Experiencing increased urination while taking prednisone? This is a common side effect. Prednisone, a corticosteroid, affects your body’s fluid balance, leading to increased thirst and frequent trips to the bathroom. Understanding this connection is key to managing the situation effectively.
To minimize this side effect, consider adjusting your fluid intake throughout the day. Avoid excessive fluid consumption, especially before bedtime. This can help reduce nighttime awakenings due to the need to urinate. Your doctor can also discuss potential medication adjustments or alternative treatments if needed.
Remember to consult your physician. They can provide personalized advice and determine if the frequent urination is solely due to the medication or indicative of another issue. Don’t hesitate to discuss your concerns; open communication with your doctor is vital for your health and well-being. They can help you develop a strategy to manage this side effect and ensure you receive the optimal benefits from your prednisone treatment.
Monitoring your fluid intake and staying hydrated in a balanced way are crucial steps in managing this side effect. This simple adjustment, along with open communication with your doctor, often proves sufficient to mitigate the discomfort associated with frequent urination caused by prednisone.
- Frequent Urination with Prednisone
- Managing Increased Urination
- Other Potential Causes
- How Prednisone Affects Your Body’s Fluid Balance
- Increased Thirst and Urination
- Potential Consequences
- Managing Fluid Retention
- Monitoring Your Condition
- Understanding Potassium Levels
- Prednisone can also affect your potassium levels, potentially leading to a deficiency. Low potassium can exacerbate some of the fluid balance issues. Your doctor might recommend potassium supplements or dietary changes to address this.
- The Link Between Prednisone and Increased Thirst
- Understanding the Mechanism
- Managing Increased Thirst
- Recognizing the Symptoms: More Than Just Frequent Trips to the Bathroom
- When to Seek Medical Attention for Frequent Urination While on Prednisone
- Lifestyle Changes to Manage Prednisone-Induced Frequent Urination
- Dietary Adjustments
- Bladder Training Techniques
- Other Considerations
- When to Seek Medical Advice
- Medication Adjustments: Discussing Options with Your Doctor
- Potential Complications of Untreated Fluid Imbalance
- Managing Your Prednisone Treatment Effectively
- Hydration and Diet
- Monitoring Your Health
- Addressing Side Effects
- Medication Interactions
Frequent Urination with Prednisone
Prednisone, a common corticosteroid, often causes increased urination. This happens because prednisone increases your body’s production of urine. Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated, but avoid excessive fluid intake close to bedtime to minimize nighttime bathroom trips.
Managing Increased Urination
Adjust your fluid intake strategically. Spread your water consumption evenly across the day. Consider reducing fluid intake a few hours before sleep. If nighttime urination significantly disrupts your sleep, discuss this with your doctor. They can help determine if the frequency is outside the normal range associated with prednisone use and explore potential solutions. They may also suggest adjustments to your prednisone dosage or prescribe alternative medication. Monitoring your fluid intake and urination patterns can provide valuable information for your doctor. Keep a log of your daily fluid intake and urination frequency to share during your next appointment.
Other Potential Causes
While prednisone is a frequent culprit, other factors can contribute to increased urination. Underlying medical conditions, like diabetes or urinary tract infections, can also cause frequent urination. If you experience other symptoms, such as pain, burning during urination, or excessive thirst, contact your doctor immediately for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. They will be able to determine the underlying cause and recommend the appropriate course of action.
How Prednisone Affects Your Body’s Fluid Balance
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, increases your body’s retention of sodium and water. This happens because prednisone influences the kidneys’ ability to excrete sodium. More sodium means your body holds onto more water, leading to increased fluid volume.
Increased Thirst and Urination
This fluid retention is why you might experience increased thirst and frequent urination while taking prednisone. Your body tries to compensate for the extra fluid by increasing urine production.
Potential Consequences
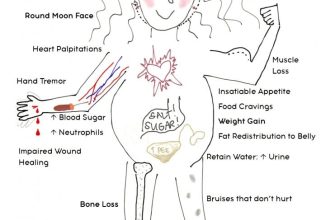
- Weight gain: The extra fluid contributes to weight gain, often noticeable in the face, legs, and abdomen.
- High blood pressure (hypertension): Increased fluid volume can strain your cardiovascular system, potentially elevating blood pressure.
- Edema (swelling): You might notice swelling in your ankles, feet, or hands.
Managing Fluid Retention
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water, but avoid excessive fluid intake, especially close to bedtime.
- Dietary Changes: Reduce your sodium intake by limiting processed foods, salty snacks, and fast food. Choose fresh fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps your body manage fluid balance and reduce swelling.
