Prednisone 20 mg isn’t a first-line treatment for gout, but it can offer rapid relief from severe inflammation. Doctors often prescribe it for acute gout attacks when immediate pain reduction is necessary. This short-term, high-dose approach targets the inflammatory process, easing joint swelling and pain quickly.
However, remember that Prednisone doesn’t address the underlying uric acid buildup causing gout. Long-term use carries significant side effects, including increased blood sugar, bone thinning, and increased risk of infection. Therefore, it’s generally used only for short, controlled periods during acute flare-ups. Your doctor will carefully monitor your treatment and adjust the dosage accordingly.
Always discuss Prednisone use with your physician. They will help determine if it’s the right choice for your specific situation, considering your overall health and other medications you might be taking. They’ll also advise on the appropriate dosage and duration of treatment, minimizing potential adverse effects. The goal is to control your gout symptoms effectively while reducing the risks associated with Prednisone.
Consider this: While Prednisone provides fast pain relief, a long-term strategy must involve managing uric acid levels to prevent future attacks. Lifestyle changes, such as dietary modifications and increased hydration, along with medications like allopurinol or febuxostat, are key components of managing gout effectively. Your doctor can guide you through these essential steps.
- Prednisone 20 mg for Gout Treatment: A Detailed Overview
- Dosage and Administration
- Potential Side Effects
- When to Consult a Doctor
- Alternative Treatment Options
- Important Note
- Further Considerations
- What is Gout and How Does it Affect the Body?
- Uric Acid Build-up: The Root Cause
- The Inflammatory Response: Pain and Swelling
- Long-Term Effects of Untreated Gout
- Prednisone: A Quick Overview of its Mechanism of Action
- Impact on Immune Response
- Gout-Specific Effects
- Important Considerations
- Prednisone’s Role in Reducing Gout Inflammation
- Dosage and Treatment Duration
- Potential Side Effects
- Prednisone and Long-Term Gout Management
- Alternative Treatments
- Dosage and Administration of Prednisone 20mg for Gout
- Potential Side Effects of Prednisone 20mg Treatment
- Gastrointestinal Issues
- Increased Blood Sugar and Blood Pressure
- When to Consider Prednisone for Gout: Indications and Contraindications
- Indications for Prednisone Use in Gout
- Contraindications and Precautions
- Other Considerations
- Comparing Prednisone to Other Gout Medications
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
- Uric Acid Lowering Medications
- Choosing the Right Treatment
- Side Effects Considerations
- Long-Term Use and Management of Prednisone for Gout
- Alternative Long-Term Gout Management
- Monitoring Prednisone Use
- Tapering Off Prednisone
- Specific Recommendations
- Monitoring Progress and Consulting Your Doctor
- Medication Adjustments
- Lifestyle Changes
Prednisone 20 mg for Gout Treatment: A Detailed Overview
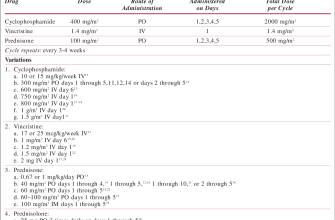
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, rapidly reduces inflammation associated with gout attacks. A 20mg daily dose is often prescribed for short-term management, typically 5-10 days. However, it’s not a long-term solution for gout.
Dosage and Administration
Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage and duration based on your individual needs and the severity of your gout flare-up. Commonly, doctors prescribe a tapering schedule to minimize side effects as your body adjusts.
- Typical dosage: 20mg daily for several days.
- Duration: Usually 5-10 days, but this varies based on the patient’s response.
- Tapering: Reducing the dose gradually is common to avoid withdrawal symptoms.
Potential Side Effects
While effective, Prednisone can cause side effects. These vary in severity and frequency. It’s important to monitor your body and report any unusual changes to your doctor.
- Increased appetite and weight gain
- Mood changes, including irritability or anxiety
- Sleep disturbances
- Increased blood sugar levels
- Fluid retention
- Increased risk of infection
When to Consult a Doctor
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe side effects or if your gout symptoms don’t improve after several days of treatment.
Alternative Treatment Options
Prednisone is a short-term solution. Long-term gout management usually involves lifestyle changes (diet, exercise) and medication like allopurinol or febuxostat to lower uric acid levels. Your doctor will discuss the best strategy for your specific situation.
