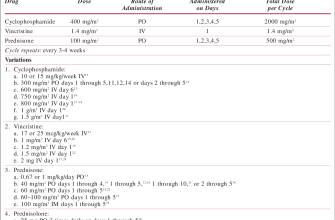
Prednisone isn’t a first-line treatment for gout, but doctors sometimes prescribe it to manage severe inflammation. Typical dosages range from 20-60 mg daily, depending on the severity of your symptoms. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dose based on your individual needs and medical history.
This medication works by suppressing your immune system, thus reducing pain and swelling associated with a gout flare-up. Remember, it does not address the underlying cause of gout, which is uric acid buildup. Expect your doctor to recommend lifestyle changes and potentially other medications to manage your uric acid levels for long-term gout control.
Important Note: Prednisone has potential side effects, including increased blood sugar, weight gain, and increased risk of infection. Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully, and report any concerning side effects immediately. Do not abruptly stop taking Prednisone without consulting your physician.
Treatment duration varies but typically involves a short course, often a few days to a week, during an acute gout attack. Your healthcare provider will monitor your progress and adjust the dosage or treatment plan as needed. Be sure to discuss any questions or concerns you have with your doctor or pharmacist.
- Normal Prednisone Dosage for Gout
- Understanding Prednisone’s Role in Gout Treatment
- Dosage and Administration
- Potential Side Effects
- Prednisone vs. Other Gout Medications
- Important Considerations Before Using Prednisone
- Monitoring and Follow-up
- Typical Prednisone Dosage Regimens for Gout Flares
- Potential Side Effects and Precautions
- Long-Term Use Considerations
- Alternatives to Prednisone and Long-Term Gout Management
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
- Lifestyle Adjustments for Long-Term Gout Control
- Medications for Uric Acid Reduction
- Seeking Professional Guidance
- Monitoring Uric Acid Levels
Normal Prednisone Dosage for Gout
Prednisone isn’t a first-line treatment for gout, but it can effectively reduce inflammation during a severe flare-up. Doctors typically prescribe a relatively high initial dose, often between 30 and 60 milligrams daily, for several days. This helps quickly quell the intense pain and swelling.
The dosage then gradually decreases over several days or weeks, under the close supervision of a physician. A common tapering schedule might involve reducing the dose by 5-10 milligrams every few days. For example, after three days at 60mg, a patient might take 50mg, then 40mg, and so on until the medication is stopped completely or a low maintenance dose is reached.
The exact duration and tapering schedule depend on individual patient response and the severity of the gout attack. Some individuals might require a longer course of treatment. Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. Never adjust your dosage without consulting them.
Remember, prednisone carries potential side effects. Long-term use can lead to complications, so it’s typically reserved for acute flare-ups rather than ongoing management.
This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Consult your healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment of gout.
Understanding Prednisone’s Role in Gout Treatment
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, doesn’t treat the underlying cause of gout (uric acid buildup), but powerfully reduces inflammation and pain. Doctors prescribe it for acute gout attacks, particularly severe ones unresponsive to other medications. It quickly lowers inflammation, providing significant pain relief within hours or days.
Dosage and Administration
Dosage varies depending on the severity of your gout and your doctor’s assessment. Typical short-term courses involve taking prednisone once daily for several days, gradually tapering the dose to avoid withdrawal symptoms. Never adjust your dosage without consulting your physician.
Potential Side Effects
While effective, prednisone comes with potential side effects, including increased blood sugar, fluid retention, increased appetite, and insomnia. Long-term use carries more serious risks. Your doctor will discuss these risks and monitor your health closely during treatment.
Prednisone vs. Other Gout Medications
Prednisone offers rapid relief, unlike many other gout medications. However, it’s typically a short-term solution for acute flare-ups. Colchicine and NSAIDs are usually preferred for long-term management or less severe attacks. Your doctor will help determine the best treatment plan for your individual needs.
