Start with the prescribed dosage. Your doctor has carefully considered your specific health needs and determined the optimal starting point. Never adjust your prednisone dose without consulting them first. This is crucial for your safety and treatment success.
Typical starting doses range from 5mg to 60mg daily, depending on the condition being treated. For example, inflammatory conditions often begin with higher doses, which are gradually tapered down. Always follow your physician’s instructions meticulously concerning both dosage and duration.
Remember that prednisone’s effects vary significantly from person to person. Factors such as age, weight, and overall health influence how your body responds. Regular monitoring is key, allowing your doctor to adjust your dose as needed for optimal results and minimize potential side effects. Closely track your progress and report any unusual symptoms promptly to your healthcare provider.
Prednisone comes with potential side effects. Common ones include increased appetite, weight gain, mood changes, and insomnia. Less frequent but serious side effects can also occur. Your physician will discuss these risks and strategies to mitigate them. Open communication with your doctor ensures safe and effective prednisone use.
- Oral Prednisone Dose: A Comprehensive Guide
- Determining the Right Prednisone Dosage
- Factors Influencing Dosage
- Dosage Ranges and Administration
- Monitoring and Adjustments
- Example Dosage Schedule (Illustrative Only)
- Potential Side Effects and Management
- Common Prednisone Dosages for Various Conditions
- Prednisone Dosage for Children: Considerations and Adjustments
- Factors Influencing Pediatric Prednisone Dosage
- Dosage Adjustment & Monitoring
- Tapering Off Prednisone: A Safe and Effective Approach
- Understanding the Tapering Process
- Managing Potential Withdrawal Symptoms
- Sample Tapering Schedule (Illustrative Only – Consult Your Doctor)
- Maintaining Your Health During Tapering
- Contacting Your Doctor
- Potential Side Effects of Prednisone and Dosage-Related Risks
- Gastrointestinal Issues
- Increased Risk of Infection
- Other Potential Side Effects
- Interactions with Other Medications: Important Considerations
- Monitoring Your Progress During Prednisone Treatment
- Blood Pressure and Blood Sugar Monitoring
- Managing Side Effects
- When to Contact Your Doctor Regarding Prednisone Dosage
- Managing Prednisone Side Effects: Practical Tips
- Managing Blood Sugar
- Addressing Other Common Side Effects
Oral Prednisone Dose: A Comprehensive Guide
Prednisone dosage depends entirely on your specific condition and your body’s response. Your doctor will determine the optimal dose, which varies widely. Typical starting doses range from 5mg to 60mg daily, but this is just a general range.
Treatment often begins with a higher dose to quickly control inflammation, followed by a gradual tapering. This gradual reduction minimizes potential side effects. Your physician will create a personalized tapering schedule. Never adjust your dose without consulting your doctor.
Common conditions treated with oral prednisone include autoimmune diseases like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, allergic reactions, asthma exacerbations, and certain cancers. The dosage differs significantly based on the condition. For example, a severe allergic reaction might warrant a higher initial dose than managing mild asthma.
Side effects are possible and vary in severity. Common ones include weight gain, increased appetite, mood changes, insomnia, and increased blood sugar. Severe side effects are less common but require immediate medical attention. Report any concerning symptoms to your doctor immediately.
Long-term prednisone use carries increased risks of osteoporosis, cataracts, and infections. Your doctor will monitor you closely for these complications and discuss preventative measures. Regular blood tests may be necessary to track your progress and identify potential problems.
Remember, this information is for general knowledge only. It does not substitute for personalized medical advice. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Discuss any questions or concerns directly with your healthcare provider.
Determining the Right Prednisone Dosage
Your doctor determines your prednisone dosage based on your specific condition, its severity, and your individual response to the medication. There’s no one-size-fits-all answer; dosages vary greatly.
Factors Influencing Dosage
Several factors play a crucial role. These include your weight, age, the specific condition being treated (like asthma, lupus, or rheumatoid arthritis), and the severity of the symptoms. Pre-existing health conditions also influence the dosage your doctor prescribes.
Dosage Ranges and Administration
Prednisone dosages are usually expressed in milligrams (mg). Common starting dosages range from 5mg to 60mg daily, though higher doses may be necessary in severe cases. Your doctor will likely prescribe a specific schedule, often involving a single daily dose taken in the morning with food to minimize stomach upset. The duration of treatment varies widely depending on your condition and response to therapy.
Monitoring and Adjustments
Regular monitoring of your condition and potential side effects is vital. Your doctor will likely schedule follow-up appointments to assess your progress and adjust the dosage as needed. They may gradually reduce your dose over time to minimize withdrawal symptoms. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Never change your dosage without consulting them.
