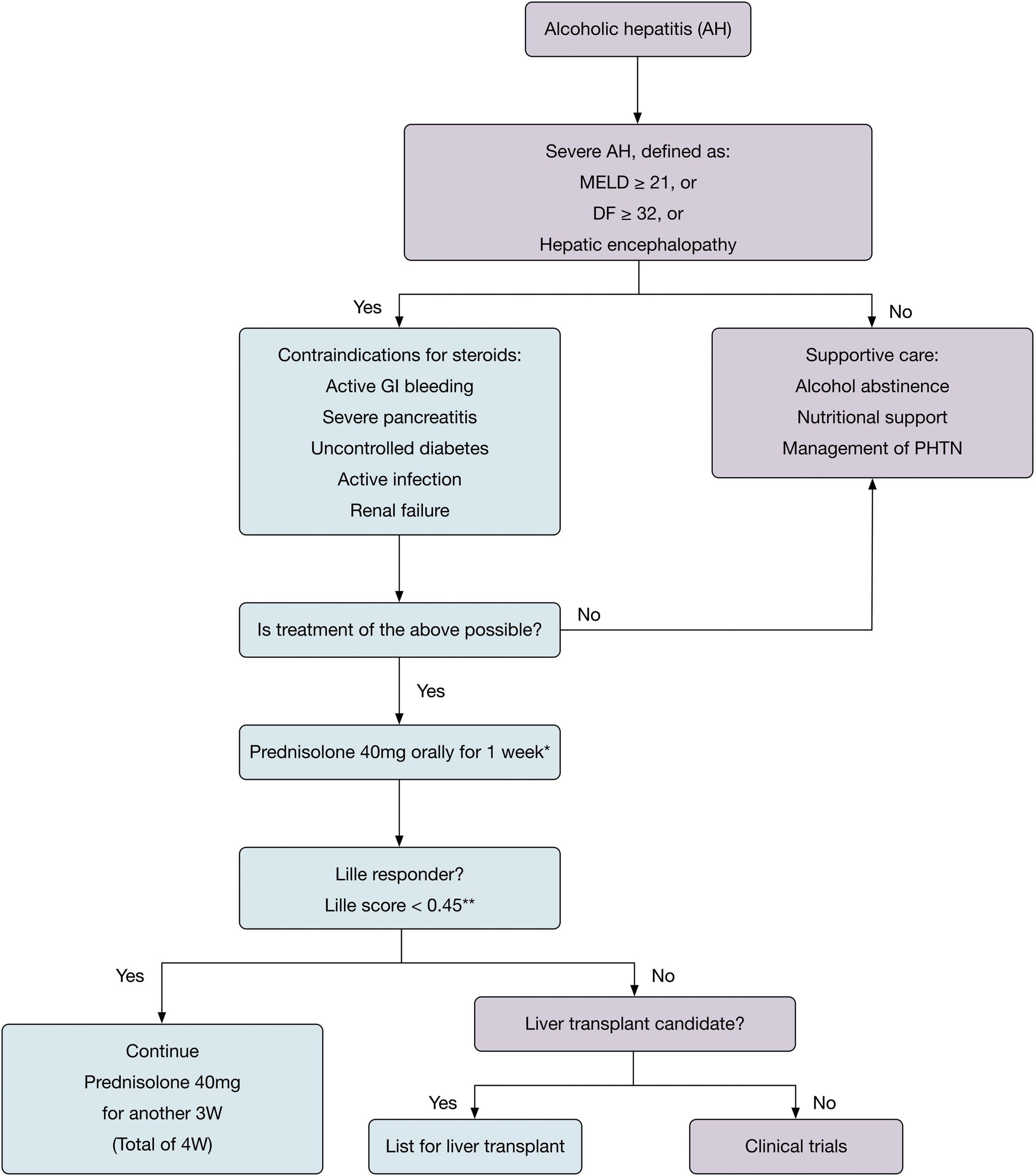
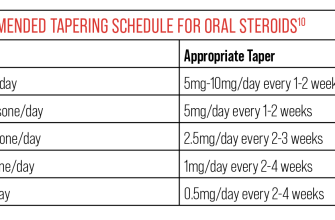
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, can interact with Hepatitis C treatment. Specifically, concurrent use may reduce the effectiveness of direct-acting antiviral (DAA) medications, the current standard of care for Hepatitis C. This means your viral load might not decrease as expected, potentially prolonging treatment and increasing the risk of resistance development.
