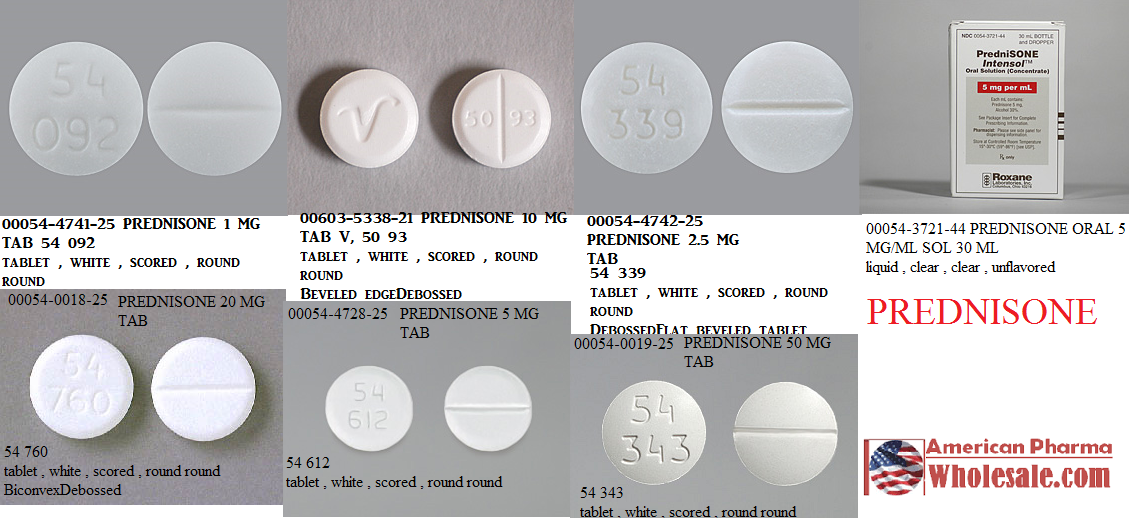
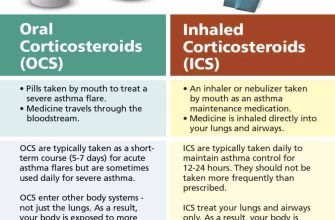
Need to understand a 500mg prednisone prescription? This dosage is a high dose, often used for severe inflammation or autoimmune conditions. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely; never adjust your dose independently.
At this level, expect potential side effects like weight gain, increased appetite, mood changes, and insomnia. Regular blood pressure monitoring is vital, as prednisone can elevate blood pressure. Your physician will likely schedule regular check-ups to assess your progress and manage these potential issues.
Managing side effects requires proactive steps. A balanced diet, regular exercise (as your doctor approves), and stress reduction techniques can help mitigate some of the negative impacts. Open communication with your doctor is key – report any concerning symptoms immediately.
Remember, 500mg prednisone is a potent medication. Do not abruptly stop taking it; tapering off under medical supervision is crucial to prevent withdrawal symptoms. This gradual reduction is specifically designed to minimize discomfort and ensure your body adjusts safely. Consult your doctor if you have any questions or experience any unexpected effects.
- 500 mg Prednisone: A Detailed Overview
- What is Prednisone and How Does it Work?
- 500 mg Prednisone: A High Dose – Understanding the Implications
- Common Uses for High-Dose Prednisone (500 mg)
- Potential Side Effects of a 500 mg Prednisone Dose
- Metabolic Effects
- Gastrointestinal Effects
- Other Potential Effects
- Important Note:
- Managing Side Effects of High-Dose Prednisone
- Addressing Common Side Effects
- Important Considerations
- Important Precautions and Drug Interactions
- Interactions with Other Medications
- Other Precautions
- Tapering Off Prednisone: A Crucial Step
- Monitoring Your Health While on 500 mg Prednisone
- When to Contact Your Doctor Regarding 500 mg Prednisone
500 mg Prednisone: A Detailed Overview
A 500 mg dose of prednisone is a high dose, typically used for severe inflammation or immune system disorders. This requires close medical supervision.
Potential Uses: This high dosage might be prescribed for conditions like severe allergic reactions, acute exacerbations of chronic inflammatory diseases (such as lupus or Crohn’s disease), or certain cancers.
Important Note: This is not a self-prescribing guide. A physician determines the appropriate dose and duration based on individual needs and response.
