Need prednisone? Understand that obtaining it without a prescription carries significant health risks. Always consult a doctor before using any medication, including over-the-counter (OTC) prednisone, as it can cause serious side effects if misused. Self-treating can be dangerous.
Prednisone is a powerful corticosteroid with potent anti-inflammatory properties. However, its widespread availability without a prescription in some regions presents a serious challenge. Long-term use, even at low doses, can lead to a range of adverse effects such as weight gain, increased blood sugar, weakened bones, and an elevated risk of infections. Short-term use also presents potential problems; always follow a doctor’s instructions exactly.
If you’re experiencing symptoms you believe require prednisone, schedule an appointment with your physician. They can assess your condition, determine the appropriate treatment, and prescribe the correct dosage. Remember, safe and effective medication use requires professional guidance. Ignoring this advice puts your health at risk.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always seek the advice of a healthcare professional for any questions about your particular health situation.
- OTC Prednisone: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding Prednisone’s Role
- Risks and Side Effects
- Alternatives to Prednisone
- Dosage and Administration
- Seeking Medical Advice
- Disclaimer
- What is Prednisone and When is it Appropriate for OTC Use?
- Prescription Only: No OTC Prednisone
- Alternative Treatments
- Potential Risks and Side Effects of Prednisone
- Gastrointestinal Issues
- Other Potential Side Effects
- Skin Reactions
- Alternatives to Prednisone for Common Ailments
- Seeking Professional Medical Advice: When to Consult a Doctor
OTC Prednisone: A Comprehensive Guide
Prednisone is not available over-the-counter (OTC). Always obtain a prescription from a doctor before using it.
Understanding Prednisone’s Role
Prednisone is a corticosteroid, a powerful anti-inflammatory medication. Doctors prescribe it to manage various conditions like allergies, asthma, and autoimmune diseases. It reduces swelling, inflammation, and allergic reactions.
Risks and Side Effects
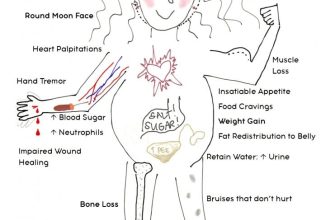
Prednisone carries potential side effects, including weight gain, increased blood sugar, mood changes, and weakened bones. Long-term use necessitates careful monitoring by a physician. Sudden cessation can cause serious withdrawal symptoms.
Alternatives to Prednisone
Depending on your condition, your doctor may suggest alternatives like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, or other medications targeted at your specific ailment. Always discuss treatment options with your healthcare provider.
Dosage and Administration
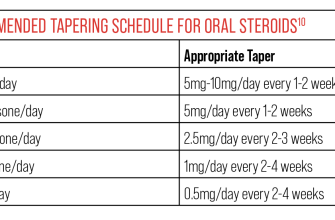
Dosage varies depending on the condition and individual patient. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dose and duration of treatment. Never adjust your dosage without consulting your doctor.
| Condition | Typical Dosage (Example – Consult your doctor) | Duration of Treatment (Example – Consult your doctor) |
|---|---|---|
| Allergic reaction | 5-60 mg daily | Several days |
| Asthma | 5-60 mg daily | Variable, depends on severity |
| Autoimmune disease | Variable, depends on severity | Long-term, potentially |
Seeking Medical Advice
Self-treating with prednisone is dangerous. Consult a doctor to discuss your symptoms and explore appropriate treatment options. They will assess your condition, consider potential drug interactions, and determine if prednisone is the right choice for you and, if so, prescribe the correct dosage.
Disclaimer
This guide provides general information and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment.
What is Prednisone and When is it Appropriate for OTC Use?
Prednisone is a corticosteroid medication; it reduces inflammation and suppresses the immune system. It’s powerful, and you shouldn’t take it without a doctor’s prescription.
