Need to manage high-dose prednisone? Prioritize regular blood pressure monitoring; aim for daily checks. Consistent monitoring helps you and your doctor quickly address potential issues.
Consume a potassium-rich diet to counteract potential side effects. Focus on foods like bananas, potatoes, and spinach. Your doctor can recommend a personalized dietary plan to ensure adequate potassium intake.
Bone density loss is a significant concern with long-term prednisone use. Discuss bone density testing with your physician; they can recommend preventative measures like calcium and Vitamin D supplements and, if necessary, medication to protect your bones.
Monitor your blood sugar levels, especially if you have a history of diabetes. Frequent monitoring and potential adjustments to your medication regimen are key to preventing serious complications. Regular exercise and a balanced diet can support blood sugar control.
Communicate openly with your doctor about any side effects you experience. Report even minor symptoms, such as mood changes, insomnia, or increased appetite, for prompt and effective management.
- High Prednisone: Understanding the Risks and Benefits
- Potential Benefits
- Significant Risks
- Managing the Risks
- Alternatives and Considerations
- Common Side Effects of High-Dose Prednisone and Management Strategies
- Metabolic Changes
- Other Potential Side Effects
- Important Note
- Tapering Off Prednisone: A Safe and Effective Approach
- Understanding Your Tapering Plan
- Managing Potential Withdrawal Symptoms
- Monitoring Your Progress
- Long-Term Health Considerations
- Alternative Treatment Options
- Long-Term Effects of High Prednisone Use and Alternative Treatments
- Minimizing Prednisone’s Impact
- Alternative Treatments
- Tapering Off Prednisone
- Monitoring Your Health While on High-Dose Prednisone
High Prednisone: Understanding the Risks and Benefits
High-dose prednisone offers powerful anti-inflammatory effects, proving invaluable in managing severe conditions like lupus flares or severe asthma attacks. However, prolonged or high-dose use carries significant risks.
Potential Benefits
Prednisone’s rapid action makes it a lifesaver in emergencies. It reduces swelling, suppresses the immune system, and alleviates symptoms quickly. This is particularly beneficial for conditions causing immediate organ damage.
Significant Risks
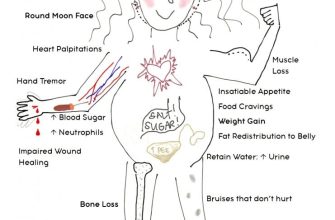
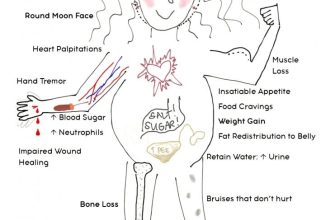
Weight gain is common, often accompanied by fluid retention and increased appetite. Osteoporosis is a serious concern; prednisone weakens bones, increasing fracture risk. Hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar, frequently occurs, potentially worsening existing diabetes or inducing it. Increased risk of infections is another significant drawback, as the medication suppresses the immune response. Mood swings, ranging from irritability to depression, are also reported. Long-term use can lead to Cushing’s syndrome, characterized by fat redistribution, thin skin, and hypertension. Additionally, the medication can raise the risk of blood clots and cataracts. Weaning off prednisone must be done gradually to minimize withdrawal symptoms and allow the body to adjust.
Managing the Risks
Regular monitoring by your doctor is critical. Blood tests, bone density scans, and regular checkups help track potential side effects and enable timely intervention. A healthy diet and regular exercise can mitigate some side effects, such as weight gain and osteoporosis. Your doctor can also prescribe medications to counteract specific side effects like hyperglycemia or osteoporosis. Open communication with your doctor is key; report any new or worsening symptoms immediately.
Alternatives and Considerations
Discuss alternatives with your doctor. Other medications might offer similar benefits with fewer risks, depending on your specific condition. The decision to use high-dose prednisone involves careful weighing of the potential benefits against the substantial risks.
Common Side Effects of High-Dose Prednisone and Management Strategies
High-dose prednisone can cause various side effects. Managing these requires careful monitoring and proactive strategies. Weight gain is frequent; focus on a balanced diet low in processed foods and refined sugars, and increase physical activity. Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly, as hyperglycemia is a common concern; discuss appropriate dietary adjustments and potential medication with your doctor.
Metabolic Changes
Increased appetite and fluid retention often accompany prednisone use. Limit sodium intake to reduce fluid retention. Consider working with a registered dietitian to create a personalized meal plan addressing your specific needs and managing calorie intake. Increased blood pressure is another possibility; regular monitoring and lifestyle changes like reducing salt intake and engaging in regular exercise are key. Discuss potential medication adjustments with your physician.
Other Potential Side Effects
Mood changes, including irritability, anxiety, and depression, are possible. Open communication with your doctor and therapist, if necessary, is vital. Consider stress management techniques like yoga or meditation. Osteoporosis risk increases; adequate calcium and vitamin D intake is crucial. Discuss bone density testing with your doctor. Insomnia is another potential side effect; maintain a regular sleep schedule and create a relaxing bedtime routine. If problems persist, discuss sleep aids with your physician. Increased risk of infection requires attention to hygiene and prompt medical attention for any signs of infection.