Potential Side Effects: High-dose prednisone carries significant side effects. These can include increased blood sugar, weight gain, fluid retention, mood changes (including anxiety and depression), insomnia, increased risk of infections, and bone thinning. Serious side effects are possible.
Monitoring: Regular blood tests and doctor visits are crucial to monitor side effects and adjust the dosage as needed. Close monitoring helps prevent or manage complications.
Tapering: Prednisone should be tapered down gradually under medical supervision. Abrupt cessation can lead to adrenal insufficiency.
Alternative Treatments: Your doctor will consider alternative treatments or a combination therapy to minimize prednisone’s side effects and treatment duration.
Specific Instructions: Follow your physician’s instructions meticulously regarding dosage, timing, and duration. Report any concerning symptoms immediately.
Lifestyle Considerations: Maintain a healthy diet and lifestyle. Regular exercise, as advised by your doctor, can support overall health and mitigate certain side effects.
This information provides a general overview. Consult your doctor for personalized guidance and treatment.
What is Prednisone and How Does it Work?
Prednisone is a corticosteroid medication, a powerful anti-inflammatory drug. It mimics the effects of cortisol, a hormone your body naturally produces to reduce swelling and inflammation.
Prednisone works by binding to specific receptors inside your cells. This binding triggers a cascade of events that decreases inflammation, suppresses your immune system, and reduces allergic reactions. It affects various bodily processes, impacting how your body handles stress and inflammation.
Doctors prescribe Prednisone for a wide range of conditions, including:
| Condition | How Prednisone Helps |
|---|---|
| Autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus, rheumatoid arthritis) | Reduces inflammation and immune system activity. |
| Allergies and asthma | Reduces inflammation in airways and decreases allergic reactions. |
| Severe skin conditions (e.g., eczema, psoriasis) | Reduces inflammation and itching. |
| Certain cancers | Reduces tumor size and related symptoms in some cases. |
| Organ transplant rejection | Suppresses immune response to prevent rejection. |
Keep in mind: Prednisone has potential side effects, including weight gain, increased blood sugar, mood changes, and weakened bones. Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully and discuss any concerns you have about the medication.
500 mg Prednisone: A High Dose – Understanding the Implications
A 500 mg daily dose of prednisone is significantly higher than typical starting doses. This high dosage carries increased risk of side effects. Close medical supervision is crucial.
Expect potential side effects like fluid retention, increased blood pressure, mood swings, increased blood sugar, and insomnia. You might experience weight gain due to increased appetite and fluid retention. These effects can vary greatly among individuals.
Gastrointestinal issues such as heartburn, nausea, and ulcers are possible. Bone thinning (osteoporosis) is a long-term concern with high-dose prednisone use. Weakened immunity increases your vulnerability to infections.
Your doctor will likely monitor your blood pressure, blood sugar, and potassium levels regularly. Regular blood tests are needed to detect and manage potential complications. They’ll also need to assess your bone density at intervals.
| Potential Side Effect | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|
| Increased Blood Pressure | Dietary changes, blood pressure monitoring, potential medication adjustments |
| Increased Blood Sugar | Dietary control, blood glucose monitoring, potential insulin or oral medication |
| Osteoporosis | Calcium and Vitamin D supplementation, weight-bearing exercise, bone density monitoring |
| Gastrointestinal Issues | Dietary adjustments, antacids, or other medication to protect the stomach lining |
| Insomnia | Avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bed, establishing a consistent sleep schedule |
Prednisone withdrawal should always be gradual, under close medical supervision. Abrupt cessation can lead to serious complications. Your doctor will design a tapering schedule to minimize withdrawal symptoms.
This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional for any questions about your treatment. Never alter your medication regimen without their guidance.
Common Uses for High-Dose Prednisone (500 mg)
High-dose prednisone (500 mg) is a powerful medication reserved for serious conditions. Its use requires close medical supervision.
- Severe Allergic Reactions: Anaphylaxis, a life-threatening allergic reaction, often necessitates this high dosage for rapid symptom control. Careful monitoring in a hospital setting is critical.
- Acute Exacerbations of Autoimmune Diseases: Diseases like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis may flare dramatically, requiring high-dose prednisone for short-term inflammation reduction. This is often a bridge to other therapies.
- Severe Asthma Attacks: Intractable asthma exacerbations, unresponsive to standard treatments, might benefit from a short course of high-dose prednisone to gain breathing control. This should be done under strict medical guidance.
- Organ Transplant Rejection: High-dose prednisone, often combined with other immunosuppressants, helps prevent organ rejection immediately after transplant surgery. It forms part of a complex treatment plan.