- Medication Adjustments: Discuss your symptoms with your doctor. They might adjust your prednisone dosage or prescribe additional medications to manage fluid retention and blood pressure.
Monitoring Your Condition
Regularly monitor your weight and blood pressure. Report any significant changes or concerning symptoms to your healthcare provider immediately. They can help you manage the side effects of prednisone and ensure your overall well-being.
Understanding Potassium Levels
Prednisone can also affect your potassium levels, potentially leading to a deficiency. Low potassium can exacerbate some of the fluid balance issues. Your doctor might recommend potassium supplements or dietary changes to address this.
The Link Between Prednisone and Increased Thirst
Prednisone affects your body’s fluid balance, leading to increased thirst. This happens because prednisone increases the amount of glucose in your bloodstream. Your kidneys work to filter out this excess glucose, and this process requires more water. The result? Your body signals increased thirst to compensate for this fluid loss.
Understanding the Mechanism
Prednisone also influences the hormone vasopressin, which regulates water retention. Prednisone can interfere with vasopressin’s function, reducing the body’s ability to retain water and thus increasing thirst and urination.
Managing Increased Thirst
Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated. However, avoid excessive fluid intake before bedtime to minimize nighttime urination. Consult your doctor; they can provide personalized advice and monitor for complications related to fluid balance. They may suggest adjustments to your medication or other strategies for managing this side effect.
Recognizing the Symptoms: More Than Just Frequent Trips to the Bathroom
Prednisone’s impact extends beyond simply increasing urination frequency. Pay close attention to these additional signs:
| Symptom | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Thirst (Polydipsia) | Feeling excessively thirsty, even after drinking fluids. | Drink plenty of water, but monitor fluid intake if you have other conditions. Contact your doctor if thirst is unquenchable. |
| Weight Gain | Noticeable increase in body weight, often due to fluid retention. | Discuss dietary adjustments with your doctor; they can advise on managing weight gain safely. |
| Elevated Blood Pressure | Readings consistently higher than your normal range. | Regularly monitor blood pressure. Report elevated readings to your doctor promptly. |
| Increased Blood Sugar | Higher than normal blood glucose levels, especially if you have diabetes. | Monitor blood sugar levels as directed by your doctor. Adjust medication as needed. |
| Muscle Weakness | Feeling unusually weak or experiencing muscle aches. | Gentle exercise might help, but avoid strenuous activity. Inform your doctor. |
| Mood Changes | Irritability, anxiety, or depression. | Communicate these changes with your healthcare provider; they may suggest strategies for coping. |
| Increased Appetite | Feeling hungrier than usual. | Focus on nutritious foods to mitigate weight gain and maintain energy. |
| Insomnia | Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep. | Maintain a regular sleep schedule and discuss sleep aids with your doctor if needed. |
These symptoms, while common, require medical attention if severe or persistent. Always consult your doctor to discuss any concerns related to prednisone use.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Frequent Urination While on Prednisone
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience frequent urination accompanied by any of the following:
- Severe thirst, indicating potential dehydration.
- Blurred vision, a possible sign of high blood sugar.
- Unexplained weight loss or gain.
- Persistent fatigue that doesn’t improve with rest.
- Fever or chills.
- Painful urination (dysuria).
- Blood in your urine (hematuria).
- Increased urination at night (nocturia) significantly disrupting sleep.
Schedule an appointment with your physician if your frequent urination is bothersome, even without these symptoms. They can assess your situation and determine the cause. A simple blood test can often identify issues like high blood sugar.
Note: This information does not replace professional medical advice. Always discuss your concerns with your doctor or other qualified healthcare provider.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Prednisone-Induced Frequent Urination
Adjust your fluid intake. Drink most of your fluids earlier in the day, reducing intake several hours before bedtime to minimize nighttime trips to the bathroom. Aim for consistent hydration throughout the day, rather than large amounts at once.
Time your diuretics. If you’re taking other diuretics alongside prednisone, coordinate their timing with your daily schedule to avoid disrupting sleep. Consult your doctor for the optimal timing.
Dietary Adjustments
Limit caffeine and alcohol. These beverages act as diuretics, exacerbating frequent urination. Reduce or eliminate their consumption, especially in the evening.
Increase potassium-rich foods. Prednisone can deplete potassium. Incorporate foods like bananas, potatoes, and spinach into your diet to counteract this effect and support kidney function. Always discuss dietary changes with your doctor.