Important Note
This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your doctor before starting, stopping, or changing any medication or treatment plan. They can tailor management strategies to your individual needs and health status.
Tapering Off Prednisone: A Safe and Effective Approach
Consult your doctor to create a personalized tapering schedule. This schedule will gradually reduce your prednisone dosage over weeks or months, minimizing withdrawal symptoms.
Understanding Your Tapering Plan
Your doctor will determine the best tapering schedule based on your individual health, the dosage you’re currently on, and the length of time you’ve been taking prednisone. Expect regular check-ups to monitor your progress and adjust the plan as needed. Common schedules involve decreasing the dosage by small increments – for example, 5 mg every few days or a week. This gradual reduction allows your body to adapt. Never abruptly stop taking prednisone without medical supervision.
Managing Potential Withdrawal Symptoms
Expect some withdrawal symptoms as your body adjusts. These might include fatigue, muscle weakness, joint pain, nausea, and mood changes. Your doctor can help you manage these symptoms. Maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and getting adequate rest can also alleviate discomfort. Open communication with your doctor is key – report any concerning symptoms promptly.
Monitoring Your Progress
Regular blood tests will help your doctor track your hormone levels and overall health during the tapering process. These tests ensure the reduction is happening safely and at the right pace. Your doctor may also adjust your plan based on these results. This approach ensures a smooth transition and minimizes potential health risks.
Long-Term Health Considerations
After completing the tapering process, maintain regular contact with your doctor for ongoing monitoring. Long-term side effects of prednisone use vary, and continuous healthcare will help detect and manage any issues that may arise. Focusing on a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, helps support overall well-being.
Alternative Treatment Options
Discuss alternative treatment options with your doctor to manage the underlying condition that necessitates prednisone. They can help you find effective alternatives to minimize your reliance on steroids in the future. This proactive approach supports long-term health management.
Long-Term Effects of High Prednisone Use and Alternative Treatments
High-dose prednisone, while effective for short-term inflammation, carries significant long-term risks. Prolonged use can weaken bones (osteoporosis), increase blood sugar (hyperglycemia), raise blood pressure, and suppress the immune system, making you susceptible to infections. Weight gain, mood swings, and cataracts are also common side effects.
Minimizing Prednisone’s Impact
To mitigate these risks, your doctor will likely prescribe the lowest effective dose for the shortest possible time. They may also recommend calcium and vitamin D supplements to protect your bones, regular blood sugar monitoring, and lifestyle changes to manage blood pressure and weight.
Alternative Treatments
Depending on the condition, alternatives to prednisone exist. These might include:
| Condition | Alternative Treatment |
|---|---|
| Asthma | Inhaled corticosteroids, leukotriene modifiers, or biologics. |
| Rheumatoid Arthritis | Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologics, or targeted synthetic DMARDs. |
| Lupus | Hydroxychloroquine, immunosuppressants, or biologics. |
| Inflammatory Bowel Disease | Aminosalicylates, immunomodulators, or biologics. |
Remember, these are just examples, and treatment depends on individual needs and the severity of the condition. Always discuss treatment options thoroughly with your doctor before making any changes to your medication regimen. They can assess your specific situation and help you create a personalized plan to minimize risks and improve your health.
Tapering Off Prednisone
Stopping prednisone abruptly is dangerous. Your doctor will gradually reduce your dose to allow your body to adjust. This process, called tapering, minimizes withdrawal symptoms like fatigue, joint pain, and nausea.
Monitoring Your Health While on High-Dose Prednisone
Schedule regular check-ups with your doctor. These visits allow for consistent monitoring of your blood pressure, blood sugar, and weight.
Monitor your blood pressure daily. High doses of prednisone can elevate blood pressure. Keep a log to share with your physician.
- Use a home blood pressure monitor for accurate readings.
- Report significant or persistent increases to your doctor immediately.
Track your blood sugar levels. Prednisone can impact blood sugar, increasing the risk of hyperglycemia. Regular monitoring is critical, especially if you have diabetes.
- Use a blood glucose meter as directed by your doctor.
- Adjust your diabetes medication as advised by your doctor.
Weigh yourself regularly. Prednisone can cause fluid retention and weight gain. Weekly weigh-ins help detect significant changes.
- Note any rapid weight fluctuations and report them to your doctor.
- Discuss dietary changes with your physician if needed.
Pay close attention to your bone health. Prednisone can weaken bones, increasing fracture risk.
- Incorporate weight-bearing exercise into your routine, if cleared by your doctor.
- Discuss bone density testing with your doctor.
Be vigilant about infections. Prednisone suppresses your immune system, making you more susceptible to infections.
- Practice good hygiene and avoid exposure to sick individuals.
- Report any signs of infection – fever, cough, or unusual pain – promptly to your doctor.
Report any unusual symptoms. This includes muscle weakness, mood changes, vision problems, or skin changes. Early detection can help manage potential side effects.
- Keep a detailed record of all symptoms and medications.
- Communicate openly with your healthcare provider about any concerns.
Follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Adherence to your prescribed dosage and medication schedule is crucial for minimizing potential complications.