Prednisone 20 mg can effectively reduce hives’ severity, but it’s not a first-line treatment. Consider it after other options like antihistamines have proven insufficient. This dosage often provides relief within 24-48 hours, reducing swelling and itching. However, remember it’s a corticosteroid, so prolonged use carries potential side effects.
Your doctor will determine the appropriate duration of Prednisone treatment based on your specific needs. Typically, short courses (a few days to a week) are preferred to minimize side effects. Always follow their instructions precisely, even if you feel better sooner. Never abruptly stop taking Prednisone; gradual tapering under medical supervision is essential.
Potential side effects include increased appetite, weight gain, mood changes, and insomnia. Less common but serious effects warrant immediate medical attention and include high blood pressure, increased blood sugar, and impaired wound healing. Open communication with your doctor about any concerns is vital throughout your treatment.
Remember: This information is for general knowledge and doesn’t replace professional medical advice. Always consult your physician before starting any medication, including Prednisone, particularly if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications. They can assess your situation, determine the best course of action, and monitor for any adverse effects.
- Prednisone 20 mg for Hives: A Detailed Guide
- Understanding Hives and Their Causes
- Common Triggers
- Less Common Causes
- Diagnosis and Treatment
- Prednisone’s Mechanism of Action in Treating Hives
- Dosage and Administration of Prednisone 20mg for Hives
- Oral Administration
- Important Considerations
- Potential Side Effects of Prednisone 20mg
- Common Side Effects
- Less Common, But Important Side Effects
- Serious Side Effects (Seek Immediate Medical Attention)
- Managing Side Effects
- Important Note
- When to Seek Medical Attention While on Prednisone
- When to Call Your Doctor for Less Urgent Issues
- Managing Prednisone Side Effects
- Alternative Treatments for Hives
- Important Considerations and Precautions
Prednisone 20 mg for Hives: A Detailed Guide
Prednisone 20mg is often prescribed for severe hives, reducing inflammation and itching quickly. However, it’s a short-term solution, not a cure.
Dosage and Duration: Your doctor determines the precise dosage and treatment length. Typical prescriptions range from a few days to a couple of weeks, depending on your response. Strictly adhere to your doctor’s instructions. Never adjust your dosage without consulting them.
- Potential Side Effects: Common side effects include increased appetite, weight gain, mood changes, insomnia, and increased blood sugar. Less frequent but more serious side effects are possible; report any concerning symptoms immediately.
- Contraindications: Prednisone is unsuitable for individuals with specific medical conditions like certain fungal infections or uncontrolled diabetes. Always inform your doctor about all your health issues and medications.
- Interactions: Prednisone can interact with several medications. Provide your doctor with a complete list of your current prescriptions, over-the-counter drugs, and supplements.
Managing Side Effects: To mitigate potential side effects, maintain a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and monitor your blood sugar levels if you have diabetes. Consult your doctor or pharmacist if side effects are bothersome.
- Long-Term Hives Management: Prednisone tackles acute flare-ups. For long-term hives control, identifying and avoiding triggers is crucial. Your doctor may suggest allergy testing or recommend alternative treatments, such as antihistamines.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Regular check-ups allow your doctor to monitor your progress, adjust medication if necessary, and address any complications. Attend all scheduled appointments.
- Emergency Situations: Seek immediate medical attention if you experience difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips, or tongue (angioedema), or a rapid heartbeat.
This information is for guidance only; it does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any medication for hives or any other health condition.
Understanding Hives and Their Causes
Hives, or urticaria, present as itchy, raised welts on your skin. These welts vary in size and can appear anywhere on your body. Several factors trigger hives; identifying the cause is key to effective treatment.
Common Triggers
Allergies frequently cause hives. Common allergens include foods (like nuts, shellfish, or dairy), medications (like penicillin or NSAIDs), and insect stings. Contact with certain plants or materials, such as latex or certain fabrics, can also trigger a reaction.
Less Common Causes
Beyond allergies, several other conditions can lead to hives. Infections, including viral or bacterial illnesses, can cause your immune system to overreact, producing hives. Autoimmune diseases sometimes manifest as hives. Physical triggers, like heat, cold, pressure, or sunlight, may also be involved. Stress and certain medical conditions can also contribute.
Diagnosis and Treatment
A dermatologist can help you pinpoint the cause of your hives through a thorough examination and possibly allergy testing. Treatment depends on the severity and cause. Antihistamines often alleviate symptoms. In severe cases, corticosteroids, like Prednisone, may be necessary to quickly control the reaction. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication, particularly corticosteroids.
Prednisone’s Mechanism of Action in Treating Hives
Prednisone reduces hive inflammation by suppressing the body’s immune response. It achieves this primarily by binding to glucocorticoid receptors within immune cells.
This binding inhibits the production of inflammatory mediators, such as histamine and leukotrienes. These mediators are key players in the allergic reactions causing hives, resulting in decreased swelling and itching.
Additionally, prednisone influences the movement of immune cells, reducing their infiltration into the skin. This lessens the allergic reaction’s intensity at its source. The reduced inflammation translates to a decrease in hive size and severity.
Prednisone also stabilizes mast cells, preventing the release of further histamine. This further contributes to the reduction of inflammation and the improvement of symptoms.
While prednisone offers rapid relief, it’s crucial to remember it addresses symptoms, not the underlying cause. Therefore, identifying and managing the allergen triggering the hives is vital for long-term control.
Dosage and Administration of Prednisone 20mg for Hives
Prednisone 20mg for hives is typically prescribed as a short-term treatment. Your doctor will determine the appropriate duration, but it’s often a few days to a week. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Never adjust the dosage yourself.
Oral Administration
Prednisone 20mg tablets are usually taken orally, once or twice daily, with food to minimize stomach upset. Drink plenty of water with each dose. Take the medication at the same time each day for consistent blood levels. Avoid crushing or chewing the tablets unless specifically instructed by your physician.
