Start with a thorough consultation with your doctor. They can assess your individual situation and discuss potential solutions, including adjusting your dosage or exploring alternative treatments. Open communication is key to finding the right path for you.
Consider lifestyle changes. Regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in zinc and vitamin D, and stress management techniques like meditation or yoga can significantly influence hormonal balance and sexual health. These factors often interact with medication effects. Aim for 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week, and incorporate stress-reducing activities into your daily routine.
Explore supplemental options. Some men find that supplements like D-aspartic acid or magnesium can support libido recovery. However, always consult your doctor before starting any new supplements, as they can interact with medications. Proper dosage and potential side effects require professional guidance.
Don’t hesitate to seek second opinions. If you’re unsatisfied with your progress, a consultation with a different specialist might offer fresh perspectives and new treatment strategies. Remember, regaining your libido is achievable with proactive approach and the right support.
Patience is crucial. Recovery timelines vary greatly among individuals. Be realistic about your expectations and work closely with your healthcare provider to monitor your progress and make adjustments as needed. Consistent effort and medical guidance will maximize your chances of success.
- Finasteride Libido Recovery: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding Finasteride-Induced Sexual Side Effects
- Identifying the Severity of Your Libido Issues
- Lifestyle Changes to Support Libido Recovery
- Exploring Potential Medical Interventions for Libido Restoration
- Addressing Underlying Medical Conditions
- Exploring Other Treatment Options
- Lifestyle Adjustments
- The Role of Supplements and Alternative Therapies
- Lifestyle Changes for Libido Support
- Alternative Therapies
- Important Considerations
- Disclaimer:
- When to Seek Professional Medical Help for Persistent Issues
- Addressing Other Potential Health Concerns
- Managing Expectations and Long-Term Outlook
- Factors Influencing Recovery
- Alternative Approaches
Finasteride Libido Recovery: A Comprehensive Guide
Seek medical advice immediately if experiencing persistent sexual side effects. Your doctor can assess your situation and discuss treatment options.
Lifestyle changes often play a crucial role. Prioritize regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, and sufficient sleep. These habits positively influence hormonal balance and overall well-being, potentially aiding recovery.
Consider supplementing your diet with specific nutrients. Zinc, magnesium, and vitamin D deficiencies can sometimes impact libido. Discuss supplementation with your physician before starting any new regimen.
Explore potential hormonal imbalances. Low testosterone levels frequently contribute to decreased libido. Blood tests can determine testosterone levels, allowing for targeted treatment if necessary.
Some men find that switching to a different medication or discontinuing Finasteride (under medical supervision) improves their symptoms. This decision requires careful medical consultation to weigh the benefits against potential risks.
Therapy, including cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), can be incredibly beneficial. CBT can help address psychological factors affecting libido, such as anxiety and depression, often associated with Finasteride side effects.
| Strategy | Description | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Medical Consultation | Discuss symptoms and explore treatment options with a doctor. | Personalized treatment plan, monitoring, and medication adjustments. |
| Lifestyle Adjustments | Exercise, balanced diet, sufficient sleep. | Improved hormonal balance and overall health. |
| Nutritional Supplementation | Zinc, magnesium, vitamin D (under medical supervision). | Address potential nutrient deficiencies impacting libido. |
| Hormone Testing | Blood tests to check testosterone levels. | Identify and address potential hormonal imbalances. |
| Medication Adjustment | Switching medications or discontinuing Finasteride (under medical supervision). | Alleviation of sexual side effects. |
| Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) | Therapy to address psychological factors. | Management of anxiety and depression impacting libido. |
Remember: Patience is key. Recovery timelines vary greatly. Maintain open communication with your healthcare provider throughout the process.
