Prednisone 20mg is a common dosage, but understanding its use requires careful attention to detail. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. This medication is a corticosteroid, powerful in suppressing inflammation but carrying potential side effects.
Expect changes in appetite, possibly weight fluctuations. Increased thirst and frequent urination are also common. Monitor your blood sugar levels, as Prednisone can affect glucose regulation. Report any significant changes immediately to your physician. Regular blood pressure checks are also recommended.
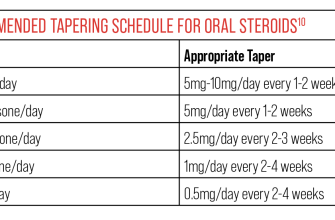
Important Note: Prednisone should not be abruptly stopped. Tapering the dosage, under medical supervision, is critical to prevent withdrawal symptoms. These can include fatigue, muscle weakness, and joint pain. Your doctor will create a personalized tapering schedule based on your individual needs and response to treatment.
Remember: This information serves as a guide, not a replacement for professional medical advice. Consult your doctor or pharmacist for any concerns or before making changes to your medication regimen. They can address your specific health situation and provide the best possible care.
- Prednisone 20 Milligrams: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding Prednisone 20mg: Dosage and Administration
- Managing Your Prednisone 20mg Prescription
- Long-Term Prednisone Use
- Common Uses of Prednisone 20mg: When is it Prescribed?
- Side Effects and Precautions: Managing Potential Risks
- Managing Common Side Effects
- Addressing Less Frequent, But Serious Concerns
- Important Considerations Before Starting Prednisone
- Interactions and Contraindications: What to Avoid
- Weaning Off Prednisone 20mg: A Safe and Gradual Process
Prednisone 20 Milligrams: A Comprehensive Guide
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Prednisone 20mg is a common dosage, but your individual needs may vary.
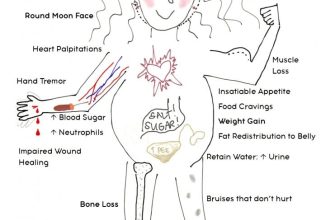
Expect potential side effects like weight gain, mood changes, and increased blood sugar. Regular monitoring is key. Discuss these with your physician.
Take Prednisone with food to minimize stomach upset. Water is the best beverage choice.
Never abruptly stop taking Prednisone. Tapering off under medical supervision is vital to prevent withdrawal symptoms.
Inform your doctor about all other medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to avoid potential interactions.
Regular blood tests help track your response to Prednisone and identify any potential complications. Follow your doctor’s schedule.
| Potential Side Effect | Action |
|---|---|
| Increased appetite | Maintain a healthy diet and monitor weight. |
| Insomnia | Establish a relaxing bedtime routine. |
| Mood swings | Communicate openly with your doctor and loved ones. |
| Increased blood pressure | Monitor blood pressure regularly as instructed by your doctor. |
Report any unusual symptoms immediately to your doctor. This could indicate a side effect or other health concern.
Prednisone can weaken your immune system. Practice good hygiene and avoid sick individuals to minimize infection risk.
This information is for educational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist for specific guidance.
Understanding Prednisone 20mg: Dosage and Administration
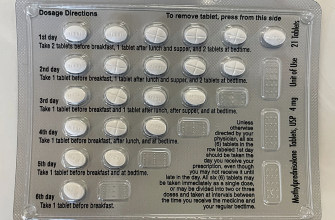
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Prednisone 20mg tablets are usually taken once daily, but your physician might prescribe a different schedule, possibly divided doses. Take the medication with food to minimize stomach upset. Consistent timing is key; try setting a daily reminder.
Managing Your Prednisone 20mg Prescription
Never adjust your dosage without consulting your doctor. Sudden changes can have serious consequences. Inform your doctor about all other medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, as interactions are possible. Report any unusual side effects immediately; common ones include weight gain, mood changes, and increased appetite. Your doctor will monitor your progress and may adjust your dosage accordingly.
Long-Term Prednisone Use
Long-term use requires careful monitoring due to potential side effects. Your doctor will likely schedule regular check-ups to assess your health and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan. Discuss any concerns you have regarding long-term use with your healthcare provider. They can help you manage potential risks and address any questions you may have.
Common Uses of Prednisone 20mg: When is it Prescribed?
Prednisone 20mg is a powerful corticosteroid frequently prescribed for various inflammatory and autoimmune conditions. Its use depends heavily on the specific diagnosis and patient response.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Prednisone effectively manages flare-ups in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis). The dosage and duration vary greatly depending on disease severity and individual needs.
- Allergic Reactions: Severe allergic reactions, such as anaphylaxis or angioedema, often necessitate immediate treatment with a high dose of prednisone, rapidly reducing inflammation and improving symptoms.
- Asthma Exacerbations: In cases of severe asthma attacks, prednisone is used to quickly reduce airway inflammation and improve breathing. It’s usually a short-term treatment alongside other asthma medications.
