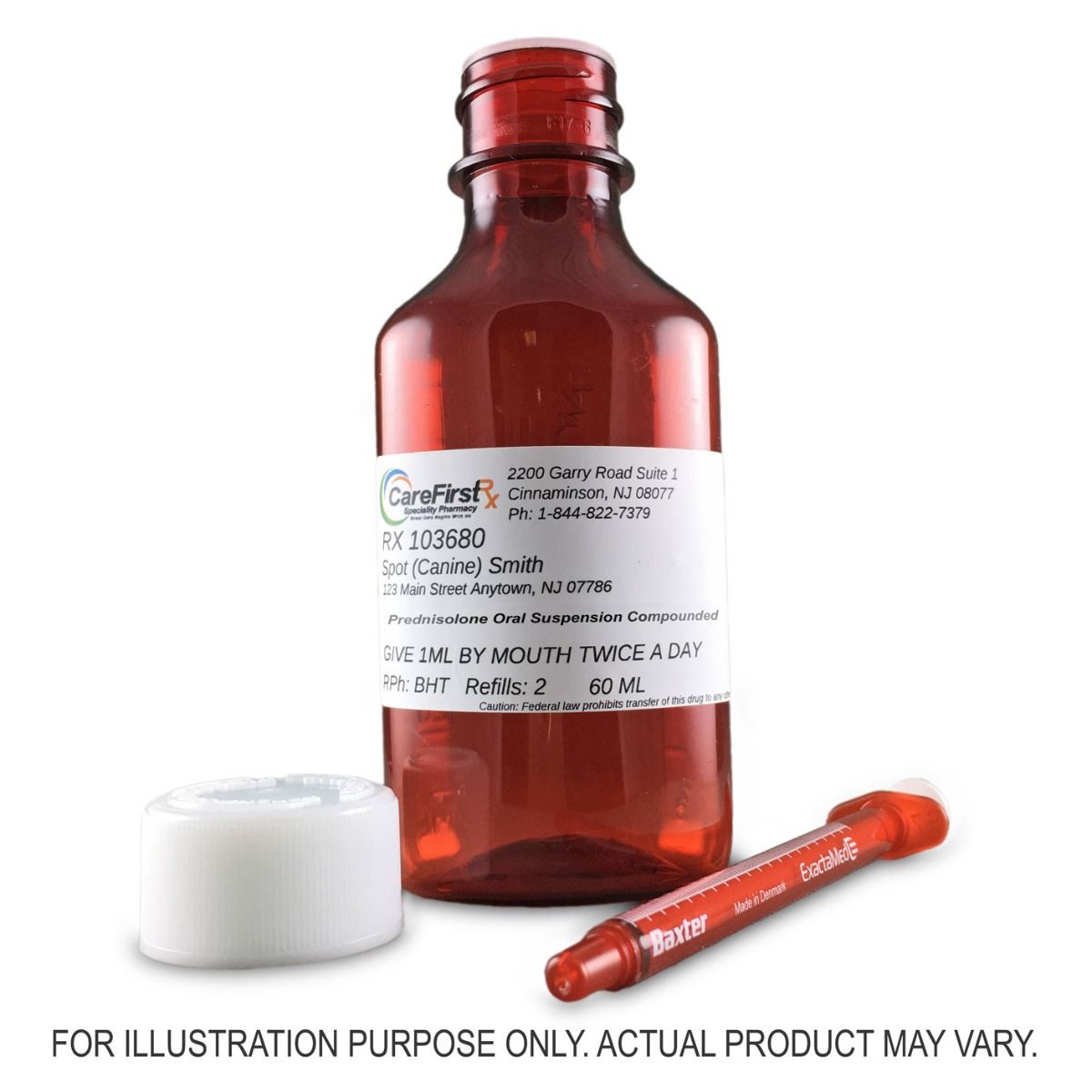
Sixty milliliters of prednisone represents a significant dose; its use requires careful monitoring and adherence to your doctor’s instructions. This amount is typically divided into daily doses, often spanning several weeks. Your specific dosage regimen is crucial.
Potential side effects, ranging from increased appetite and mood changes to more serious complications like weakened immunity and increased risk of infection, necessitate regular check-ups with your physician. Open communication about any symptoms you experience is paramount for managing your treatment effectively.