Understanding Finasteride-Induced Sexual Side Effects
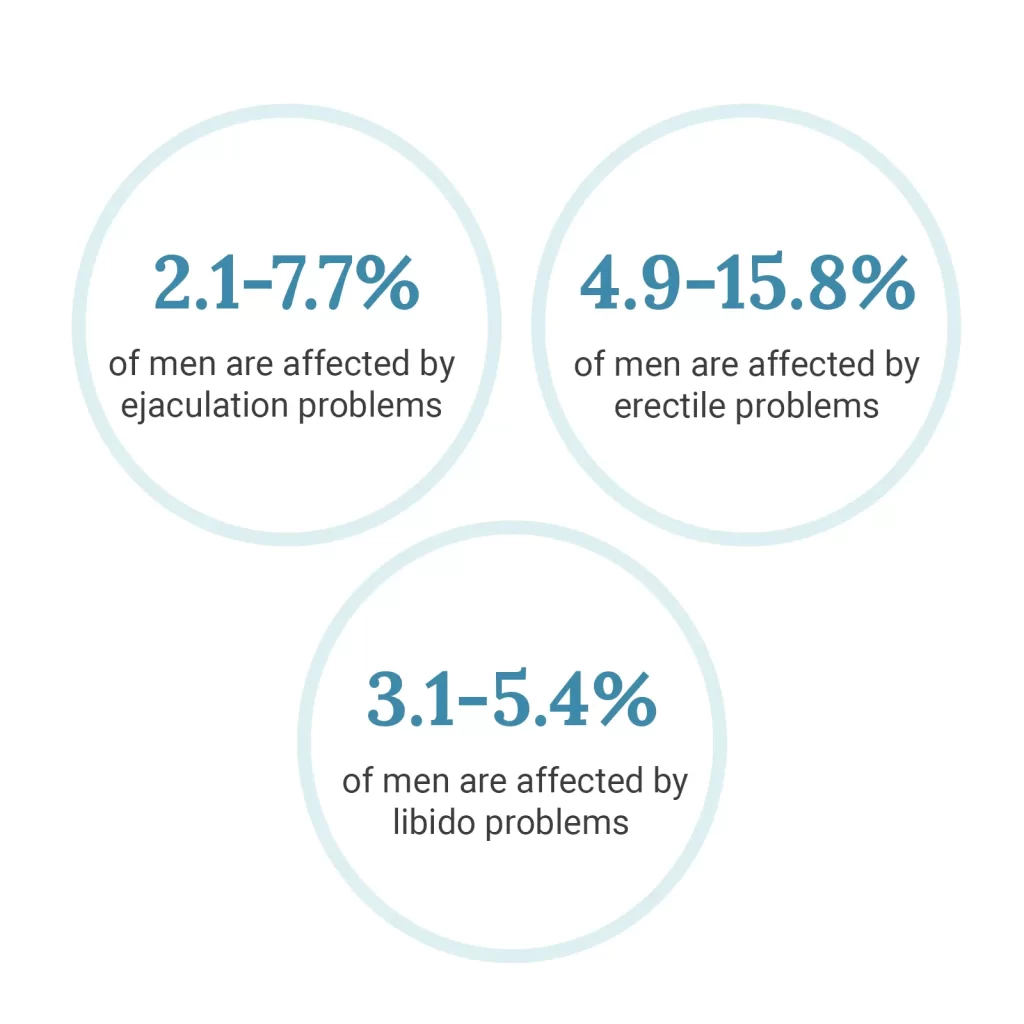
Finasteride can sometimes cause sexual side effects, including decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and ejaculation problems. These effects are usually temporary and resolve once you stop taking the medication. However, for some individuals, these effects can persist, even after discontinuation, a phenomenon known as Post-Finasteride Syndrome (PFS).
The exact mechanism causing these side effects isn’t fully understood, but it’s believed to involve disruption of androgen receptor activity. The severity varies widely between individuals. Some experience mild discomfort, while others report significantly impacting their quality of life.
If you experience these side effects, open communication with your doctor is crucial. They can assess your situation and explore potential management strategies, including medication adjustments or alternative treatments. Keeping a detailed journal of your symptoms can aid in this process.
Research into PFS is ongoing, and understanding of long-term effects continues to develop. While many recover fully, others may require extensive support. Various support groups and online communities exist, offering resources and shared experiences.