Example Dosage Schedule (Illustrative Only)
| Day | Dosage (mg) |
|---|---|
| 1-7 | 40 |
| 8-14 | 30 |
| 15-21 | 20 |
| 22-28 | 10 |
| 29+ | 5 (then gradual discontinuation) |
Disclaimer: The table above provides a sample schedule only. Your actual dosage and tapering schedule will be personalized based on your individual needs and determined by your doctor.
Potential Side Effects and Management
Potential side effects can include weight gain, increased blood sugar, mood changes, and increased risk of infection. Open communication with your doctor about any side effects you experience is essential for appropriate management and potential dosage adjustments.
Common Prednisone Dosages for Various Conditions
Prednisone dosages vary significantly depending on the specific condition being treated and the patient’s individual response. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely.
- Asthma Exacerbation: Initial doses often range from 30-60 mg daily, tapered gradually over several weeks.
- Allergic Rhinitis: Lower doses, typically 5-20 mg daily, are common, again tapered as symptoms improve.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Doses can vary widely, from 5-60 mg daily depending on severity, often administered in divided doses. Careful monitoring is crucial.
- Lupus: Dosage depends on the severity of symptoms and the organs involved. It can range from low to high daily doses, requiring careful titration.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): High initial doses (40-60 mg daily) are frequently employed for acute flares, followed by gradual tapering.
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): Prednisone is used for MS relapses, often in high doses (1000mg for 3 days, then tapering) for a short period.
Important Note: These are examples only. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage and duration based on your specific needs. They will monitor your progress closely and adjust the dosage accordingly. Never alter your medication regimen without first consulting your physician.
- Tapering: Abruptly stopping prednisone can lead to withdrawal symptoms. Always taper the dose gradually under medical supervision.
- Side Effects: Be aware of potential side effects, such as weight gain, mood changes, high blood sugar, and increased risk of infections. Report any concerns to your doctor immediately.
- Monitoring: Regular check-ups with blood tests are common while taking prednisone to monitor for potential complications.
This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any medication.
Prednisone Dosage for Children: Considerations and Adjustments
Dosage for children differs significantly from adult dosages and depends heavily on the child’s weight, age, and specific condition. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely.
Factors Influencing Pediatric Prednisone Dosage
- Weight: Prednisone is often prescribed based on milligrams per kilogram (mg/kg) of body weight. A smaller child will receive a lower dose than a larger child, even with the same condition.
- Age: Younger children may metabolize medication differently, necessitating careful dose adjustments.
- Specific Condition: The severity and type of illness greatly influences the dosage. For example, a severe inflammatory condition will necessitate a higher dose compared to a milder one.
- Response to Treatment: Your doctor will monitor the child’s response and adjust the dosage based on effectiveness and any side effects. Regular blood tests may be required to monitor response.
Dosage Adjustment & Monitoring
Expect regular follow-up appointments to assess the child’s progress. Your doctor will likely adjust the dosage gradually, increasing or decreasing it as needed.
- Initial Dose: The starting dose is determined by the physician and varies based on the factors mentioned above.
- Gradual Tapering: Prednisone should never be stopped abruptly. The dosage is typically reduced gradually to minimize withdrawal symptoms and allow the body to adjust.
- Side Effect Monitoring: Parents should closely watch for potential side effects, including increased appetite, weight gain, mood changes, insomnia, and increased blood sugar. Report any unusual symptoms immediately to the doctor.
- Regular Check-ups: Regular monitoring is key to ensure the treatment is safe and effective for your child.
Remember, this information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with your child’s physician before administering any medication.