- Certain Cancers: In some cases, prednisone at high doses plays a role in cancer treatment, typically as part of a chemotherapy regimen. The specifics depend heavily on the type and stage of cancer.
- Brain Swelling (Cerebral Edema): Reducing brain swelling after a serious head injury or stroke sometimes necessitates high-dose corticosteroids like prednisone. This is usually a short-term intervention.
Remember: High-dose prednisone has significant side effects. Your doctor will weigh the risks and benefits carefully. This information is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always discuss treatment options with your physician.
- Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely regarding dosage and duration.
- Report any unusual side effects immediately.
- Understand the potential long-term effects of high-dose steroid use.
Potential Side Effects of a 500 mg Prednisone Dose
A 500 mg dose of prednisone is a high dose, significantly increasing the risk of side effects. Expect potential impacts on various body systems.
Metabolic Effects
Weight gain is common, often stemming from increased appetite and fluid retention. Monitor your weight and adjust your diet accordingly. Increased blood sugar can occur, potentially triggering or worsening diabetes. Regular blood glucose monitoring is advised. Increased cholesterol and triglycerides are also possible, increasing cardiovascular risk. Discuss these with your doctor, and consider lifestyle changes like diet and exercise.
Gastrointestinal Effects
Prednisone can cause gastritis and ulcers. Your doctor might prescribe medication to protect your stomach lining. Nausea, vomiting, and heartburn are also possible. Small, frequent meals can help mitigate these.
Other Potential Effects
Fluid retention can lead to swelling in the legs and ankles. Increased blood pressure is a serious concern, requiring regular monitoring. Mood changes ranging from anxiety and irritability to depression are possible. Open communication with your doctor is critical for managing these. Weakened immune system increases susceptibility to infections. Practice good hygiene and inform your doctor immediately if you develop any signs of infection. Long-term use can cause osteoporosis; discuss bone density monitoring with your physician. Muscle weakness and thinning skin can also occur.
Important Note:
This information is not exhaustive. Your individual experience may vary. Always consult your doctor regarding any concerns or side effects you experience while taking prednisone.
Managing Side Effects of High-Dose Prednisone
High-dose prednisone (500mg) can cause significant side effects. Address these proactively for better management.
Addressing Common Side Effects
- Weight gain: Maintain a balanced diet low in processed foods, refined sugars, and unhealthy fats. Increase physical activity gradually. Consult a dietitian for personalized guidance.
- Fluid retention: Reduce sodium intake. Drink plenty of water to flush out excess fluids. Your doctor might suggest diuretics.
- Increased blood sugar: Monitor blood glucose levels regularly, especially if you have diabetes. Your doctor might adjust your diabetes medication. Follow a diabetic-friendly diet.
- Mood changes (irritability, anxiety, depression): Communicate openly with your doctor. They may recommend therapy or medication to manage mood swings. Prioritize stress-reduction techniques like meditation or yoga.
- Insomnia: Avoid caffeine and alcohol before bed. Establish a relaxing bedtime routine. Your doctor might suggest sleep aids, but only with their approval.
- Muscle weakness: Engage in gentle exercise, such as walking or swimming, to maintain muscle strength. Avoid strenuous activity. Consult a physical therapist for guidance.
- Osteoporosis risk: Increase calcium and vitamin D intake through diet or supplements. Engage in weight-bearing exercises. Your doctor may prescribe medication to protect your bones.
- Increased risk of infection: Practice good hygiene. Avoid crowds during flu season. Report any signs of infection immediately to your doctor.
- Gastrointestinal issues (heartburn, ulcers): Consume smaller, more frequent meals. Avoid spicy or acidic foods. Your doctor may prescribe medication to protect your stomach lining.
Important Considerations
- Regular monitoring: Attend all scheduled appointments with your doctor for blood tests and check-ups.
- Gradual tapering: Prednisone should be tapered gradually under medical supervision to minimize withdrawal symptoms. Never stop abruptly.
- Open communication: Report any new or worsening symptoms to your doctor immediately.
- Support system: Lean on family and friends for emotional and practical support. Consider joining a support group.
Remember, managing side effects is crucial for successful prednisone treatment. Active participation and close communication with your healthcare provider are key.
Important Precautions and Drug Interactions
Avoid alcohol while taking prednisone; it increases the risk of stomach ulcers and bleeding. Monitor your blood sugar regularly, especially if you have diabetes, as prednisone can raise blood sugar levels. Report any unusual bruising or bleeding to your doctor immediately. Prednisone weakens your immune system, so avoid contact with sick individuals.