Bladder Training Techniques
Practice bladder training exercises. Gradually increase the time between bathroom visits. This helps strengthen your bladder muscles and reduce the urgency to urinate frequently.
Other Considerations
Manage stress. Stress can aggravate urinary frequency. Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation to help manage stress levels.
Maintain a regular sleep schedule. Consistent sleep patterns can improve overall health and reduce symptoms associated with prednisone use, including frequent urination.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Contact your doctor if you experience severe or persistent urinary problems, pain during urination, or changes in urine color or odor. These could indicate a more serious underlying issue.
Medication Adjustments: Discussing Options with Your Doctor
Schedule a follow-up appointment to discuss your frequent urination. Your doctor might adjust your prednisone dosage. A lower dose could alleviate the symptom, but this must be done under medical supervision to ensure your condition is still managed effectively.
Explore alternative medications. Sometimes, switching to a different corticosteroid or using a medication to manage the urinary frequency directly proves beneficial. Discuss these possibilities with your doctor to find the best solution for your specific needs.
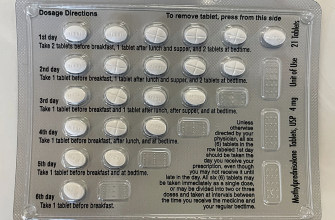
Consider a medication schedule change. Instead of taking prednisone once daily, your doctor may suggest splitting the dose into two smaller doses throughout the day. This can help minimize side effects, including frequent urination, by evening out the drug’s presence in your system.
Don’t hesitate to report any changes in your condition. Open communication is key. If your frequent urination persists or worsens, or you experience other side effects, contact your doctor immediately. Timely communication allows for prompt adjustments to your treatment plan.
Ask about additional management strategies. Lifestyle changes, such as increasing fluid intake during the day and limiting fluids before bed, may help manage the urinary frequency. Discuss these with your healthcare provider to ascertain their suitability for your case.
Potential Complications of Untreated Fluid Imbalance
Ignoring fluid imbalance caused by prednisone can lead to serious health issues. Prompt medical attention is crucial.
- Dehydration: Severe dehydration causes dizziness, fatigue, and potentially kidney problems. Drink plenty of fluids, especially water, to counteract this effect.
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Prednisone can disrupt sodium, potassium, and calcium levels. This imbalance increases the risk of heart problems, muscle weakness, and seizures. Regular blood tests monitor these levels.
- Increased Blood Pressure: Fluid retention contributes to hypertension. This raises your risk of stroke and heart disease. Regular blood pressure monitoring and lifestyle adjustments (diet and exercise) are recommended.
- Heart Failure: In individuals with pre-existing heart conditions, fluid overload from prednisone can exacerbate heart failure, leading to shortness of breath and chest pain. Close monitoring by a cardiologist is necessary.
- Edema: Swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet is a common symptom. This swelling can become severe, impairing circulation and causing discomfort. Elevation of legs and compression stockings may provide relief. Your doctor can prescribe diuretics if necessary.
Your doctor will help manage these risks. Open communication about your symptoms ensures appropriate treatment and reduces potential complications.
- Report any significant changes in urination frequency or volume immediately.
- Follow your doctor’s instructions regarding fluid intake and medication.
- Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments.
Managing Your Prednisone Treatment Effectively
Schedule your prednisone doses consistently, ideally at the same time each day. This helps maintain stable blood levels and minimizes fluctuations. Take your medication with food to reduce stomach upset. A light snack or meal should suffice.
Hydration and Diet
Drink plenty of water throughout the day to counteract the diuretic effect of prednisone, especially if you experience increased urination. Include potassium-rich foods in your diet, such as bananas, potatoes, and spinach, as prednisone can deplete potassium levels. Consult your doctor or a registered dietitian for personalized dietary guidance.
Monitoring Your Health
Regularly monitor your blood pressure and weight. Report any significant changes to your doctor promptly. Prednisone can affect blood pressure and cause weight gain. Furthermore, keep track of your blood sugar levels if you have diabetes, as prednisone can impact blood glucose control. Closely observe any new or worsening symptoms and communicate them to your healthcare provider.
Addressing Side Effects
Communicate openly with your doctor about any side effects you experience, including increased urination, insomnia, or mood changes. They can adjust your dosage or suggest strategies for managing these issues. Be proactive in seeking solutions. Don’t hesitate to ask questions.
Medication Interactions
Inform your doctor and pharmacist about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking. Prednisone can interact with other drugs. This precaution helps avoid adverse reactions or reduce the effectiveness of either medication. Always ensure your healthcare team has a complete picture of your medication profile.