Consult your doctor immediately before taking Prednisone 200mg. This dosage is significantly high and requires close medical supervision.
Potential Uses & Considerations
Prednisone 200mg is rarely prescribed as a starting dose. It’s usually reserved for severe conditions like severe allergic reactions, autoimmune disorders (in flare-ups), or certain cancers. Your physician will carefully weigh the benefits against the significant potential side effects.
Side Effects: Be Aware
- Increased blood sugar: Monitor blood glucose levels closely.
- Weight gain: Expect fluid retention and changes in appetite.
- Mood changes: Irritability, anxiety, and insomnia are common.
- Muscle weakness: This can affect daily activities.
- Increased risk of infection: Your immune system is suppressed.
- High blood pressure: Regular monitoring is critical.
This isn’t an exhaustive list. Discuss all potential side effects with your doctor.
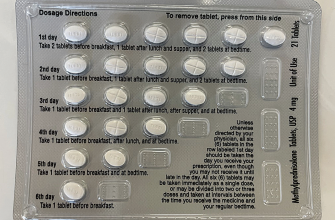
Dosage & Duration
Your doctor will determine the precise duration of your treatment and the correct tapering schedule. Abruptly stopping Prednisone 200mg can cause serious health problems. Expect a gradual reduction in dosage under strict medical guidance.
Important Precautions
Do not take Prednisone 200mg without a prescription. Inform your doctor about all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, you are currently taking. This includes herbal remedies. Report any unusual symptoms immediately.
Specific Interactions
- Warfarin (blood thinner): Increased bleeding risk.
- Digoxin (heart medication): Potential for increased toxicity.
- Insulin or oral diabetes medications: Prednisone raises blood sugar.
This list isn’t complete. Complete transparency with your physician is crucial for safe treatment.
This information serves as a brief overview and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always follow your doctor’s instructions.
Interactions with Other Medications and Substances
Prednisone’s high dosage (200mg) significantly increases the risk of drug interactions. Always inform your doctor and pharmacist about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen increase the risk of stomach ulcers and bleeding when combined with Prednisone. Monitor for any stomach pain or dark stools.
Warfarin (a blood thinner) and Prednisone interact, potentially affecting your blood’s clotting ability. Regular blood tests are crucial to manage this interaction.
Digoxin (a heart medication) interactions with Prednisone can lead to increased digoxin levels in your blood, causing irregular heartbeat. Close monitoring of your heart rhythm is necessary.
Diabetes medications may require adjustments, as Prednisone can raise blood sugar levels. Your doctor might need to modify your diabetes treatment plan.
Antibiotics like rifampin and rifabutin can reduce the effectiveness of Prednisone. Your doctor may need to increase your Prednisone dose.
Oral contraceptives may become less effective while taking Prednisone. Discuss alternative birth control methods with your healthcare provider.
Alcohol consumption should be minimized, as it can exacerbate Prednisone’s side effects, such as stomach upset and liver damage.
This information is not exhaustive. Consult your doctor or pharmacist for a personalized assessment of potential interactions specific to your health condition and medications.