Administer liquid prednisolone to your cat using a calibrated oral syringe. Accurate dosing is paramount; always follow your veterinarian’s instructions precisely. Incorrect dosage can lead to serious health complications.
Store prednisolone at room temperature, away from direct sunlight and moisture. A consistent storage environment helps maintain the medication’s potency. Check the expiration date regularly and discard expired medication appropriately.
Monitor your cat closely for side effects such as increased thirst, increased urination, or changes in appetite. These are common, but report any concerning symptoms to your vet immediately. Long-term prednisolone use may require blood tests to check for potential complications.
Never abruptly stop prednisolone administration without consulting your veterinarian. Sudden cessation can trigger withdrawal symptoms. Your vet will help develop a safe tapering schedule to minimize potential side effects.
Remember: This information is for guidance only. Always consult your veterinarian for diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of your cat’s condition. They can provide personalized advice tailored to your cat’s specific needs and health history. Never self-medicate your pet.
- Liquid Prednisolone for Cats
- Administering Liquid Prednisolone
- Monitoring Your Cat
- Storage and Safety
- Understanding Prednisolone’s Role in Feline Health
- Treating Specific Feline Illnesses
- Managing Side Effects
- Working with Your Veterinarian
- Administering Liquid Prednisolone: Dosage and Methods
- Oral Administration
- Mixing with Food
- Monitoring Your Cat
- Common Side Effects and How to Manage Them
- Potential Drug Interactions with Liquid Prednisolone
- When to Seek Veterinary Attention Regarding Prednisolone Use
- Monitoring for Adverse Reactions
- Addressing Specific Concerns
- Long-Term Effects and Tapering Off Prednisolone
- Storing and Handling Liquid Prednisolone Safely
- Optimal Storage Conditions
- Safe Handling Practices
- Disposal of Unused Medication
- Monitoring Your Cat
- Information Accuracy
Liquid Prednisolone for Cats
Always consult your veterinarian before giving your cat liquid prednisolone. They will determine the correct dosage based on your cat’s weight, age, and specific condition. Typical dosages range from 0.5 to 2 mg per kilogram of body weight, administered once or twice daily. Your vet will provide precise instructions, including the frequency and duration of treatment.
Administering Liquid Prednisolone
Many cats find the taste unpleasant. To make administration easier, mix the prednisolone with a small amount of palatable food, such as tuna or chicken. Ensure your cat consumes the entire mixture. Never force your cat to swallow the medication, as this can cause stress and injury. If your cat consistently refuses the medication mixed with food, your vet might recommend an alternative administration method.
Monitoring Your Cat
Closely monitor your cat for side effects, including increased thirst and urination, increased appetite, changes in behavior (such as increased activity or aggression), and vomiting. Report any unusual symptoms to your veterinarian immediately. Regular veterinary checkups are crucial during prednisolone treatment to monitor your cat’s progress and adjust the dosage as needed. Prednisolone can interact with other medications, so always inform your vet about all your cat’s medications and supplements. Long-term use can lead to various health problems. Weaning your cat off prednisolone must be done gradually under your vet’s guidance to prevent withdrawal symptoms.
Storage and Safety
Store liquid prednisolone in a cool, dark place away from children and pets, as directed on the prescription label. Discard any leftover medication as instructed by your veterinarian or pharmacist. Always follow your veterinarian’s guidance regarding administration and monitoring of your cat’s health throughout the treatment.
Understanding Prednisolone’s Role in Feline Health
Prednisolone, a corticosteroid, acts as a powerful anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressant medication for cats. It reduces swelling, inflammation, and allergic reactions by influencing the body’s immune response. This makes it valuable in treating various feline conditions.
Treating Specific Feline Illnesses
Veterinarians frequently prescribe prednisolone for conditions like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), asthma, allergies (including flea allergies), and certain autoimmune disorders. It also finds use in managing conditions causing pain and discomfort, such as arthritis. The dosage and duration depend entirely on the cat’s specific condition and response to treatment. Always follow your vet’s instructions precisely.
Managing Side Effects
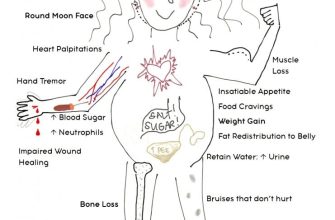
While beneficial, prednisolone can cause side effects, including increased thirst and urination, increased appetite leading to weight gain, and a weakened immune system. Long-term use may also contribute to other health problems. Regular veterinary checkups are vital to monitor your cat’s health and adjust the medication accordingly. Promptly report any concerning changes in your cat’s behavior or health to your vet.