Consult your hepatologist before starting prednisone if you’re undergoing or planning Hepatitis C treatment. They’ll assess your individual needs and possibly adjust your DAA regimen or monitor you closely for side effects. This personalized approach is key to successful Hepatitis C eradication.
Important Considerations: The impact of prednisone on DAA efficacy varies depending on factors including the specific DAA used, the dose and duration of prednisone, and your overall health. Some studies suggest that prednisone’s influence might be more significant with certain DAA combinations than others. Open communication with your healthcare team is paramount to address any concerns and optimize your treatment strategy.
Remember that managing both Hepatitis C and any other medical condition requires a collaborative approach. Your physician can provide tailored advice, answer your questions, and monitor your progress to ensure the safest and most successful outcome. Don’t hesitate to discuss your concerns about potential drug interactions.
- Hepatitis C and Prednisone: Understanding the Interaction
- Impact on Treatment Outcomes
- Recommended Actions
- Monitoring and Adjustments
- Specific Considerations
- Prednisone’s Mechanism of Action and Potential Effects on the Liver
- Increased Liver Enzyme Levels
- Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI)
- Interactions with Hepatitis C Medications
- Recommendations
- How Prednisone Might Affect Hepatitis C Treatment Outcomes
- Increased Risk of Hepatitis C Complications with Prednisone Use
- Why Prednisone Increases Risk
- Managing the Risk
- Specific Concerns
- Conclusion
- Monitoring Liver Function During Concurrent Prednisone and Hepatitis C Treatment
- Key Liver Enzymes to Watch
- Reporting Changes
- Specific Considerations for Patients with Hepatitis C and Existing Liver Conditions
- Alternative Treatment Options to Minimize Prednisone’s Impact on Hepatitis C
- Lifestyle Modifications
- Dietary Supplements
- Stress Management Techniques
- Close Medical Monitoring
- Consulting Your Doctor: Importance of Open Communication Regarding Prednisone and Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C and Prednisone: Understanding the Interaction
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, can interact with Hepatitis C treatment. Specifically, it may reduce the effectiveness of direct-acting antiviral (DAA) medications used to treat Hepatitis C. This interaction happens because prednisone suppresses the immune system, and a strong immune response is beneficial for viral clearance.
Impact on Treatment Outcomes
Studies show that concurrent use of prednisone and DAAs might lead to lower sustained virological response (SVR) rates – meaning a lower chance of successfully eliminating the virus. The degree of this impact varies depending on factors like the prednisone dosage, the duration of use, and the specific DAA regimen. Higher doses and longer treatment periods with prednisone are associated with a greater risk of reduced DAA effectiveness.
Recommended Actions
Open Communication is Key: Discuss your Hepatitis C treatment and any other medications, including prednisone, with your healthcare provider. They will carefully weigh the benefits of prednisone against the potential risk of reduced DAA effectiveness. Alternative treatments for your underlying condition may be considered, if possible.
Monitoring and Adjustments
Careful Monitoring: Your doctor may recommend more frequent monitoring of your viral load during treatment if you are also taking prednisone. This allows for early detection of treatment failure and the opportunity to adjust the treatment strategy. Regular liver function tests are also important.
Specific Considerations
The interaction between prednisone and DAAs is complex and depends on many individual factors. There’s no one-size-fits-all answer. Your doctor will assess your specific circumstances to determine the best course of action. Always prioritize open communication with your healthcare team.
Prednisone’s Mechanism of Action and Potential Effects on the Liver
Prednisone, a glucocorticoid, reduces inflammation by binding to intracellular receptors, influencing gene expression. This impacts various immune system components, suppressing the inflammatory response. However, this potent anti-inflammatory action carries liver-related risks.
Increased Liver Enzyme Levels
Prednisone can elevate liver enzyme levels (ALT and AST), indicating potential liver damage. This rise doesn’t always signify actual liver cell death; it often reflects inflammation within the liver. Regular blood tests monitor this.
Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI)
While rare, prednisone can cause DILI. Symptoms may include jaundice, fatigue, and abdominal pain. Immediate medical attention is crucial if these develop. Careful monitoring and prompt intervention are key to preventing serious complications.