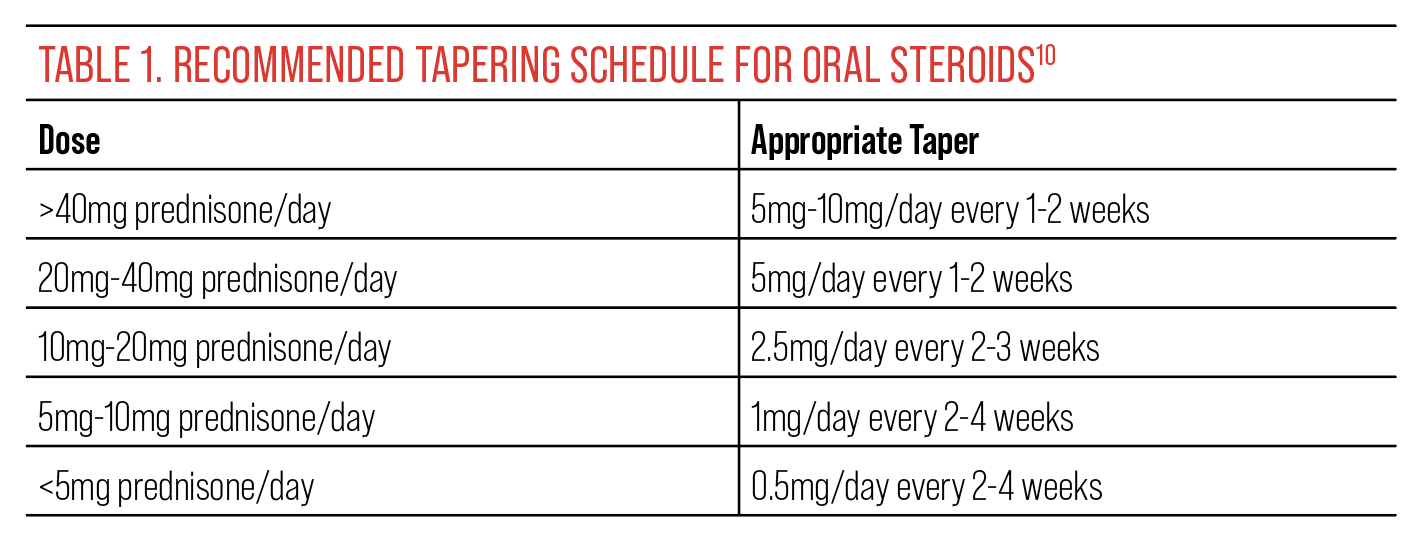
Tapering Off Prednisone: A Safe and Effective Approach
Always work closely with your doctor to create a personalized tapering schedule. A gradual reduction, rather than abrupt cessation, minimizes withdrawal symptoms and prevents rebound inflammation.
Understanding the Tapering Process
Your doctor will likely prescribe a slow reduction, often involving decreases of 2.5-5mg every few days or weeks. The specific rate depends on the initial dose, duration of treatment, and your individual response. Frequent monitoring of your condition is crucial.
Managing Potential Withdrawal Symptoms
Expect potential symptoms like fatigue, joint pain, muscle weakness, and increased inflammation. These are common, and usually manageable with careful monitoring and, in some cases, supplemental medications prescribed by your doctor. Adequate hydration and a balanced diet can also help.
Sample Tapering Schedule (Illustrative Only – Consult Your Doctor)
| Day | Prednisone Dose (mg) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1-7 | 40 | Initial dose (example only) |
| 8-14 | 35 | Reduce by 5mg |
| 15-21 | 30 | Reduce by 5mg |
| 22-28 | 25 | Reduce by 5mg |
| 29-35 | 20 | Reduce by 5mg |
| 36-42 | 15 | Reduce by 5mg |
| 43-49 | 10 | Reduce by 5mg |
| 50-56 | 5 | Reduce by 5mg |
| 57-63 | 0 | Complete cessation |
This is a sample schedule; your doctor will tailor a plan based on your needs. Regular blood tests may be recommended to monitor your progress and adjust the schedule as necessary.
Maintaining Your Health During Tapering
Maintain a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise (as tolerated), and sufficient rest. Open communication with your doctor is paramount throughout the tapering process.
Contacting Your Doctor
Don’t hesitate to contact your doctor if you experience any concerning symptoms or have questions about your tapering schedule. They will guide you through the process to ensure a safe and successful outcome.
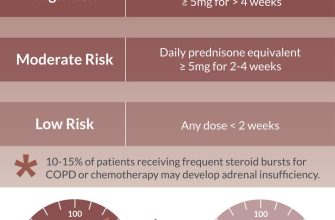
Potential Side Effects of Prednisone and Dosage-Related Risks
Prednisone, while highly effective, carries potential side effects directly related to dosage. Higher doses and longer treatment durations increase the risk. Common side effects include weight gain, increased appetite, fluid retention, and mood changes (irritability, anxiety, insomnia). These are often manageable with lifestyle adjustments. For example, a balanced diet and regular exercise can help mitigate weight gain.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Prednisone can irritate the stomach lining, leading to heartburn, indigestion, and in some cases, ulcers. Taking it with food can help minimize these effects. Severe gastrointestinal complications are rare, but prompt medical attention is necessary if you experience severe abdominal pain, vomiting blood, or black stools.
Increased Risk of Infection
Prednisone suppresses the immune system, making you more vulnerable to infections. Avoid contact with sick individuals, practice good hygiene, and notify your doctor immediately if you develop any signs of infection, such as fever, cough, or sore throat. This risk is particularly elevated with higher doses.
Other Potential Side Effects
Less common, but still possible, side effects include increased blood sugar (especially in individuals with diabetes), high blood pressure, thinning of the bones (osteoporosis), muscle weakness, and glaucoma. Regular monitoring of blood pressure and blood sugar levels is crucial, especially during long-term treatment. Discuss bone density testing with your physician if you are on a high dose or long-term treatment.
Remember, this information is for general knowledge and doesn’t replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor to discuss potential risks and benefits before starting or changing your prednisone dosage.
