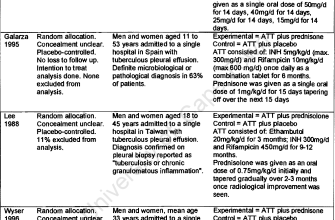
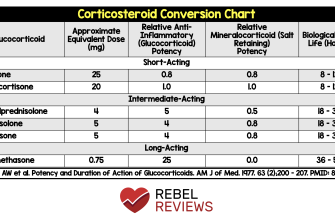
Consult your doctor before starting any prednisone regimen. Dosage depends entirely on your specific condition and health profile. Typical starting doses range from 5mg to 60mg daily, adjusted based on response and potential side effects. Close monitoring is key.
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, powerfully reduces inflammation. This makes it effective for various conditions, including autoimmune diseases, allergies, and certain cancers. However, long-term use carries risks, including increased blood sugar, bone thinning, and increased susceptibility to infections. Your physician will carefully weigh the benefits against these potential risks.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Never abruptly stop taking prednisone; tapering the dose is crucial to avoid potentially harmful withdrawal symptoms. Regular blood tests help track your progress and identify any adverse effects promptly.
Remember: This information serves as a general overview, not medical advice. Individual needs vary greatly. A personalized treatment plan, developed in consultation with your healthcare provider, is paramount for safe and effective prednisone management.
- Mg Prednisone: A Detailed Guide
- Understanding Prednisone Doses
- Possible Side Effects
- Managing Side Effects
- Medication Interactions
- Long-Term Use
- Understanding Prednisone Dosage in Milligrams (mg)
- Typical Prednisone Dosages
- Factors Influencing Dosage
- Tapering Off Prednisone
- Always Consult Your Doctor
- Common Side Effects and Management Strategies of Prednisone
- Prednisone and Interactions: Medication and Lifestyle Considerations
- Dietary Recommendations
- Lifestyle Adjustments
- Important Note:
Mg Prednisone: A Detailed Guide
Always consult your doctor before starting or changing any medication, including prednisone. Dosage depends entirely on your individual needs and health condition. Your physician will determine the appropriate milligram (mg) amount and duration of treatment.
Understanding Prednisone Doses
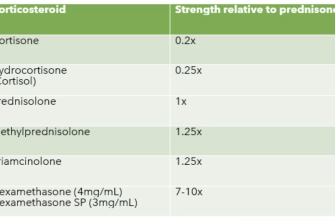
Prednisone dosages are typically prescribed in milligrams (mg) per day. Common starting dosages range from 5 mg to 60 mg daily, depending on the specific condition being treated. Higher doses are usually needed for severe conditions, while lower doses might suffice for milder cases. The doctor might prescribe a tapering schedule, gradually reducing the daily dose to minimize withdrawal effects. This process ensures your body adjusts to the decreasing levels of the medication.
Possible Side Effects
Common side effects include weight gain, increased appetite, mood changes (including irritability and anxiety), insomnia, and increased risk of infection. Serious side effects, although less frequent, can include high blood pressure, osteoporosis, and increased blood sugar levels. Regular monitoring by your healthcare provider is crucial to detect and manage any adverse effects.
Managing Side Effects
Your doctor can suggest strategies for managing side effects. For instance, a healthy diet and regular exercise can help mitigate weight gain. Discussing potential mood changes with your doctor can help you find appropriate solutions. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and closely following your doctor’s recommendations plays a key role in minimizing the risks associated with prednisone use. Remember, open communication with your doctor is key.
Medication Interactions
Prednisone can interact with other medications. Be sure to inform your physician of all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are currently taking to avoid potential complications. This includes over-the-counter medications. Providing a complete medication list enables your doctor to make informed decisions about your treatment plan.
Long-Term Use
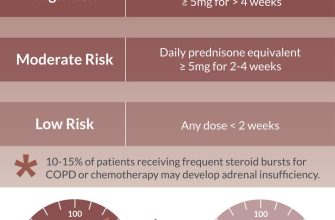
Long-term use of prednisone carries a higher risk of serious side effects. Your doctor will weigh the benefits against the risks, carefully monitoring your health and adjusting the dosage as needed. Regular check-ups are essential to ensure your well-being and to detect any potential issues early.
Understanding Prednisone Dosage in Milligrams (mg)
Prednisone dosage is highly individualized, determined by your doctor based on your specific condition and response to treatment. Don’t adjust your dosage without consulting your physician.