Interactions with Hepatitis C Medications
Prednisone’s impact on liver function requires careful consideration when used alongside Hepatitis C medications. Some antiviral drugs may have additive effects on liver enzymes, necessitating close monitoring of liver health. Your healthcare provider should carefully assess any potential drug interactions. They can adjust medication regimens accordingly to minimize liver stress.
Recommendations
Regular liver function tests are strongly recommended during prednisone treatment, especially if you have Hepatitis C. Open communication with your doctor is vital, reporting any new or worsening symptoms immediately. Your physician can tailor the medication regimen and monitoring plan to optimize outcomes and minimize liver-related risks.
How Prednisone Might Affect Hepatitis C Treatment Outcomes
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, can interfere with Hepatitis C treatment. Specifically, it may reduce the effectiveness of direct-acting antiviral (DAA) medications. This happens because prednisone influences the body’s immune response, a key player in eliminating the virus. Studies show a correlation between higher prednisone doses and lower sustained virologic response (SVR) rates – meaning the virus might not be completely cleared.
The impact varies depending on factors like the specific DAA regimen, prednisone dosage, and the patient’s overall health. For instance, patients receiving higher doses of prednisone for extended periods are at greater risk of treatment failure. This is because prednisone can suppress the immune system, hindering the body’s ability to fight the virus even with the help of DAAs.
It’s important to inform your healthcare provider about all medications you’re taking, including prednisone, before beginning Hepatitis C treatment. They can assess the risks and benefits, potentially adjusting the treatment plan or monitoring you more closely for treatment response. This might include more frequent blood tests to monitor viral load. A change in DAA medication might be considered depending on the circumstances.
| Factor | Potential Impact on Hepatitis C Treatment |
|---|---|
| Prednisone Dosage | Higher doses generally correlate with reduced SVR rates. |
| Duration of Prednisone Use | Longer use increases the risk of treatment failure. |
| Specific DAA Regimen | Some DAAs may be more susceptible to prednisone’s interference than others. |
| Patient’s Overall Health | Pre-existing conditions can influence the response to both prednisone and DAA therapy. |
Open communication with your doctor is crucial. They can help you weigh the risks and benefits of continuing prednisone alongside Hepatitis C treatment and develop a tailored approach that optimizes your chances of successful treatment. Don’t hesitate to ask questions and express your concerns.
Increased Risk of Hepatitis C Complications with Prednisone Use
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, can worsen Hepatitis C. This means you’re more likely to experience complications if you’re taking prednisone while battling Hepatitis C.
Why Prednisone Increases Risk
Prednisone suppresses your immune system. A weakened immune system allows the Hepatitis C virus to replicate more easily, leading to a faster disease progression.
- Increased viral load: Prednisone can significantly increase the amount of Hepatitis C virus in your blood.
- Slower treatment response: If you’re undergoing Hepatitis C treatment, prednisone may interfere with its effectiveness, delaying your recovery.
- Higher risk of liver damage: Prednisone contributes to liver inflammation, potentially accelerating liver fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Managing the Risk
Open communication with your doctor is paramount. They need to carefully weigh the benefits of prednisone against the potential risks to your liver health.
- Regular monitoring: Frequent blood tests to monitor your viral load and liver function are crucial.
- Alternative treatments: Your doctor may explore alternative medications to treat your condition, minimizing prednisone use.
- Lifestyle adjustments: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and avoiding alcohol, can mitigate potential complications.
Specific Concerns
Some studies show a link between prednisone use and faster progression to liver cirrhosis in individuals with Hepatitis C. This highlights the need for proactive management and close medical supervision.
Conclusion
Using prednisone while you have Hepatitis C increases the chance of serious complications. Work closely with your healthcare provider to minimize risks and optimize your treatment plan.
Monitoring Liver Function During Concurrent Prednisone and Hepatitis C Treatment
Regular monitoring of your liver function is absolutely vital when taking prednisone alongside Hepatitis C treatment. Your doctor will schedule blood tests to track specific liver enzyme levels.
Key Liver Enzymes to Watch
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT): Elevated ALT indicates potential liver damage. Significant increases necessitate immediate attention.
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST): Similar to ALT, elevated AST levels also point to liver injury. The ALT/AST ratio can offer further diagnostic insight.
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP): While not specific to the liver, increased ALP might suggest bile duct issues, potentially complicating Hepatitis C and prednisone treatment.