Never adjust your prednisone dosage without consulting your doctor. Abruptly stopping the medication can lead to serious health consequences. Consistent communication with your healthcare provider allows for accurate assessment and necessary adjustments to the treatment plan based on your individual response and progress. Remember, your health and safety are the primary concern.
This information is for educational purposes only and does not substitute for professional medical advice. Consult your doctor or pharmacist for any questions or concerns regarding your prednisone prescription.
- 60 ml of Prednisone: A Detailed Overview
- Understanding Prednisone Dosage
- Factors Affecting Dosage
- Typical Dosage Ranges
- Tapering Off Prednisone
- Potential Side Effects
- Monitoring & Follow-Up
- Disclaimer
- Potential Side Effects of High-Dose Prednisone
- Common Side Effects
- Less Common, but Serious Side Effects
- Long-Term Effects and Tapering Off Prednisone
- Interactions with Other Medications and Substances
- When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
- Other Urgent Situations
60 ml of Prednisone: A Detailed Overview
Sixty milliliters of prednisone represents a substantial quantity, significantly exceeding typical prescription dosages. This volume necessitates immediate medical attention. Contact your physician or seek emergency care immediately.
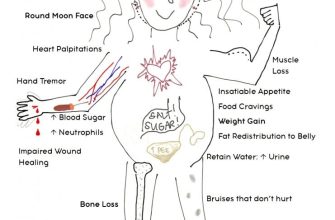
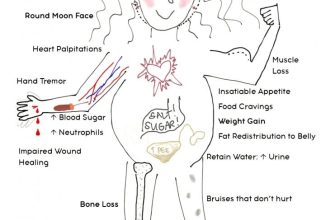
Prednisone is a potent corticosteroid; ingesting this volume could lead to severe adverse effects. Potential consequences include, but are not limited to, Cushing’s syndrome symptoms (like weight gain, fluid retention, and moon face), increased blood sugar, weakened immunity, and electrolyte imbalances. Severe cases can trigger heart problems and mental health issues.
Dosage is crucial. Prednisone’s effectiveness depends heavily on the prescribed amount and frequency. Self-medicating or altering prescribed dosages is extremely dangerous. Never adjust your prednisone regimen without consulting a healthcare professional.
If you’ve accidentally ingested 60 ml of prednisone, act quickly. Report the incident completely and honestly to medical personnel, including the exact amount ingested. Your prompt action can significantly influence the outcome of treatment.
This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor or other qualified healthcare professional for any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never self-treat.
Understanding Prednisone Dosage
A 60ml bottle of prednisone likely contains a high concentration, possibly 5mg/ml or higher, depending on the formulation. Always check the label for the precise concentration. This is crucial for accurate dosing.
Factors Affecting Dosage
Your doctor determines your prednisone dosage based on several factors: your specific condition, weight, age, and overall health. They carefully consider potential side effects and adjust the dose accordingly. Never adjust your dosage without consulting your physician.
Typical Dosage Ranges
Prednisone dosages vary widely. Common starting doses range from 5mg to 60mg daily, often in divided doses. Maintenance doses are typically much lower.
| Condition | Typical Starting Dose (mg/day) |
|---|---|
| Severe allergic reactions | 30-60 |
| Autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus) | 5-20 |
| Inflammatory conditions (e.g., asthma) | 5-40 |
The table above provides general examples; actual doses are individualized.
Tapering Off Prednisone
Prednisone should always be tapered off gradually, never stopped abruptly. This helps minimize withdrawal symptoms like fatigue and muscle weakness. Your doctor provides a specific tapering schedule.
Potential Side Effects
Common side effects include weight gain, increased appetite, mood changes, and insomnia. Serious side effects are rare but possible. Report any concerns to your physician promptly.
Monitoring & Follow-Up
Regular checkups are necessary to monitor your response to prednisone and manage any side effects. Your doctor may order blood tests to check for potential complications.
Disclaimer
This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance on prednisone dosage and treatment.
Potential Side Effects of High-Dose Prednisone
Taking 60ml of prednisone is a significant dose, so understanding potential side effects is crucial. Many side effects depend on dosage and duration of treatment. Always discuss concerns with your doctor.
Common Side Effects
- Weight gain: Prednisone can cause fluid retention and increased appetite, leading to weight gain. Monitor your weight and discuss dietary adjustments with your doctor or a registered dietitian.