Addressing these side effects requires a multifaceted approach. Lifestyle modifications, such as stress reduction techniques and regular exercise, can sometimes help. Nutritional changes may also prove beneficial. Always consult your healthcare provider before making significant changes to your diet or supplement regimen.
Remember, you are not alone. Many men experience these side effects, and help is available. Proactive communication with your doctor and seeking support are key to managing these challenges and improving your well-being.
Identifying the Severity of Your Libido Issues
Honestly assess your experience. Use this scale to gauge your situation:
- Mild: Noticeable decrease in libido, but still experience sexual desire occasionally. Intercourse is still possible, though maybe less frequent.
- Moderate: Significant reduction in libido. Sexual desire is infrequent and initiating intimacy is challenging. Spontaneous sexual activity is rare.
- Severe: Almost complete absence of sexual desire. Initiating or engaging in sexual activity is extremely difficult or impossible. This significantly impacts your quality of life and relationships.
Consider these factors:
- Frequency of sexual thoughts: How often do you think about sex? A significant decrease could indicate a problem.
- Erectile function: Are you experiencing difficulties achieving or maintaining an erection? This is a separate issue but often correlates with low libido.
- Relationship impact: Is your reduced libido affecting your relationship with your partner? Open communication is key.
- Daily life disruption: Does your low libido affect your mood, energy levels, or overall sense of well-being? A substantial impact suggests a more serious issue.
This self-assessment helps determine if you need professional medical advice. A doctor can accurately diagnose the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Lifestyle Changes to Support Libido Recovery
Prioritize sleep. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep nightly. Insufficient sleep significantly impacts hormone regulation, including testosterone.
Manage stress effectively. Incorporate daily stress-reducing activities like meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature. Consider professional counseling if stress is overwhelming.
Regular exercise is key. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week, combined with strength training twice a week. Exercise boosts testosterone and overall well-being.
Optimize your diet. Focus on whole, unprocessed foods, including plenty of fruits, vegetables, and lean protein. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive alcohol consumption.
Maintain a healthy weight. Obesity can negatively affect hormone production. Aim for a healthy BMI through diet and exercise.
Hydrate adequately. Drink plenty of water throughout the day to support overall bodily functions, including hormone balance.
Limit exposure to endocrine disruptors. Reduce your exposure to chemicals found in plastics, pesticides, and personal care products.
Consider supplements. Consult a doctor before taking any supplements, but some, like zinc and magnesium, may support hormone health. Dosage and suitability must be determined by a healthcare professional.
Quit smoking. Smoking negatively impacts vascular health, potentially affecting libido.
Address underlying medical conditions. Consult a doctor to rule out any underlying medical conditions that might be contributing to low libido.
Exploring Potential Medical Interventions for Libido Restoration
Consider testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) if low testosterone is contributing to your decreased libido. Your doctor will conduct blood tests to assess your levels and determine if TRT is appropriate. This treatment involves administering testosterone via injections, gels, or patches, thereby increasing testosterone levels and potentially improving libido.
Addressing Underlying Medical Conditions
Many medical conditions can impact libido. Diabetes, thyroid disorders, and depression are common culprits. Addressing these conditions directly with appropriate medication and lifestyle changes often improves sexual function. Work closely with your physician to identify and treat any underlying health issues.
Note: TRT is not a universally effective solution and carries potential side effects. Discuss potential risks and benefits thoroughly with your doctor.
Exploring Other Treatment Options
Bupropion, an antidepressant, has shown some promise in improving libido in certain individuals. This medication works differently than typical antidepressants and may positively affect sexual function for some men. However, it’s not a guaranteed solution and can have side effects. Consult your doctor about this possibility.
Additionally, PDE5 inhibitors, commonly prescribed for erectile dysfunction, can sometimes indirectly improve libido by enhancing sexual confidence and improving the overall experience. Discuss this possibility with your doctor, and always follow prescribed usage instructions.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep play significant roles in overall health and can positively impact libido. These lifestyle changes can work synergistically with medical interventions to maximize results.