Working with Your Veterinarian
Prednisolone is a prescription medication. Never administer it without a veterinarian’s diagnosis and guidance. They will determine the appropriate dosage, monitor your cat’s progress, and make necessary adjustments based on your cat’s individual needs. Open communication with your vet is key to ensuring the safe and effective use of this medication.
Administering Liquid Prednisolone: Dosage and Methods
Always follow your veterinarian’s instructions precisely. The correct dosage depends on your cat’s weight, the specific condition being treated, and other factors. Typical dosages range from 0.5 to 2 mg per kilogram of body weight, administered once or twice daily. Your vet will provide a precise amount for your cat.
Oral Administration
Use a clean oral syringe to administer the medication. Gently restrain your cat, placing them on a stable surface. Open your cat’s mouth carefully and slowly dispense the liquid prednisolone to the back of their tongue, avoiding the teeth. Allow your cat to swallow naturally. Avoid squirting directly into their throat, which can cause choking. Reward your cat with a small treat afterward.
Mixing with Food
If your cat resists taking the medication directly, try mixing a small amount of the liquid prednisolone into a palatable food, like wet cat food or tuna. Ensure your cat consumes all the food to guarantee they receive the full dose. Monitor your cat for any adverse reactions.
Monitoring Your Cat
Closely observe your cat for any side effects, such as increased thirst, increased urination, increased appetite, or changes in behavior. Report any unusual symptoms to your veterinarian immediately. Regular veterinary check-ups are necessary to monitor your cat’s progress and adjust the dosage as needed. Prednisolone treatment is generally temporary, and your vet will determine the appropriate duration.
Common Side Effects and How to Manage Them
Monitor your cat closely for potential side effects. Increased thirst and urination are common. Provide fresh water freely and consider a litter box that’s easy to access.
Increased appetite is also possible. Adjust food portions accordingly to avoid weight gain. Choose a high-quality diet.
Some cats experience vomiting or diarrhea. If this happens, contact your vet. They might recommend a bland diet or medication to help.
Prednisolone can suppress the immune system, increasing the risk of infection. Observe your cat for any signs of illness, such as lethargy, fever, or discharge. Seek veterinary attention immediately if you notice any.
Behavioral changes, such as increased aggression or restlessness, are also potential side effects. A calm, quiet environment can help. Consult your veterinarian if the changes are significant or concerning.
| Side Effect | Management |
|---|---|
| Increased thirst and urination (Polydipsia/Polyuria) | Ensure access to fresh water; consider diet adjustments. |
| Increased appetite (Polyphagia) | Adjust food portions; opt for a high-quality diet. |
| Gastrointestinal upset (Vomiting, Diarrhea) | Contact your veterinarian; consider bland diet. |
| Immunosuppression | Monitor for infections; seek veterinary care if needed. |
| Behavioral changes | Provide a calm environment; consult veterinarian if severe. |
Remember, this information is for guidance only. Always follow your veterinarian’s instructions and contact them immediately if you have any concerns about your cat’s health while on prednisolone.
Potential Drug Interactions with Liquid Prednisolone
Always inform your veterinarian about all medications your cat is taking, including supplements and herbal remedies. Prednisolone can interact negatively with several drug classes.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Combining prednisolone with NSAIDs like ibuprofen or aspirin increases the risk of stomach ulcers and gastrointestinal bleeding. Avoid concurrent use.
- Aspirin: This poses similar risks to other NSAIDs, significantly increasing the chance of gastrointestinal complications.
- Potassium-depleting diuretics: Prednisolone can increase potassium loss. Concomitant use with diuretics, such as furosemide, may lead to dangerously low potassium levels (hypokalemia).
- Insulin and other diabetes medications: Prednisolone can increase blood sugar levels, potentially requiring adjustments to insulin or other diabetic medications. Close monitoring of blood glucose is vital.
- Drugs metabolized by the liver (e.g., many antibiotics): Prednisolone can affect liver enzymes, altering how the body processes other drugs. This might lead to either reduced effectiveness or increased side effects of other medications.