Interactions with Other Medications: Important Considerations
Always inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies. Prednisone can significantly alter how other drugs work, and vice versa. This includes both prescription and non-prescription medications.
Blood thinners (anticoagulants): Prednisone can reduce the effectiveness of blood thinners like warfarin, increasing your risk of blood clots. Close monitoring of your INR (International Normalized Ratio) is necessary.
Diabetes medications: Prednisone can raise blood sugar levels, potentially making your diabetes harder to manage. Your doctor may need to adjust your diabetes medication dosage.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Combining prednisone with NSAIDs like ibuprofen or naproxen increases the risk of stomach ulcers and bleeding. Use caution and discuss this combination with your physician.
Immunosuppressants: Taking prednisone with other immunosuppressants (like cyclosporine or azathioprine) dramatically increases your risk of infection. Your doctor will carefully monitor your health and may adjust dosages.
Potassium-wasting diuretics: Prednisone can deplete potassium levels; using potassium-wasting diuretics simultaneously exacerbates this effect, potentially leading to serious heart rhythm problems. Your doctor will monitor your potassium levels regularly.
Digoxin: Prednisone may increase the risk of digoxin toxicity. Regular monitoring of your digoxin levels is crucial.
This is not an exhaustive list. Many other medications can interact with prednisone. Open communication with your healthcare provider about all your medications ensures your safety and optimal treatment.
Monitoring Your Progress During Prednisone Treatment
Regularly track your weight. Significant weight changes can indicate side effects and require adjustment to your medication. Keep a daily log. Report any unexpected changes to your doctor immediately.
Blood Pressure and Blood Sugar Monitoring
Monitor your blood pressure at home using a reliable device. Prednisone can elevate blood pressure. If you have diabetes, diligently check your blood sugar levels as prescribed. Inform your physician of any fluctuations outside of your target range. Consistent monitoring helps prevent complications.
Pay close attention to your mood. Prednisone can affect your mental state. Note any changes in mood, sleep patterns, or anxiety levels. Discuss these observations with your healthcare provider. Early intervention is key.
Observe your skin for any signs of thinning or bruising. Report any unusual changes to your doctor. These could indicate a need for dosage modification or additional support.
Schedule regular check-ups with your doctor as directed. These appointments allow for thorough assessments and necessary medication adjustments based on your individual response to treatment. Don’t hesitate to contact your doctor between appointments if you have concerns.
Managing Side Effects
Document any side effects, including, but not limited to, increased thirst, frequent urination, muscle weakness, or vision changes. These notes will assist your physician in tailoring your treatment plan for optimal results and minimizing adverse reactions.
When to Contact Your Doctor Regarding Prednisone Dosage
Call your doctor immediately if you experience severe side effects, such as severe abdominal pain, difficulty breathing, or significant changes in your mood, including suicidal thoughts.
Contact your physician if you notice any unexpected weight gain exceeding 2 pounds per week, development of excessive thirst or increased urination, or the appearance of purplish or reddish streaks on your skin.
Report any persistent insomnia, increased anxiety, or muscle weakness that impacts daily activities.
If your blood sugar levels fluctuate significantly or you notice symptoms of infection, like fever or persistent cough, seek medical attention promptly.
Also, contact your doctor if you have any questions concerning the tapering process of your prednisone dosage or experience any new or worsening symptoms while taking the medication.
Don’t hesitate to reach out if your current dosage isn’t managing your symptoms effectively. Open communication is key to successful treatment.
Managing Prednisone Side Effects: Practical Tips
Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated, counteracting potential fluid retention.
Eat a balanced diet rich in potassium. Bananas, sweet potatoes, and spinach are good sources, helping mitigate potential potassium loss.
Increase your calcium and vitamin D intake. Dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods are helpful. Consider supplements if needed, but consult your doctor first.
Managing Blood Sugar
- Monitor your blood sugar regularly, especially if you have diabetes or a family history of it.
- Maintain a consistent carbohydrate intake to prevent significant blood sugar fluctuations.
- Discuss blood sugar management strategies with your doctor or diabetes educator.
Addressing Other Common Side Effects
- Weight Gain: Focus on portion control and regular exercise. A balanced diet with plenty of fruits and vegetables is key.
- Mood Changes: Communicate openly with your doctor and loved ones. Consider stress-reducing techniques like meditation or yoga.
- Insomnia: Establish a regular sleep schedule. Avoid caffeine and alcohol before bed. Consider light exercise earlier in the day.
- Increased Appetite: Choose nutritious, low-calorie options to satisfy hunger without excess calorie consumption.
- Muscle Weakness: Gentle exercise, like walking or swimming, can help maintain muscle strength. Consult your doctor before starting any new exercise program.
Remember to report any concerning side effects to your doctor immediately. They can adjust your dosage or prescribe additional medication to help manage the symptoms.