Important Considerations Before Using Prednisone
| Factor | Details |
|---|---|
| Existing Conditions | Inform your doctor about all your health conditions, especially diabetes, heart disease, or high blood pressure. |
| Medications | List all current medications you are taking to identify any potential drug interactions. |
| Pregnancy/Breastfeeding | Discuss prednisone use with your doctor if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or planning pregnancy. |
Monitoring and Follow-up
Regular check-ups with your doctor are essential while taking prednisone, especially during a course of treatment. This allows your doctor to monitor your response to the medication and address any side effects that may arise. Close monitoring ensures you receive the most benefit and experience minimal risks.
Typical Prednisone Dosage Regimens for Gout Flares
Prednisone dosages for gout flares vary depending on the severity of your symptoms and your doctor’s assessment. A common starting point is 30-60 mg daily for several days. Your doctor may recommend a higher initial dose for severe flares, then gradually taper the dosage down.
A typical tapering schedule might look like this: After a few days of the initial higher dose, reduce to 40mg daily. Then, decrease to 30 mg daily, followed by 20 mg, 10 mg, and finally 5 mg before completely stopping the medication. This schedule is a guideline; your doctor will adjust the tapering pace based on your response to treatment.
Important Note: Never adjust your Prednisone dosage without consulting your doctor. Sudden stops can lead to adverse effects. Always follow your doctor’s prescribed regimen carefully. They will monitor your progress and make adjustments as needed to ensure you receive optimal treatment while minimizing potential side effects. Be sure to discuss any concerns or side effects you experience.
Remember, this information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with your physician before starting or altering any medication regimen.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Prednisone, while effective for managing gout inflammation, carries potential side effects. Common side effects include increased appetite, weight gain, fluid retention, and mood changes. Some individuals experience insomnia or increased blood sugar levels. Less common but more serious side effects involve increased risk of infections, osteoporosis, and stomach ulcers. Regular monitoring of blood pressure and blood sugar is recommended during treatment.
Long-Term Use Considerations
Prolonged prednisone use increases the likelihood of experiencing these side effects. Your doctor will carefully weigh the benefits against the risks and may recommend the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration possible. They’ll also discuss strategies for gradually reducing the dosage to minimize withdrawal symptoms. Be sure to report any unusual symptoms to your healthcare provider immediately.
Before starting prednisone, inform your doctor about all other medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, as interactions may occur. Pre-existing conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, or weakened immunity, need to be communicated to enable informed treatment decisions.
Alternatives to Prednisone and Long-Term Gout Management
Colchicine remains a first-line treatment for acute gout attacks, offering rapid pain relief. It works differently than prednisone, targeting inflammation at a cellular level.
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs like ibuprofen or naproxen provide effective pain and inflammation relief. Always follow prescribed dosages and consult your doctor about potential side effects, especially for those with kidney or stomach issues.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Long-Term Gout Control
- Dietary changes: Limit purine-rich foods (red meat, organ meats, shellfish) and sugary drinks. Increase your intake of low-purine vegetables, fruits, and whole grains. This significantly impacts uric acid levels.
- Weight management: Obesity increases uric acid production. Weight loss, even modest, can improve gout symptoms.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps flush uric acid from your body, promoting its excretion through urine.
- Regular exercise: Physical activity aids in weight management and improves overall health, potentially reducing gout flares.
Medications for Uric Acid Reduction
- Allopurinol: This medication lowers uric acid production, preventing future gout attacks. It’s typically used long-term.
- Febuxostat: Another uric acid-lowering medication, often prescribed if allopurinol isn’t tolerated.
- Pegloticase: A more advanced option, used for patients who don’t respond to other treatments. It’s administered intravenously.
Seeking Professional Guidance
Remember, these are general recommendations. Consult your doctor or rheumatologist for personalized advice based on your medical history and current health condition. They can help you create a comprehensive management plan tailored to your needs.
Monitoring Uric Acid Levels
Regular blood tests to monitor uric acid levels are crucial for effective gout management. These tests help track your progress and guide medication adjustments.