Interactions with Other Medications
Prednisone interacts with many medications. Warfarin (Coumadin) and other blood thinners increase the risk of bleeding when combined with prednisone. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen raise the risk of stomach ulcers and bleeding. Certain antifungal medications and some medications for HIV can also interact negatively with prednisone. Always inform your doctor and pharmacist of all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking.
Other Precautions
Be cautious of sudden stops of prednisone; your doctor should help you taper off the medication to prevent withdrawal symptoms. Report any symptoms such as vision changes, severe headache, or swelling in your legs or ankles to your doctor promptly. Maintain a healthy diet and exercise regularly to mitigate potential side effects. Prednisone can increase your appetite, leading to weight gain. Regular monitoring of your blood pressure is recommended, as it can fluctuate with prednisone use.
Tapering Off Prednisone: A Crucial Step
Never stop prednisone abruptly. A gradual reduction, or tapering, is vital to prevent adrenal insufficiency and other withdrawal symptoms. Your doctor will create a personalized tapering schedule, but a common approach involves decreasing your dose by a small amount (e.g., 5 mg) every few days or weeks.
Monitor for symptoms. Carefully watch for signs of adrenal insufficiency, such as fatigue, muscle weakness, nausea, dizziness, and low blood pressure. Report these immediately to your physician. A cortisol level test may be necessary to check adrenal function.
Expect some withdrawal effects. These can range from mild discomfort to more significant issues. Common symptoms include headaches, joint pain, and mood changes. Your doctor can help manage these with medication or other strategies.
Follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Don’t adjust your dosage without consulting them. Skipping doses or reducing too quickly can lead to serious complications.
Stay hydrated. Prednisone can cause fluid retention, so increasing your water intake during tapering helps flush out excess fluid and supports overall health.
Maintain a healthy lifestyle. Proper nutrition, regular exercise (as advised by your doctor), and stress management techniques aid in recovery and minimize withdrawal symptoms.
Schedule regular check-ups. These are vital to monitor your progress, adjust your tapering schedule if needed, and address any arising health concerns.
Tapering off prednisone takes time and patience. Work closely with your doctor throughout this process to ensure a safe and successful transition.
Monitoring Your Health While on 500 mg Prednisone
Schedule regular appointments with your doctor. Blood pressure and blood sugar checks are crucial, ideally weekly at the start of treatment. Monitor your weight daily; significant changes warrant immediate doctor contact.
Pay close attention to your diet. Increase potassium intake through foods like bananas and potatoes to counteract prednisone’s effects. Limit sodium and processed foods to control blood pressure. Maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables.
Be vigilant about infections. Even minor symptoms like a cough or sore throat require prompt medical attention. Your immune system is suppressed while on this dosage. Practice diligent hygiene.
Observe your mood and mental state. Prednisone can impact mood, causing irritability, anxiety, or depression. Don’t hesitate to discuss any mental health changes with your doctor or therapist. Consider support groups.
Track your bone density. High-dose prednisone increases the risk of osteoporosis. Discuss bone density testing with your physician and consider preventative measures such as calcium and Vitamin D supplements.
Monitor for fluid retention and swelling. Note any swelling in your ankles, feet, or face. This can indicate a need for adjustments to your medication or treatment plan. Report this immediately.
Keep a detailed log. Record your daily weight, blood pressure, blood sugar levels (if you are monitoring), any symptoms you experience, and any medications you take. Share this log with your doctor at every appointment.
Follow your doctor’s specific instructions carefully. Dosage adjustments and monitoring frequency will vary depending on your individual health status and response to the medication. Do not change your medication schedule without consulting your doctor.
When to Contact Your Doctor Regarding 500 mg Prednisone
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience any of the following:
- Severe or persistent vomiting
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Severe abdominal pain
- Rapid heartbeat
- Swelling in your legs, ankles, or feet
- Sudden weight gain
- Increased thirst or urination
- Blurred vision
- Severe mood changes or depression
- Muscle weakness or pain
- Easy bruising or bleeding
- Seizures
- High fever
Also call your doctor if you notice:
- Any new or worsening symptoms.
- Symptoms that don’t improve after a few days of treatment.
- Side effects that bother you or interfere with your daily activities.
Your doctor can help manage your prednisone treatment and address any concerns you have. Open communication is key to successful treatment.