Important Note
Never alter your Prednisone dosage without consulting your physician. Abrupt cessation can lead to serious complications. This information is for educational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice.
Further Considerations
- Discuss any other medications you’re taking with your doctor before starting Prednisone, as interactions are possible.
- Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels may be necessary, especially if you have diabetes.
- Consider lifestyle changes to help prevent future gout attacks.
What is Gout and How Does it Affect the Body?
Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis caused by a buildup of uric acid crystals in your joints. This excess uric acid, a byproduct of purine breakdown, crystallizes, forming sharp needle-like structures that inflame the joint lining. The most common site affected is the big toe, but gout can impact any joint.
Uric Acid Build-up: The Root Cause
Your body produces uric acid naturally. However, if your body produces too much, or your kidneys don’t eliminate it efficiently enough, uric acid levels climb, leading to hyperuricemia. This elevated level increases the risk of crystal formation and subsequent gout attacks. Certain foods, like red meat and organ meats, are high in purines, accelerating this process. Alcohol consumption also contributes to increased uric acid levels.
The Inflammatory Response: Pain and Swelling
Once uric acid crystals deposit in the joints, your immune system reacts. White blood cells attack the crystals, triggering a significant inflammatory response. This manifests as intense, sudden pain, swelling, redness, and warmth in the affected joint. Gout attacks can last for several days, even weeks, if untreated, and recurring attacks cause progressive joint damage.
Long-Term Effects of Untreated Gout
Repeated gout attacks can permanently damage joints, causing deformity, stiffness, and limited range of motion. Furthermore, gout is linked to kidney stones due to uric acid crystal deposition in the kidneys. Addressing elevated uric acid levels through diet, medication, and lifestyle changes is vital for managing gout and preventing long-term complications.
Prednisone: A Quick Overview of its Mechanism of Action
Prednisone, a glucocorticoid, powerfully reduces inflammation by binding to intracellular glucocorticoid receptors. This binding initiates a cascade, affecting gene transcription. Specifically, it inhibits the production of inflammatory mediators like cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1) and prostaglandins.
Impact on Immune Response
This mechanism also dampens the immune response. Prednisone stabilizes lysosomal membranes, preventing the release of enzymes that contribute to inflammation. It also reduces the number of circulating lymphocytes and other immune cells, further limiting the inflammatory process.
Gout-Specific Effects
In gout, this anti-inflammatory action directly targets the uric acid crystal-induced inflammation in the joints. By decreasing the production and activity of inflammatory cells, prednisone rapidly reduces pain and swelling associated with gout attacks. Note: Prednisone doesn’t address the underlying cause of gout (hyperuricemia).
Important Considerations
Remember, Prednisone has significant side effects, and long-term use should be carefully considered and monitored by a physician. It’s a powerful medication with a specific role in managing acute gout flare-ups.
Prednisone’s Role in Reducing Gout Inflammation
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, powerfully suppresses the inflammatory response driving gout attacks. It acts by reducing the production of inflammatory chemicals like cytokines, thus lessening pain and swelling. This makes it a valuable tool for managing acute gout flares.
Dosage and Treatment Duration
A typical dosage for acute gout is 20-60mg daily, depending on severity. Your doctor will tailor the dosage to your specific needs. Prednisone usually isn’t a long-term solution for gout; doctors typically prescribe it for a short period–a few days to a couple of weeks–to control the flare-up.
Potential Side Effects
While effective, Prednisone carries potential side effects. These include increased blood sugar, weight gain, and increased risk of infection. Long-term use is linked to more serious complications. Your doctor will weigh the benefits against these risks. Always report any concerning symptoms immediately.
Prednisone and Long-Term Gout Management
Prednisone isn’t a long-term gout treatment. It addresses symptoms; it doesn’t treat the underlying cause–uric acid buildup. Your doctor will likely recommend lifestyle changes and/or other medications, like allopurinol or febuxostat, to manage uric acid levels and prevent future flares.
Alternative Treatments
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and colchicine are common alternatives for acute gout. Your doctor can help determine the best treatment option based on your medical history and preferences.
