisone weakens your immune system, making you more vulnerable to illness. Practicing good hygiene, getting enough sleep, and receiving recommended vaccinations are vital. Report any signs of infection to your doctor immediately.
Prednisone can cause glucose intolerance and increase your chances of developing diabetes. Regular blood sugar checks are necessary. Maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and following a balanced diet will help control blood sugar levels. Your doctor might prescribe medication for diabetes if needed.
Mood changes, such as anxiety and depression, can occur with long-term prednisone use. Open communication with your doctor and, if necessary, a mental health professional is vital. Consider stress-reduction techniques like meditation or yoga.
Cataracts and glaucoma are potential eye problems associated with prolonged prednisone use. Regular eye exams are crucial. Your ophthalmologist can detect and manage these conditions.
Muscle weakness and thinning of the skin are other possible long-term effects. A balanced diet, strength training, and use of moisturizers can help alleviate some symptoms. However, discuss any significant concerns with your doctor immediately.
Monitoring Your Health While on Prednisone
Schedule regular check-ups with your doctor. These appointments allow for monitoring blood pressure, blood sugar, and weight.
Track your weight daily. Prednisone can cause fluid retention and weight gain; consistent monitoring helps you and your doctor identify changes promptly.
Monitor your blood pressure regularly at home. Prednisone can increase blood pressure; consistent measurements help detect potential problems.
Pay close attention to your blood sugar levels, especially if you have diabetes or pre-diabetes. Prednisone can impact blood sugar control.
Observe your skin for any unusual bruising or thinning. These are potential side effects; report any concerns to your physician immediately.
Watch for changes in your mood or sleep patterns. Prednisone can affect mental well-being and sleep; discuss any significant shifts with your doctor.
Report any muscle weakness or bone pain. Prednisone can weaken bones and muscles, increasing fracture risk.
Maintain a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean protein. A balanced diet supports overall health while on medication.
Engage in regular, low-impact exercise, as approved by your doctor. Exercise helps manage weight and improve mood.
Report any new or worsening symptoms to your doctor immediately. Early detection of complications is key to successful management.
When to Consult Your Doctor
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience severe stomach pain, vomiting, or difficulty breathing. These could indicate serious side effects.
Report any unusual bruising or bleeding. Prednisone can thin your blood, increasing your risk.
If you notice changes in your mood, such as increased anxiety, depression, or irritability, schedule an appointment. Mental health changes are a potential side effect.
Increased thirst, frequent urination, or blurred vision may signal high blood sugar. Alert your physician to these symptoms.
Muscle weakness or bone pain warrants immediate medical attention. Prednisone can weaken bones, increasing fracture risk.
If you experience any new or worsening health problems, even seemingly unrelated to prednisone, inform your doctor. Open communication helps ensure optimal health.
Regular monitoring of blood pressure and blood sugar levels is recommended during prednisone treatment. Follow your doctor’s instructions for these checks.
Don’t hesitate to contact your doctor if you have questions or concerns about your prednisone treatment, regardless of severity. Your doctor is your best resource.