Important Considerations
Inform your doctor about all medications you are currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, as interactions are possible. Report any side effects, such as increased thirst, frequent urination, or changes in mood, immediately. Your doctor may need to adjust your dosage or prescribe alternative treatment options if side effects are severe or persistent. Sudden discontinuation of Prednisone can cause withdrawal symptoms, so always follow a tapering schedule outlined by your healthcare provider.
Potential Side Effects of Prednisone 20mg
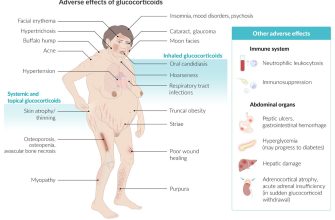
Prednisone, while effective for hives, can cause side effects. These vary in severity and frequency, depending on individual factors and dosage. A 20mg dose is generally considered relatively low, but awareness is key.
Common Side Effects
Expect some common side effects such as increased appetite, leading to weight gain; fluid retention, potentially causing swelling in your face, ankles, or feet; insomnia; and mood changes, ranging from mild irritability to anxiety. These usually subside once you stop taking the medication.
Less Common, But Important Side Effects
Less frequently, but still possible, are increased blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia), which is particularly relevant for individuals with diabetes. You might experience increased blood pressure and headaches. Stomach upset, including heartburn and nausea, can also occur.
Serious Side Effects (Seek Immediate Medical Attention)
While rare at this dosage, serious side effects warrant immediate medical attention. These include severe allergic reactions (difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat), muscle weakness, and vision problems.
Managing Side Effects
| Side Effect | Possible Management Strategies |
|---|---|
| Increased Appetite/Weight Gain | Maintain a balanced diet and incorporate regular exercise. |
| Fluid Retention | Reduce salt intake and increase water consumption. |
| Insomnia | Avoid caffeine and alcohol before bed; maintain a regular sleep schedule. |
| Mood Changes | Practice stress-reduction techniques (yoga, meditation); talk to your doctor. |
Important Note
This information is for general knowledge and doesn’t substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor before starting or stopping any medication, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions. Report any unusual symptoms to your healthcare provider immediately.
When to Seek Medical Attention While on Prednisone
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience any of the following:
- Severe allergic reaction: Difficulty breathing, swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat, hives spreading rapidly.
- Severe stomach pain or vomiting blood.
- Sudden weight gain exceeding 2 pounds in a day.
- Persistent or worsening high blood pressure (over 140/90 mmHg).
- Increased blood sugar levels, particularly if you have diabetes.
- Mood changes, such as severe anxiety, depression, or unusual irritability.
- Muscle weakness or severe muscle pain.
- Blurred vision or other vision changes.
- Any signs of infection, such as fever, chills, or worsening sores.
When to Call Your Doctor for Less Urgent Issues
While not emergencies, these symptoms warrant a call to your doctor for assessment and potential dosage adjustments:
- Increased thirst or frequent urination.
- Insomnia or difficulty sleeping.
- Headache.
- Increased appetite.
- Hives not improving after a few days of prednisone.
Managing Prednisone Side Effects
Remember, prednisone can have side effects. Discuss any concerns with your doctor. They can help manage side effects and ensure you’re receiving the proper care.
Alternative Treatments for Hives
Consider cool compresses. Apply a cool, damp cloth to the affected area for 10-15 minutes to reduce itching and inflammation. This simple remedy provides immediate relief.
Oatmeal baths offer soothing relief. Colloidal oatmeal, available at most pharmacies, can calm irritated skin. Add a cup to your bathwater and soak for 15-20 minutes. The natural anti-inflammatory properties help reduce itching.
Explore over-the-counter antihistamines. Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) or cetirizine (Zyrtec) can effectively manage mild to moderate hives. Always follow package directions.
Try topical hydrocortisone cream. This 1% cream, available without a prescription, can reduce inflammation and itching when applied directly to hives. Apply thinly and only as directed.
Identify and avoid triggers. Common triggers include certain foods (nuts, shellfish), medications, and insect bites. Keeping a diary to track potential triggers can be beneficial in managing future outbreaks.
Consult an allergist. If hives are severe, persistent, or accompanied by other symptoms, see an allergist for proper diagnosis and management. They can perform allergy testing and recommend appropriate treatment plans.
Important Considerations and Precautions
Always inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, before starting Prednisone. This helps prevent harmful interactions.
Prednisone can increase your blood sugar levels. Monitor your blood sugar regularly, especially if you have diabetes.
Avoid alcohol consumption while taking Prednisone, as it can increase the risk of stomach ulcers and other side effects.
Report any unusual bruising or bleeding to your doctor immediately. Prednisone can affect blood clotting.
Be aware that Prednisone can weaken your immune system, making you more susceptible to infections. Practice good hygiene and avoid contact with sick individuals.
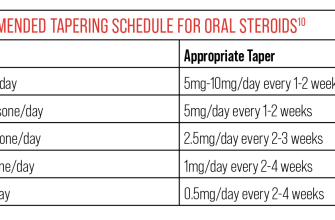
Gradual tapering of Prednisone is necessary to avoid withdrawal symptoms. Never stop taking Prednisone suddenly without your doctor’s guidance.
Long-term Prednisone use can lead to various side effects, including weight gain, osteoporosis, and mood changes. Discuss these potential risks with your physician.
Prednisone may interact negatively with certain vaccines. Consult your doctor before receiving any vaccinations while on Prednisone.
Inform your doctor if you experience any side effects, such as insomnia, increased appetite, or mood swings. Many of these can be managed.
Regular check-ups with your doctor are necessary to monitor your progress and adjust the dosage if needed.