Prescription Only: No OTC Prednisone
Prednisone is never available over-the-counter (OTC). Its potent effects require careful medical supervision. Misuse can lead to serious side effects like increased risk of infections, high blood pressure, and changes in blood sugar levels. Always consult a physician before using prednisone or any corticosteroid medication.
Alternative Treatments
For mild inflammation or allergic reactions, your doctor might suggest OTC medications like ibuprofen or antihistamines. These offer relief for common symptoms without the risks associated with prednisone. They are readily available without a prescription at most pharmacies.
Potential Risks and Side Effects of Prednisone
Prednisone, while effective, carries potential risks. Understand these to manage them properly. Increased blood sugar is common, especially in those with diabetes. Monitor your blood glucose levels closely and discuss adjustments to your diabetes medication with your doctor. Weight gain is another frequent side effect, often due to fluid retention and increased appetite. A balanced diet and regular exercise can help mitigate this.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Prednisone can irritate your stomach lining, leading to heartburn, indigestion, or ulcers. Take prednisone with food to minimize this. If you experience severe stomach pain, seek medical attention immediately. Also, be aware of the risk of increased susceptibility to infections due to immunosuppression.
Other Potential Side Effects
Mood changes, including irritability, anxiety, and depression, are possible. Insomnia is also common. Maintain a regular sleep schedule and discuss these changes with your doctor. High blood pressure can occur; regular monitoring is crucial. Long-term use can lead to osteoporosis, so discuss preventative measures with your physician. Always inform your doctor about all medications you take, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to avoid harmful interactions. Never abruptly stop taking prednisone; a gradual reduction under medical supervision is necessary to prevent withdrawal symptoms.
Skin Reactions
Thinning skin and bruising are possible. Use sunscreen to protect your skin from the sun. Report any unusual skin changes to your doctor. Prednisone’s potential for serious side effects necessitates careful monitoring and open communication with your healthcare provider.
Alternatives to Prednisone for Common Ailments
For allergies, consider over-the-counter antihistamines like cetirizine or fexofenadine. These often provide sufficient relief for mild to moderate symptoms. If symptoms persist, consult your doctor.
Dealing with inflammation? NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can effectively reduce pain and swelling associated with conditions like arthritis. Remember to follow dosage instructions carefully.
If you’re experiencing asthma symptoms, your doctor might recommend inhaled corticosteroids like fluticasone or budesonide, which target inflammation directly in your airways, offering localized relief.
For skin conditions like eczema, topical corticosteroids are commonly prescribed, but alternatives include calcineurin inhibitors like tacrolimus or pimecrolimus, offering a different approach to managing inflammation.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) often benefits from bronchodilators, medications that relax the airways, improving breathing. Your doctor will determine the best approach for your specific needs.
Always discuss treatment options with your healthcare provider before making changes to your medication regimen. They can help you weigh the benefits and risks of different alternatives and create a personalized plan.
Seeking Professional Medical Advice: When to Consult a Doctor
Consult your doctor immediately if you experience severe side effects, such as severe allergic reactions (rash, swelling, difficulty breathing), high blood pressure, mood swings leading to suicidal thoughts, or signs of infection (fever, chills).
Schedule an appointment with your physician if:
- Your symptoms don’t improve after a reasonable period of self-treatment (as recommended by a healthcare professional).
- Your condition worsens despite using over-the-counter prednisone.
- You have underlying health conditions that might interact with prednisone.
- You need to take prednisone for longer than a few days.
- You’re experiencing significant weight gain, muscle weakness, or changes in appetite.
- You develop cataracts, glaucoma, or other eye problems.
- You experience changes in your blood sugar levels (particularly if you have diabetes).
- You notice increased bruising or bleeding easily.
- You have questions or concerns about prednisone use or possible interactions with other medications.
Remember: Self-treating can be risky. A doctor can tailor a treatment plan to your specific needs and monitor you for potential complications. Don’t hesitate to seek professional medical advice – your health is paramount.
For emergency situations, call emergency services immediately. This includes situations such as severe allergic reactions or life-threatening symptoms.