- Increased blood sugar: Prednisone can elevate blood sugar levels, even in people without diabetes. Regular blood sugar monitoring might be necessary, especially if you have diabetes or risk factors.
- Mood changes: Irritability, anxiety, depression, and insomnia are common. Maintain open communication with your doctor and support system. Consider stress management techniques.
- Increased blood pressure: Prednisone can raise blood pressure. Regular monitoring is important. Your doctor might adjust your medication or recommend lifestyle changes.
- Muscle weakness: Prednisone can weaken muscles, increasing the risk of falls. Gentle exercise, as approved by your doctor, can help mitigate this.
- Osteoporosis risk: Long-term use increases the risk of bone thinning. Your doctor might suggest calcium and vitamin D supplements or other preventative measures.
Less Common, but Serious Side Effects
- Increased risk of infections: Prednisone suppresses the immune system, making infections more likely. Report any signs of infection immediately.
- Cataracts and glaucoma: Long-term use can increase the risk of eye problems. Regular eye exams are recommended.
- Peptic ulcers: Prednisone can damage the stomach lining, increasing ulcer risk. Your doctor might prescribe medication to protect your stomach.
- Skin thinning: The skin becomes more fragile and prone to bruising. Use gentle skincare products and avoid harsh chemicals.
This list isn’t exhaustive. Always consult your doctor for a personalized assessment and management plan. They can help you weigh the benefits of prednisone against the potential risks. Open communication is key to safe and effective treatment.
Long-Term Effects and Tapering Off Prednisone
Prolonged prednisone use, especially at higher doses, carries risks. Common long-term effects include weight gain, increased blood sugar, osteoporosis, and increased risk of infections. Less common, but serious, side effects can include cataracts, glaucoma, and increased blood pressure.
Never stop prednisone abruptly. Sudden cessation can trigger adrenal insufficiency, a potentially life-threatening condition. Your doctor will create a tapering schedule, gradually reducing your dose over weeks or months. This minimizes withdrawal symptoms, like fatigue, muscle aches, and joint pain.
The tapering schedule is personalized. Factors considered include your dosage, duration of treatment, and overall health. Expect regular blood tests to monitor your adrenal function during the tapering process. Closely follow your doctor’s instructions, and report any concerning symptoms immediately.
During tapering, maintain a healthy lifestyle. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management techniques can help mitigate potential side effects. Ask your doctor about calcium and vitamin D supplements to protect bone health. Open communication with your healthcare provider is key to a safe and successful prednisone withdrawal.
Interactions with Other Medications and Substances
Prednisone can interact with many medications. Always inform your doctor and pharmacist of all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs. This includes aspirin, ibuprofen, and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), as these can increase the risk of stomach ulcers and bleeding when combined with prednisone.
Concurrent use with certain anticoagulants, like warfarin, may increase bleeding risk. Your doctor may need to adjust your dosage of either medication or monitor you closely for bleeding. Similarly, prednisone interacts with drugs used to control diabetes, potentially elevating blood sugar levels. Careful monitoring of blood sugar is necessary.
Drugs affecting the immune system, like immunosuppressants or vaccines, may have their effects altered when taken with prednisone. This means weakened immunity, possibly increasing the risk of infection. Discuss your vaccination schedule with your doctor before starting prednisone.
Alcohol consumption can worsen side effects of prednisone, including stomach irritation and increased risk of ulcers. Limit or avoid alcohol while on prednisone. Grapefruit juice also affects the metabolism of some medications, including some which are metabolized similarly to prednisone; avoid grapefruit juice while taking prednisone.
This is not an exhaustive list. Consult your healthcare provider for a personalized assessment of potential interactions specific to your individual medication profile. They can provide tailored advice based on your health status and all the medications you take.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Contact emergency services immediately if you experience severe allergic reactions like swelling of your face, lips, or throat, difficulty breathing, or hives after taking prednisone. These symptoms require immediate medical intervention.
Other Urgent Situations
Seek immediate medical attention if you develop severe stomach pain, vomiting blood, or black, tarry stools. These could indicate serious gastrointestinal complications. Also, contact your doctor or go to the emergency room if you experience unusual bruising or bleeding, persistent muscle weakness, or significant changes in your mental state, such as confusion or disorientation. Rapid weight gain (more than 2 pounds in a day or 5 pounds in a week), severe headache, or vision changes also warrant an urgent call to your physician or a visit to the emergency room. Don’t delay treatment; your health is paramount.