- Respiratory Conditions: Conditions like bronchitis, pneumonia, and sarcoidosis might benefit from prednisone to manage inflammation. It assists in mitigating symptoms, but it’s frequently used in conjunction with other therapies.
- Skin Conditions: Certain severe skin conditions, such as severe eczema, psoriasis, and dermatomyositis, respond favorably to prednisone treatment, reducing inflammation and improving skin lesions.
- Eye Conditions: Severe uveitis (inflammation of the eye) and other inflammatory eye diseases often require prednisone to reduce swelling and protect vision. A physician will determine the most appropriate course of action.
- Cancer Treatment: Prednisone is sometimes used in conjunction with chemotherapy or radiation therapy for certain types of cancer, such as leukemia and lymphoma, to control tumor growth and reduce side effects. The specifics are determined by oncologists.
- Organ Transplantation: Prednisone, usually in conjunction with other immunosuppressants, helps prevent organ rejection after transplantation. This is a specialized application requiring close medical supervision.
Important Note: Prednisone is a potent medication with potential side effects. It should only be used under the direct supervision of a physician. Never start or stop taking prednisone without consulting your doctor. They will carefully weigh the benefits against the risks and tailor the dosage and treatment duration to your specific needs.
Side Effects and Precautions: Managing Potential Risks
Prednisone, while effective, carries potential side effects. Monitor yourself for common issues like increased appetite, weight gain, mood changes, and trouble sleeping. Report any significant changes to your doctor.
Managing Common Side Effects
Increased blood sugar is a possibility, especially for individuals with diabetes. Regular blood sugar monitoring is recommended. High blood pressure is another concern; regular check-ups with your doctor will help manage this risk. Fluid retention can also occur. Reducing sodium intake and increasing physical activity can help mitigate this. Remember to drink plenty of water.
Addressing Less Frequent, But Serious Concerns
Osteoporosis is a risk with long-term Prednisone use. Discuss bone density testing with your physician, and consider calcium and vitamin D supplements. Increased risk of infection is another important consideration; practice good hygiene and avoid contact with sick individuals. Gastrointestinal issues such as heartburn or ulcers might arise. Your doctor may prescribe medication to protect your stomach lining.
Important Considerations Before Starting Prednisone
Inform your doctor about your complete medical history, including any allergies and other medications you’re taking. This includes over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Never abruptly stop taking Prednisone; gradual tapering under medical supervision is crucial to prevent withdrawal symptoms. Follow your doctor’s instructions closely regarding dosage and duration of treatment. Regular follow-up appointments are recommended for monitoring your progress and managing any side effects.
Interactions and Contraindications: What to Avoid
Avoid grapefruit and grapefruit juice. These can significantly increase Prednisone levels in your blood, leading to stronger side effects.
Don’t combine Prednisone with NSAIDs (like ibuprofen or naproxen) without consulting your doctor. This combination increases your risk of stomach ulcers and bleeding.
Be cautious with blood thinners (anticoagulants like warfarin). Prednisone can affect how well they work, potentially increasing bleeding risk. Close monitoring is necessary.
Inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Many can interact negatively with Prednisone.
Alcohol consumption should be limited or avoided entirely while on Prednisone. It can worsen side effects like stomach upset and increase liver stress.
People with diabetes need careful monitoring of blood sugar levels as Prednisone can elevate blood glucose.
Individuals with glaucoma or high eye pressure should use caution. Prednisone might exacerbate these conditions.
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should discuss Prednisone use with their doctor. The risks and benefits need careful consideration.
Avoid vaccination while taking Prednisone, especially live vaccines. Your immune system’s response may be weakened, compromising the vaccine’s effectiveness and potentially leading to complications.
Report any unusual symptoms, such as severe stomach pain, rapid weight gain, blurred vision, or changes in mood, to your doctor immediately.
Weaning Off Prednisone 20mg: A Safe and Gradual Process
Never stop Prednisone abruptly. Your doctor will create a personalized tapering schedule. This usually involves reducing your dose by a small amount, perhaps 2.5mg to 5mg, every few days or weeks.
Expect potential side effects during tapering, such as fatigue, joint pain, and mood changes. These are common and usually manageable. Discuss these with your physician; they might adjust the tapering speed or prescribe supportive medication.
Regular blood tests monitor your progress and ensure your body adapts well. These checks help your doctor fine-tune the weaning process.
Monitor your blood pressure and weight closely throughout the process and report any significant changes to your healthcare provider.
Maintain a healthy lifestyle–balanced diet, regular exercise, and sufficient rest–to support your body during this transition. This helps minimize side effects and aids a smoother weaning.
Complete the prescribed tapering schedule, even if you feel better prematurely. Stopping too quickly can lead to serious withdrawal symptoms.
Close communication with your doctor is key. Report any concerns promptly; they can provide guidance and modifications to your tapering plan.
Remember, each individual’s response to Prednisone is unique. Your doctor’s guidance tailored to your specific health profile ensures a safe and successful weaning process.