Dosage and Administration of Prednisone 20mg for Gout
Prednisone 20mg is typically prescribed for acute gout attacks to rapidly reduce inflammation and pain. Your doctor will determine the optimal dosage and duration based on your individual needs and response to treatment. A common regimen involves taking a single 20mg dose daily for several days. The duration of treatment may range from a few days to a week, depending on symptom improvement.
Always take Prednisone exactly as prescribed. Do not adjust the dose or discontinue treatment prematurely without consulting your physician. Take the medication with food to minimize potential stomach upset. Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully regarding the timing of your dose (e.g., morning or evening).
Potential side effects, though not experienced by everyone, include increased appetite, weight gain, fluid retention, mood changes, and increased blood sugar levels. Report any unusual symptoms to your healthcare provider immediately. Long-term use of Prednisone carries additional risks, so it is typically prescribed only for short, acute treatments of gout.
Remember, Prednisone is a powerful medication. It addresses the symptoms of gout, not the underlying cause. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a proper diet and regular exercise, is critical to preventing future gout attacks.
Always discuss your medication plan with your doctor or pharmacist to understand potential risks and benefits, and ensure you are using Prednisone safely and effectively.
Potential Side Effects of Prednisone 20mg Treatment
Prednisone, while effective for managing gout flares, can cause several side effects. These vary depending on the dose and duration of treatment, but even at 20mg, you should be aware of potential issues. Common side effects include increased appetite, leading to weight gain, and fluid retention, potentially causing swelling in your ankles or face. You might also experience insomnia or mood changes, ranging from mild irritability to more significant anxiety or depression.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Prednisone can irritate your stomach lining. This can manifest as heartburn, indigestion, or even nausea and vomiting. To minimize this, take prednisone with food. If gastrointestinal issues persist or worsen, contact your doctor immediately. They might adjust your medication or suggest additional treatments.
Increased Blood Sugar and Blood Pressure
Prednisone can raise your blood sugar levels, posing a concern for individuals with diabetes or those at risk. Regular monitoring of blood sugar is recommended. Similarly, it can temporarily elevate blood pressure. Regular check-ups with your physician are crucial to monitor and manage these potential side effects.
Remember, this information isn’t a replacement for medical advice. Always consult your doctor before starting or stopping any medication, including Prednisone. They can assess your individual risk factors and help you manage any side effects effectively.
When to Consider Prednisone for Gout: Indications and Contraindications
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, is a powerful anti-inflammatory medication sometimes used for acute gout attacks. Consider it when other treatments, like NSAIDs, aren’t sufficient or are contraindicated. This usually means the gout is severe, causing significant pain and functional impairment.
Indications for Prednisone Use in Gout
Doctors may prescribe Prednisone for gout if you experience intense joint pain, swelling, and redness that significantly impacts your ability to perform daily activities. This is especially true if the attack is resistant to or you cannot tolerate NSAIDs.
Prednisone quickly reduces inflammation, providing faster pain relief than many other gout treatments. This is beneficial for individuals with severe attacks or those with comorbidities that make them high risk for NSAID-related complications.
Contraindications and Precautions
Prednisone isn’t suitable for everyone. It carries potential side effects, and certain conditions make its use inadvisable. Always discuss all your health conditions and medications with your doctor.
| Condition | Reason for Caution or Contraindication |
|---|---|
| Diabetes | Prednisone can elevate blood sugar levels. |
| Osteoporosis | Long-term Prednisone use increases fracture risk. |
| High Blood Pressure | Prednisone may worsen hypertension. |
| Peptic Ulcers | Prednisone can increase ulcer risk. |
| Glaucoma | Prednisone can increase intraocular pressure. |
| Infections | Prednisone can suppress the immune system. |
| Pregnancy and Breastfeeding | Use requires careful evaluation of risks and benefits. |
Other Considerations
Remember, Prednisone is usually a short-term treatment for acute gout attacks. Long-term use carries significant risks. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage and duration of treatment, tailoring it to your individual needs and health status. They will also likely discuss the importance of addressing underlying causes of gout and implementing long-term management strategies such as dietary changes and urate-lowering therapy.
Comparing Prednisone to Other Gout Medications
Prednisone offers rapid pain relief, making it a valuable option for acute gout attacks. However, it’s not a long-term solution and carries potential side effects. Let’s compare it to other common gout treatments:
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
- Ibuprofen and Naproxen: These provide similar rapid pain relief to Prednisone, but with a lower risk of side effects for shorter treatment durations. However, they can cause gastrointestinal issues in some individuals.