Remember to always consult your physician before starting any new treatment, including supplements or herbal remedies, to ensure safety and compatibility with existing conditions or medications. They can help you determine the best course of action for your individual needs and circumstances.
The Role of Supplements and Alternative Therapies
Consider adding specific nutrients to your diet. Zinc, magnesium, and vitamin D deficiencies are sometimes linked to low libido. Supplementing with these can potentially improve symptoms, but consult your doctor before starting any new supplements, especially if you’re already taking medication.
Lifestyle Changes for Libido Support
- Improve Sleep Hygiene: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep nightly. Poor sleep significantly impacts hormone regulation and libido.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress negatively affects testosterone production. Incorporate stress-reducing techniques like yoga, meditation, or regular exercise.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity boosts testosterone levels and overall well-being, positively influencing libido.
- Healthy Diet: Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean protein. Avoid processed foods, excessive sugar, and saturated fats.
Alternative Therapies
Some men find relief through alternative therapies. These should always be discussed with your doctor before implementation. These include:
- Acupuncture: May improve blood flow and hormone balance.
- Herbal Remedies: Specific herbs like Ashwagandha have shown some promise in improving libido, but research is ongoing and individual responses vary. Always use reputable brands and consult a healthcare professional.
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT): In some cases, low testosterone is the underlying cause of decreased libido. TRT is a medical intervention, and its suitability must be assessed by a doctor.
Important Considerations
Remember, results vary considerably. What works for one person might not work for another. Patience and consistency are crucial. A holistic approach, combining dietary changes, lifestyle adjustments, and possibly supplements or alternative therapies under medical guidance, is often most effective.
Disclaimer:
This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with your doctor or a qualified healthcare professional before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.
When to Seek Professional Medical Help for Persistent Issues
Contact your doctor if libido issues persist for more than three months after stopping finasteride. This timeframe allows for natural hormonal fluctuations to resolve. If symptoms remain, a medical professional can help determine the underlying cause.
Addressing Other Potential Health Concerns
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of the following alongside libido problems: persistent depression, anxiety that significantly impacts daily life, or unexplained weight changes. These could indicate underlying conditions requiring treatment.
If you notice any signs of gynecomastia (breast enlargement) or changes in prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels, schedule a consultation without delay. These warrant careful evaluation by a doctor to rule out serious complications.
Your doctor may suggest blood tests to assess hormone levels and rule out other medical conditions. They can also discuss alternative treatment options if needed. Open communication with your healthcare provider is crucial for successful management of these issues.
Managing Expectations and Long-Term Outlook
Recovery timelines vary significantly. While some men see improvements within weeks, others experience a longer, more gradual return of libido. Patience is key; complete recovery can take months or even years for some individuals. Don’t be discouraged by slow progress.
Factors Influencing Recovery
Several factors influence recovery speed. These include the severity of your initial symptoms, your age, overall health, and adherence to your doctor’s recommendations. Lifestyle choices, such as diet, exercise, and stress management, also play a significant role. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle promotes overall well-being, which can positively impact libido.
Regular communication with your doctor is crucial. They can monitor your progress, adjust your treatment plan if necessary, and address any concerns you may have. Openly discuss your experience and any persistent symptoms. Consider keeping a detailed journal to track your progress and identify any patterns or triggers.
Alternative Approaches
If libido doesn’t return fully after discontinuing finasteride, explore alternative strategies with your doctor. These might include hormone testing and potential supplementation under medical supervision. They can also help rule out other underlying medical conditions that may be affecting your libido. Remember to always consult with your doctor before making any changes to your treatment plan or starting new supplements. Self-treating can be dangerous.
Focusing on overall health and well-being often improves libido. Prioritize sleep, manage stress, and engage in regular physical activity. These factors significantly influence hormonal balance and sexual function. A balanced diet, rich in nutrients, also supports healthy hormone production.