Typical Prednisone Dosages
Common starting doses range from 5 mg to 60 mg daily, often administered in divided doses. Higher doses are usually reserved for severe conditions and are tapered down gradually. Lower doses may be used for maintenance therapy. The duration of treatment also varies considerably.
- Low Doses (5-10mg): Often used for long-term management of inflammatory conditions.
- Moderate Doses (10-30mg): Frequently used for moderate inflammatory issues.
- High Doses (30mg+): Typically prescribed for severe flares of inflammatory diseases or autoimmune conditions.
Factors Influencing Dosage
- Your Condition: The severity and type of condition significantly influence the required dose. For example, lupus may necessitate a higher dose than allergic rhinitis.
- Your Body Weight: Dosage may be adjusted based on your weight, although this isn’t always the primary factor.
- Your Response to Treatment: Your doctor will monitor your response and adjust the dose accordingly. Improvement may lead to a dosage reduction, while lack of response might require an increase (within safe limits).
- Other Medications: Interactions with other medications can affect prednisone’s efficacy and necessitate dose adjustments.
- Age and Overall Health: Older adults or individuals with underlying health problems may require lower doses or more cautious monitoring.
Tapering Off Prednisone
Abruptly stopping prednisone can lead to serious withdrawal symptoms. Your doctor will create a tapering schedule to gradually reduce your dose, minimizing the risk of adverse effects. This schedule is personalized and depends on several factors, including the duration and dosage of your treatment.
Always Consult Your Doctor
This information is for general knowledge only and should not substitute for professional medical advice. Your doctor is the best resource for determining the appropriate prednisone dosage for your individual needs. Always discuss any concerns or questions you have with them.
Common Side Effects and Management Strategies of Prednisone
Monitor your blood sugar regularly, especially if you have diabetes or a family history of it. Prednisone can elevate blood sugar levels. Adjust your diabetes medication as advised by your doctor.
Expect potential weight gain. Maintain a balanced diet low in processed foods and saturated fats. Increase physical activity gradually to help manage weight and improve overall health.
Increased appetite is common. Focus on nutritious choices to minimize unhealthy weight gain. Plan your meals and snacks to avoid overeating.
Mood changes, including irritability and anxiety, are possible. Practice stress-reduction techniques like yoga or meditation. Open communication with your doctor and loved ones is crucial.
Insomnia can occur. Establish a regular sleep schedule. Avoid caffeine and alcohol before bed. Consider creating a relaxing bedtime routine.
Increased risk of infections is a concern. Practice good hygiene, including frequent handwashing. Avoid crowds during peak flu and cold seasons. Report any signs of infection to your doctor immediately.
High blood pressure is a potential side effect. Regular blood pressure monitoring is necessary. Follow your doctor’s advice on dietary changes and medication if necessary.
Muscle weakness and bone thinning are potential long-term effects. Engage in weight-bearing exercises and discuss bone density testing with your physician.
Consult your doctor immediately if you experience severe side effects, such as severe abdominal pain, blurred vision, or difficulty breathing.
Prednisone and Interactions: Medication and Lifestyle Considerations
Always inform your doctor about all medications you take, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies. Prednisone interacts with many medications, potentially increasing or decreasing their effectiveness or causing side effects. For example, it can increase blood sugar levels, potentially worsening diabetes. It can also weaken the immune system, making you more susceptible to infections. Combining prednisone with blood thinners like warfarin may increase bleeding risk. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen taken with prednisone raise the risk of stomach ulcers.
Dietary Recommendations
Maintain a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean protein. Prednisone can increase appetite and lead to weight gain, so mindful eating is crucial. Limit your intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive sodium. Calcium and vitamin D supplementation may be necessary to counteract potential bone loss, a known side effect of long-term prednisone use. Consult your physician or a registered dietitian for personalized guidance.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Regular exercise is beneficial, but avoid strenuous activity, especially during initial treatment, as prednisone can weaken muscles. Prioritize adequate sleep, manage stress through relaxation techniques like meditation or yoga, and stay hydrated. Monitor your blood pressure and blood sugar regularly as advised by your doctor. Avoid alcohol, as it can interact negatively with prednisone and increase the risk of side effects. Report any unusual symptoms or side effects to your doctor immediately.
Important Note:
This information is for general knowledge and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting, stopping, or changing any medication, including prednisone, or making significant lifestyle changes.