- Bilirubin: Increased bilirubin levels signify impaired liver function in processing bile. Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes) often accompanies high bilirubin.
Frequency of blood tests depends on your individual response to treatment and the severity of your Hepatitis C. Expect more frequent tests initially, then possibly less often if levels remain stable.
Reporting Changes
- Report any noticeable symptoms like fatigue, jaundice, dark urine, or pale stools immediately to your healthcare provider.
- Don’t hesitate to contact your doctor if you experience any unusual symptoms, even if they seem minor. Early detection can prevent serious complications.
- Maintain open communication with your medical team; they need accurate information to adjust your treatment plan as needed.
Consistent monitoring allows your doctor to promptly detect and address any liver damage, optimizing both your Hepatitis C and prednisone treatment. Your proactive participation is key to a successful outcome.
Specific Considerations for Patients with Hepatitis C and Existing Liver Conditions
Patients with Hepatitis C and pre-existing liver conditions, such as cirrhosis or liver fibrosis, require close monitoring during prednisone treatment. Prednisone can increase liver enzyme levels, potentially masking Hepatitis C progression or worsening underlying liver damage. Regular blood tests are vital to track liver function and adjust treatment accordingly.
Close collaboration between your hepatologist and other healthcare providers is crucial. They will work together to create a tailored treatment plan balancing the benefits of prednisone for your specific condition against potential risks to your liver. This collaboration ensures your safety and best possible outcome.
Your doctor will carefully assess your individual risk profile. Factors considered include the severity of your Hepatitis C, the extent of your existing liver disease, and your overall health. This information helps determine the appropriate prednisone dosage, duration of treatment, and frequency of monitoring.
Be aware that prednisone can interact with other medications, including those used to treat Hepatitis C. Always inform your doctor of all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking. This is vital for avoiding potentially dangerous drug interactions and adverse effects.
Report any new or worsening symptoms promptly, including fatigue, jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes), abdominal pain, or swelling in your legs or ankles. These could indicate liver complications requiring immediate medical attention. Open communication with your healthcare team is paramount.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle throughout treatment is beneficial. This includes following a balanced diet, abstaining from alcohol, and adhering to any recommended physical activity guidelines provided by your doctor. These lifestyle choices support overall health and liver function.
Alternative Treatment Options to Minimize Prednisone’s Impact on Hepatitis C
Prioritize a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins to support your immune system and overall health while on prednisone. This helps mitigate potential side effects.
Lifestyle Modifications
Regular, moderate exercise strengthens the immune system and combats prednisone-induced weight gain and muscle weakness. Aim for at least 30 minutes of activity most days of the week. Adequate sleep (7-9 hours nightly) is also crucial for recovery and reduces stress, further minimizing side effects.
Dietary Supplements
Consult your doctor before taking any supplements. Some studies suggest that certain supplements, like Vitamin D and Omega-3 fatty acids, might help counteract some of prednisone’s negative impacts. However, individual responses vary greatly, and professional guidance is necessary.
Stress Management Techniques
Prednisone can exacerbate stress and anxiety. Implement stress-reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises. These practices have shown positive effects on overall well-being and may help manage side effects.
Close Medical Monitoring
Regular blood tests to monitor liver function and blood glucose levels are essential. This allows your doctor to adjust your medication and address any arising complications promptly. Open communication with your healthcare team is key to successful management.
Consulting Your Doctor: Importance of Open Communication Regarding Prednisone and Hepatitis C
Always inform your doctor about your Hepatitis C diagnosis before starting any medication, including prednisone. This allows them to assess potential interactions and adjust your treatment plan accordingly.
Describe all your symptoms clearly. Mention any changes in your health, even seemingly unrelated ones, as they might influence the decision on prednisone use or its dosage. Provide a complete medical history, including previous treatments for Hepatitis C.
Ask specific questions about potential side effects. Understand how prednisone might affect your liver and your Hepatitis C treatment. Inquire about monitoring strategies to detect and manage complications.
Discuss alternative treatments. If prednisone poses significant risks, explore other options suitable for your condition. Your doctor will help you find a balance between managing your current symptoms and long-term health.
Actively participate in decisions about your care. Do not hesitate to express your concerns and preferences. Open communication is vital for successful management of both Hepatitis C and any medication you are taking.
Maintain a detailed record of your conversations with your doctor and any changes to your medication. This detailed log will be invaluable during follow-up appointments.