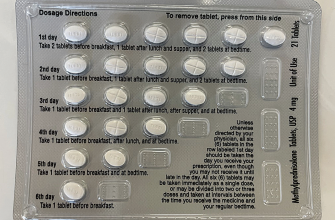
Prednisone 50 mg is a potent corticosteroid; understand its dosage is crucial for managing potential side effects. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Never adjust your dosage without consulting them.
This dose often treats severe inflammation or autoimmune conditions. Common applications include managing severe allergic reactions, inflammatory bowel disease flares, and lupus exacerbations. However, long-term use carries significant risks, including increased blood sugar, bone thinning, and increased susceptibility to infections. Regular monitoring of blood pressure and blood sugar levels is vital.
Short-term use (a few weeks) typically presents fewer risks than long-term use. Your physician will carefully assess your condition and tailor the treatment duration, aiming for the shortest effective course. Always discuss potential side effects and mitigation strategies with your doctor. They can help you manage any discomfort and monitor for serious complications. Remember: open communication with your healthcare provider is paramount.
This information is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Consult your physician or pharmacist for personalized guidance regarding 50 mg prednisone treatment.
- 50 mg Prednisone: A Detailed Overview
- Prednisone 50mg: Dosage and Administration
- Oral Administration
- Important Considerations
- Potential Side Effects
- Specific Instructions
- Common Side Effects of 50mg Prednisone
- Potential Interactions with Other Medications
- Drugs Affected by Prednisone
- Drugs Affecting Prednisone
- Long-Term Use and Withdrawal of 50mg Prednisone
- Tapering Off Prednisone
- Monitoring and Support
- When to Consult a Doctor Regarding 50mg Prednisone
- Understanding Your Prednisone Treatment
- Prednisone and Your Lifestyle
50 mg Prednisone: A Detailed Overview
Prednisone at this dosage is a potent corticosteroid, requiring careful monitoring. Consult your doctor immediately if you experience severe side effects.
Common side effects include:
- Increased appetite and weight gain
- Mood swings and insomnia
- Fluid retention and swelling
- Increased blood sugar
- Muscle weakness
Less common, but serious side effects warrant immediate medical attention:
- Severe allergic reactions (rash, hives, difficulty breathing)
- Vision changes
- Severe stomach pain
- Easy bruising or bleeding
- Slow wound healing
Managing 50 mg Prednisone effectively involves:
- Following your doctor’s prescribed dosage and duration precisely.
- Regular blood tests to monitor blood sugar, potassium, and other vital indicators.
- Maintaining a healthy diet to mitigate weight gain and blood sugar fluctuations. Focus on fruits, vegetables, and lean protein.
- Regular exercise, as tolerated, to help manage weight and mood.
- Careful monitoring for side effects and promptly reporting any concerns to your doctor.
- Gradual tapering of the dosage under your doctor’s guidance to minimize withdrawal symptoms.
Note: This information is for general knowledge and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting, stopping, or changing any medication.
Prednisone 50mg: Dosage and Administration
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Prednisone dosage varies greatly depending on your specific condition and response to treatment. A 50mg dose is considered a high dose and is typically used for severe inflammation or autoimmune disorders.
Oral Administration
Prednisone 50mg tablets are usually taken once daily, often in the morning with food to minimize stomach upset. Some doctors may prescribe a divided dose to reduce side effects. Never crush or chew the tablets; swallow them whole with water.
Important Considerations
Regular blood tests are needed to monitor your response to prednisone and check for side effects. Your doctor will adjust your dose based on these results. Never abruptly stop taking prednisone; tapering off the medication under medical supervision is critical to prevent withdrawal symptoms.
Potential Side Effects
High-dose prednisone can cause various side effects, including weight gain, increased blood sugar, mood changes, and increased risk of infection. Report any new or worsening symptoms to your doctor immediately. They may adjust your dose or prescribe other medications to manage side effects.
Specific Instructions
Your doctor provides personalized instructions based on your health. These may include specific timing for medication intake, dietary recommendations, and activity limitations. Adherence to these guidelines is vital for successful treatment and minimizing risks.
Common Side Effects of 50mg Prednisone
Taking 50mg of prednisone daily can cause various side effects. Expect some changes in your body, and monitor yourself closely.
Weight gain is common, often noticeable around the midsection. Increased appetite contributes to this. Maintain a healthy diet and increase physical activity to mitigate this.
Mood swings are frequently reported. Irritability, anxiety, and even depression can occur. Talk to your doctor; they might suggest support or adjust your medication.
High blood sugar is a risk, especially if you have diabetes. Regular blood sugar checks are critical. Your doctor can help manage this with diet adjustments or other medications.