- Colchicine: Colchicine reduces inflammation and pain, but its effectiveness varies. It’s often used in conjunction with NSAIDs or other treatments.
Uric Acid Lowering Medications
- Allopurinol: This medication lowers uric acid levels, preventing future gout attacks. It’s usually not used during an acute attack because it can sometimes worsen inflammation initially. Long-term use is key.
- Febuxostat: An alternative to allopurinol, it also lowers uric acid, providing similar long-term benefits. It may be better tolerated by some patients who have issues with allopurinol.
- Probenecid: This medication increases the excretion of uric acid through the kidneys. It’s sometimes used in conjunction with other medications.
Choosing the Right Treatment
The best gout medication depends on several factors, including the severity of your symptoms, your medical history, and any other medications you’re taking. Your doctor will help you determine the most appropriate treatment plan. Prednisone works best for acute pain relief, while uric acid-lowering medications are essential for long-term management and prevention.
Side Effects Considerations
- Prednisone: Potential side effects include increased blood sugar, weight gain, fluid retention, and increased risk of infections. Short-term use minimizes these risks.
- NSAIDs: Stomach upset, ulcers, and kidney problems are possible side effects, especially with long-term use.
- Colchicine: Diarrhea and nausea are common side effects, often manageable with appropriate dosing.
- Uric Acid Lowering Medications: Allopurinol can cause rashes, while febuxostat can rarely cause liver problems. Regular monitoring is important.
Always discuss your treatment options with your doctor to find the safest and most effective approach for managing your gout.
Long-Term Use and Management of Prednisone for Gout
Prednisone shouldn’t be a long-term solution for gout. Its anti-inflammatory effects offer quick relief, but prolonged use carries significant risks, including osteoporosis, increased blood sugar, and weakened immunity. Doctors generally prescribe it for short, intense flares.
Alternative Long-Term Gout Management
For chronic gout, your doctor will likely recommend lifestyle changes and medications designed for sustained management. These include dietary modifications, weight loss (if needed), regular exercise, and medication such as allopurinol or febuxostat to lower uric acid levels. These treatments prevent future attacks, unlike prednisone which only treats existing inflammation.
Monitoring Prednisone Use
If you are prescribed prednisone for a gout flare, close monitoring is crucial. Your physician will likely schedule regular check-ups to assess your blood pressure, blood sugar, and bone density. They might also recommend supplements like calcium and vitamin D to mitigate the risk of osteoporosis. Open communication with your doctor about any side effects is vital for safe and effective management.
Tapering Off Prednisone
Stopping prednisone abruptly can cause serious withdrawal symptoms. Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding tapering the dose gradually to minimize adverse effects. This slow reduction allows your body to adjust to reduced levels of the drug, improving overall health and reducing risks of complications.
Specific Recommendations
Always consult your doctor before starting, stopping, or changing the dosage of any medication, including prednisone. Self-treating gout can lead to serious health problems. Follow your doctor’s plan, and ask questions if anything is unclear. Regular follow-up appointments ensure that your treatment remains effective and safe. Your healthcare team is there to support you through this.
Monitoring Progress and Consulting Your Doctor
Track your pain levels daily using a pain scale (0-10). Note any changes in swelling, redness, or warmth around the affected joint. Record this information in a journal or use a mobile app. Report significant improvements or worsening symptoms to your doctor immediately.
Medication Adjustments
Your doctor will likely schedule follow-up appointments to assess your response to prednisone. Be prepared to discuss your pain levels, any side effects you’re experiencing (such as increased thirst, difficulty sleeping, or increased appetite), and the overall impact on your daily activities. Your doctor might adjust your prednisone dosage based on your progress. Remember, never stop taking prednisone abruptly; always follow your doctor’s instructions. Discuss any concerns about potential long-term use with your doctor.
Lifestyle Changes
Maintain a gout-friendly diet low in purines, drink plenty of water, and get regular exercise as advised by your doctor. This helps manage gout symptoms and improve overall health. Regular check-ups are key for preventing future flare-ups. Communicate honestly about your adherence to these lifestyle changes during your appointments.