Prednisone offers significant therapeutic benefits, but understanding its potential side effects is crucial for safe and effective use. This article focuses on common complications, providing practical information to help patients and caregivers make informed decisions.
Weight gain, often a noticeable side effect, stems from increased appetite and fluid retention. Regular monitoring of weight and dietary adjustments, such as focusing on nutrient-dense foods, can help manage this. Consult your doctor about potential strategies for mitigating weight gain, including exercise recommendations tailored to your health status.
Increased blood sugar levels are another concern, particularly in individuals with pre-existing diabetes or a family history. Frequent blood glucose monitoring and adjustments to diabetes medication, under the guidance of your physician, are necessary. Dietary modifications, focusing on low glycemic index foods, can also contribute to blood sugar control.
Osteoporosis, a weakening of bones, is a significant long-term risk. Discuss preventative measures with your doctor, including calcium and vitamin D supplementation, weight-bearing exercise, and perhaps medication to protect bone density. Regular bone density screenings might be recommended.
High blood pressure is another potential complication. Regular blood pressure monitoring and lifestyle modifications such as a low-sodium diet and regular physical activity are paramount. Your physician may adjust your medication accordingly.
Remember: This information is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before making any decisions about your treatment plan.
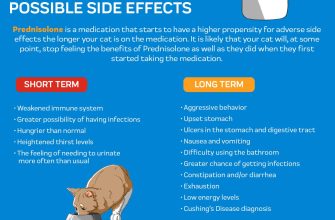
Complications with Prednisone
Prednisone, while highly effective, carries potential side effects. Understanding these risks allows for informed decision-making and proactive management.
Common Side Effects:
- Weight gain: Fluid retention contributes significantly. Maintain a balanced diet and increase physical activity.
- Increased blood sugar: Prednisone can elevate glucose levels. Monitor blood sugar regularly, especially if diabetic, and adjust medication as needed.
- Mood changes: Irritability, anxiety, and insomnia are common. Talk to your doctor about coping strategies and potential medication adjustments.
- Increased blood pressure: Regular monitoring and lifestyle changes (diet, exercise) are crucial.
- Osteoporosis: Prednisone weakens bones. Discuss calcium and vitamin D supplementation with your physician.
- Thinning skin: Increased fragility and bruising are possible. Use caution to prevent injury.
- Muscle weakness: Gradual exercise can help mitigate this. Consult a physical therapist for tailored guidance.
Serious Side Effects (requiring immediate medical attention):
- Severe allergic reactions: Symptoms include hives, swelling, difficulty breathing. Seek immediate emergency care.
- Infections: Prednisone suppresses the immune system, increasing susceptibility. Report any signs of infection promptly.
- Glaucoma and cataracts: Regular eye exams are recommended, especially for those with a history of eye problems.
- Increased risk of bleeding: This includes ulcers and gastrointestinal bleeding. Be aware of any signs of bleeding and report them to your doctor.
Managing Side Effects:
- Follow your doctor’s instructions precisely.
- Report any concerns immediately.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle. Regular exercise and a balanced diet can significantly lessen side effects.
- Discuss alternative therapies. Your physician may suggest modifications to the treatment plan to minimize side effects.
Remember: This information is for general knowledge and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor before starting or stopping any medication.
Gastrointestinal Issues and Prednisone
Prednisone can irritate your stomach lining, leading to heartburn, nausea, and stomach upset. To mitigate this, take prednisone with food or milk. Consider antacids if symptoms persist. Severe cases might require a prescription medication from your doctor.
Ulcers and Prednisone
Prednisone increases your risk of developing peptic ulcers, which are sores in the lining of your stomach or small intestine. Regular check-ups with your doctor are recommended, especially if you experience persistent abdominal pain, black or bloody stools, or vomiting blood. Your doctor might recommend a course of protective medication to prevent ulcers.
Constipation and Diarrhea
Changes in bowel habits, including constipation and diarrhea, are common side effects. Increase your fiber intake with fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to manage constipation. If diarrhea is severe or persistent, talk to your doctor; they might suggest medications to help. Staying hydrated is vital to manage both constipation and diarrhea. Remember to drink plenty of fluids throughout the day.
Metabolic and Endocrine Side Effects of Prednisone
Prednisone’s impact on your metabolism is significant. Expect weight gain, often centered around the abdomen and face, due to increased appetite and fluid retention. Monitor your diet carefully; a balanced diet with portion control is key. Regular exercise helps mitigate weight gain and improve overall health.
Increased blood sugar is another common metabolic side effect. This can lead to hyperglycemia, even in individuals without pre-existing diabetes. Regular blood glucose monitoring is strongly advised, particularly if you have a family history of diabetes. Your doctor might adjust your diabetes medication or recommend lifestyle changes.
Prednisone interferes with your body’s natural production of cortisol, a crucial hormone. This suppression can lead to adrenal insufficiency if prednisone is stopped abruptly. Always taper off prednisone gradually under your doctor’s supervision to avoid this serious complication. Your doctor will provide a specific tapering schedule.
High blood pressure (hypertension) frequently accompanies prednisone use. Regular blood pressure checks are necessary. Lifestyle changes like reducing sodium intake and engaging in regular physical activity can help manage hypertension. Your doctor might prescribe antihypertensive medication if necessary.
Elevated cholesterol and triglyceride levels are also possible side effects. Regular lipid panels are important to monitor these levels. Dietary changes and exercise are vital in managing lipid levels. Your doctor may recommend medication if lifestyle modifications are insufficient.
Osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weakened bones, is a long-term risk with prolonged prednisone use. Weight-bearing exercises and sufficient calcium and vitamin D intake are crucial to minimize bone loss. Your physician might recommend bone density testing and prescribe medications to protect your bones.
Immunosuppression and Infection Risks with Prednisone
Prednisone weakens your immune system, increasing susceptibility to infections. This risk is directly related to the dose and duration of treatment. Higher doses and longer treatment periods significantly heighten your vulnerability.
Monitor for infection symptoms: Pay close attention to any fever, cough, sore throat, or unusual fatigue. These could signal an infection requiring prompt medical attention. Don’t hesitate to contact your doctor immediately if you experience any of these.
Specific infections are more likely with prednisone use. These include opportunistic infections like pneumonia (caused by Pneumocystis jirovecii), herpes simplex, and tuberculosis reactivation. Your doctor may recommend preventative measures depending on your risk factors.
Vaccination considerations: Discuss vaccination strategies with your physician. Some live vaccines may be contraindicated during prednisone treatment. However, others, such as the influenza and pneumococcal vaccines, are usually recommended to help protect against common infections.
Hygiene practices: Maintain excellent hand hygiene to prevent the spread of infection. Avoid contact with individuals suffering from contagious illnesses whenever possible. This simple step can greatly reduce your risk.
Regular monitoring is key. Your doctor will likely schedule regular check-ups to monitor your health and assess your risk of infection. Open communication with your physician about any concerns is critical for managing this risk effectively.