Increased blood pressure is another potential side effect. Regular monitoring is needed. Your doctor might recommend lifestyle changes or prescribe medication to control it.
Insomnia is quite common. Establishing a relaxing bedtime routine, ensuring a dark and quiet sleep environment, and avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bed can help.
Muscle weakness and thinning of the bones (osteoporosis) are long-term risks. Weight-bearing exercises and a calcium-rich diet can help minimize bone loss. Discuss bone density testing with your physician.
Fluid retention can lead to swelling in your ankles, face, and hands. Reducing sodium intake and increasing potassium intake may help. Consult your physician regarding this symptom.
These are just some of the possibilities. Report any concerning symptoms to your doctor immediately. They can help manage side effects and adjust your treatment plan accordingly.
Potential Interactions with Other Medications
Always inform your doctor and pharmacist about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs. Prednisone, at a 50mg dose, can interact with various medications. This includes but isn’t limited to:
Drugs Affected by Prednisone
Blood thinners (anticoagulants): Prednisone may reduce the effectiveness of warfarin and other anticoagulants, increasing your risk of blood clots. Regular blood tests are needed to monitor your clotting time while on prednisone. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Combining prednisone with NSAIDs like ibuprofen or naproxen increases the risk of stomach ulcers and bleeding. Your doctor might suggest protective medications. Diabetes medications: Prednisone can raise blood sugar levels, potentially requiring adjustments to your diabetes medication. Close monitoring of blood sugar is vital. Potassium-wasting diuretics: Prednisone can exacerbate potassium loss, potentially leading to dangerously low potassium levels. Your doctor will likely monitor your potassium levels.
Drugs Affecting Prednisone
Certain antifungal medications: Some antifungals can increase prednisone levels in your body. Your doctor may adjust your prednisone dosage if you’re taking antifungals. Drugs that affect liver enzymes: Since prednisone is metabolized by the liver, medications that affect liver enzymes can alter prednisone levels. This requires careful monitoring and potential dose adjustments. Immunosuppressants: Taking prednisone with other immunosuppressants elevates your risk of infection and other side effects. Your doctor will carefully consider this combination.
This information is not exhaustive. Consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized advice about potential drug interactions with your specific medications and health conditions.
Long-Term Use and Withdrawal of 50mg Prednisone
50mg of prednisone is a high dose, and long-term use carries significant risks. Your doctor should carefully monitor you for side effects. These can include weight gain, increased blood sugar, high blood pressure, bone thinning (osteoporosis), increased risk of infection, mood changes, and cataracts. Regular blood tests are crucial to manage these potential complications.
Tapering Off Prednisone
Stopping prednisone abruptly after prolonged use is dangerous and can lead to adrenal insufficiency, a life-threatening condition. Your doctor will create a gradual tapering schedule, slowly reducing your dose over weeks or months. This prevents sudden hormonal shifts. A typical tapering plan might involve reducing the dose by 5-10mg every few days or weeks, depending on your individual response and the duration of your treatment. Close monitoring is vital throughout the process. During this time, expect potential withdrawal symptoms like fatigue, joint pain, and nausea. Your doctor can help manage these symptoms.
Monitoring and Support
Regular checkups are necessary to monitor your progress, adjust your medication, and address any issues promptly. Open communication with your doctor is key. Don’t hesitate to discuss any concerns or changes in your health. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle – including diet, exercise, and stress management – supports your body during this transition. Remember, consistency with your prescribed plan is paramount for a safe and successful withdrawal.
When to Consult a Doctor Regarding 50mg Prednisone
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms while taking 50mg of prednisone:
- Severe headache
- Vision changes
- Rapid heartbeat
- Swelling in your legs or ankles
- Increased thirst or urination
- Muscle weakness
- Easy bruising or bleeding
- Severe stomach pain
- Difficulty breathing
- Mental changes, such as confusion or irritability
These symptoms could indicate serious side effects. Prompt medical attention is necessary.
Understanding Your Prednisone Treatment
Regularly scheduled check-ups are vital throughout your prednisone course. Your doctor will monitor your blood pressure, blood sugar, and other relevant factors to assess your response to the medication and make necessary adjustments.
Prednisone and Your Lifestyle
Inform your doctor about all medications you take, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Discuss any dietary changes or exercise plans you intend to implement. This helps your doctor ensure your safety and efficacy of the treatment.
| Symptom | Action |
|---|---|
| Mild side effects (e.g., mild indigestion) | Discuss with your doctor; they may suggest adjustments or alternative treatments. |
| Severe side effects (listed above) | Seek immediate medical attention. |
| Concerns about medication or treatment | Contact your doctor for clarification and guidance. |