- Live vaccines: Prednisolone can suppress the immune system, making live vaccines less effective. Delay vaccination until prednisolone treatment concludes.
This list isn’t exhaustive; other interactions are possible. Discuss any concerns with your vet before giving your cat prednisolone, especially if your cat takes other medications.
- Regularly monitor your cat’s health: Watch for any unusual signs or symptoms.
- Report any changes immediately: Contact your veterinarian if you notice any unexpected reactions or changes in your cat’s condition.
Your veterinarian can help manage potential drug interactions and ensure the safest and most effective treatment for your cat.
When to Seek Veterinary Attention Regarding Prednisolone Use
Contact your vet immediately if your cat shows any signs of increased thirst or urination, vomiting, diarrhea, or loss of appetite. These can be signs of serious side effects.
Monitoring for Adverse Reactions
Report any changes in your cat’s behavior, such as increased aggression, lethargy, or changes in coat condition. Weight gain should also be reported to your veterinarian. These symptoms may indicate problems with the medication’s effects. Regular monitoring, as directed by your vet, is key.
Addressing Specific Concerns
If your cat develops any skin infections, eye problems, or difficulty breathing, seek veterinary care at once. These could indicate a more severe reaction to prednisolone and require immediate treatment. Don’t hesitate to contact your vet if you have any questions or concerns, no matter how minor they may seem. Early intervention improves outcomes.
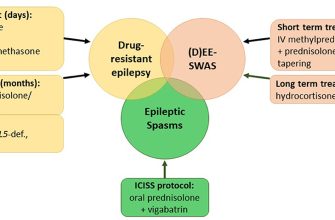
Long-Term Effects and Tapering Off Prednisolone
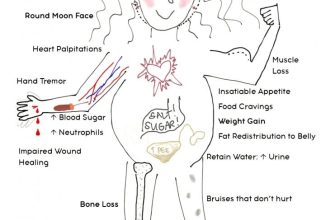
Always consult your veterinarian before starting or stopping prednisolone. Long-term prednisolone use can cause significant side effects in cats. These include increased thirst and urination (polydipsia and polyuria), increased appetite with potential weight gain, weakened immune system making them more susceptible to infections, and potentially elevated blood sugar.
Cushing’s disease is a serious long-term risk. This occurs when the body becomes reliant on the medication and doesn’t produce its own cortisol adequately. Symptoms include a pot-bellied appearance, muscle wasting, thinning skin, and hair loss.
Tapering off prednisolone is crucial to minimize these risks. Your vet will create a specific tapering schedule, typically involving a gradual reduction in dosage over several weeks or months. Never stop prednisolone abruptly; this can cause serious health problems.
During the tapering process, monitor your cat closely for any changes in behavior, appetite, or elimination habits. Report any concerns immediately to your vet. They may need to adjust the tapering schedule based on your cat’s response.
Regular blood work can help your vet monitor your cat’s cortisol levels and ensure the tapering process is progressing safely. This will help avoid potential complications and ensure a smooth transition.
Storing and Handling Liquid Prednisolone Safely
Always refrigerate liquid prednisolone after opening. This extends its shelf life and maintains potency.
Optimal Storage Conditions
- Keep the medication in its original container to prevent contamination and ensure proper labeling.
- Store between 2°C and 8°C (36°F and 46°F). Avoid freezing.
- Discard any unused medication after the expiration date printed on the label.
Properly label the container with the medication name, your cat’s name, and the date you opened it. This helps avoid confusion and accidental misuse.
Safe Handling Practices
- Wash your hands thoroughly before and after handling the medication.
- Use a clean, dry syringe or oral dosing device each time you administer the prednisolone. Never reuse syringes or dosing devices.
- Avoid touching the tip of the syringe or dosing device to anything other than your cat’s mouth.
- Keep the medication out of reach of children and other pets.
Disposal of Unused Medication
Never flush liquid prednisolone down the toilet or drain. Follow your veterinarian’s instructions or local guidelines for safe disposal. Many pharmacies offer medication take-back programs.
Monitoring Your Cat
Closely monitor your cat for any adverse effects after administering liquid prednisolone. Contact your veterinarian immediately if you observe any unusual behavior or symptoms.
Information Accuracy
This information is for guidance only and does not replace veterinary advice. Always consult your veterinarian for specific instructions regarding your cat’s treatment and medication handling.