Always consult your veterinarian before administering Prednisone to your dog. Dosage depends entirely on your dog’s weight, condition, and the veterinarian’s specific instructions. Never exceed the prescribed dosage.
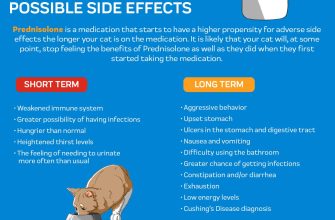
Prednisone 5mg tablets are a common treatment for various canine inflammatory conditions, including allergies, arthritis, and autoimmune diseases. The medication works by suppressing the immune system, reducing inflammation and relieving pain. However, long-term use can carry potential side effects, such as increased thirst, urination, and appetite. Weight gain is also a possibility.
Closely monitor your dog for any adverse reactions, such as vomiting, diarrhea, or changes in behavior. Report any unusual symptoms to your vet immediately. Regular veterinary check-ups during Prednisone treatment are crucial for monitoring your dog’s health and adjusting the dosage as needed. Remember, responsible pet ownership includes careful medication management.
Proper storage is vital. Keep Prednisone tablets in a cool, dry place, away from children and other pets. Always follow the veterinarian’s instructions for administration and duration of treatment. Never abruptly stop Prednisone without veterinary guidance, as this can lead to serious complications.
- Prednisone 5mg Tablets for Dogs: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding Prednisone’s Role in Canine Health
- Dosage and Administration: A Vet’s Guidance is Crucial
- Potential Side Effects and Monitoring Your Dog
- Gastrointestinal Issues
- Other Potential Side Effects
- Important Note on Tapering
- Long-Term Use and Tapering Off Prednisone
- When to Seek Veterinary Attention
Prednisone 5mg Tablets for Dogs: A Comprehensive Guide
Always consult your veterinarian before giving your dog Prednisone. Dosage depends entirely on your dog’s weight, condition, and other medications.
Prednisone is a powerful corticosteroid. It reduces inflammation and suppresses the immune system. Common uses include treating allergies, inflammatory conditions (like arthritis), and autoimmune diseases.
- Typical Dosage: Your vet will determine the correct dose, typically ranging from 0.5mg to 2mg per pound of body weight, once or twice daily. This is just a guideline; never self-medicate.
- Administration: Prednisone tablets can be given directly or hidden in food. If your dog refuses the medication, discuss alternative administration methods with your vet.
- Duration of Treatment: Treatment length varies significantly depending on the condition. Your vet will create a tapering schedule to gradually reduce the dosage to avoid withdrawal symptoms.
Potential Side Effects: While Prednisone is beneficial, it can cause side effects including increased thirst and urination, increased appetite, weight gain, vomiting, diarrhea, and changes in behavior. Long-term use can lead to more serious issues like Cushing’s disease.
- Monitor your dog closely for any changes in appetite, behavior, or elimination habits. Report any concerns to your veterinarian immediately.
- Follow your vet’s instructions carefully. Never adjust the dosage or discontinue treatment without consulting them.
- Regular veterinary checkups are crucial to monitor your dog’s health and adjust medication accordingly.
Drug Interactions: Prednisone can interact with other medications. Inform your veterinarian about all medications your dog is currently taking.
Storage: Store Prednisone tablets in a cool, dry place, away from children and pets.
This information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult your veterinarian for diagnosis and treatment of your dog’s condition.
Understanding Prednisone’s Role in Canine Health
Prednisone, a glucocorticoid, acts as a powerful anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressant in dogs. It reduces swelling, pain, and immune system activity.
Veterinarians prescribe Prednisone to manage various canine conditions. These include allergies, inflammatory diseases like arthritis, and autoimmune disorders. It also helps with certain cancers and helps treat shock.
Dosage varies significantly depending on the dog’s size, condition, and severity. Always follow your vet’s instructions precisely. Incorrect dosage can lead to serious side effects.
Potential side effects include increased thirst and urination, increased appetite, weight gain, and changes in behavior. More serious side effects are possible, so regular monitoring by your veterinarian is vital.
Long-term Prednisone use requires careful management to minimize side effects. Your vet might recommend gradual tapering of the dose to avoid withdrawal symptoms.
Never administer Prednisone without veterinary guidance. Discuss any concerns or changes in your dog’s health with your vet immediately.
Dosage and Administration: A Vet’s Guidance is Crucial
Never administer Prednisone to your dog without your veterinarian’s explicit instructions. Dosage depends heavily on your dog’s weight, age, overall health, and the specific condition being treated. A typical starting dose might range from 0.5 to 1 mg per pound of body weight, but this varies widely.
Your vet will determine the appropriate dosage and frequency. They might prescribe a daily dose, or a schedule involving multiple administrations throughout the day. Follow their instructions precisely. Never adjust the dosage yourself.
Prednisone often comes as tablets, which can be easily crushed and mixed with food to improve palatability if your dog is reluctant to take medication directly. Your veterinarian can advise on the best method for administering the medication to your pet.
Regular veterinary check-ups are vital throughout the treatment period. Your vet will monitor your dog’s response to the medication and may adjust the dosage accordingly. They will also check for potential side effects, such as increased thirst, increased urination, or changes in appetite.
Sudden cessation of Prednisone can lead to serious health problems. Always follow your veterinarian’s instructions for tapering the dosage to avoid withdrawal symptoms. Open communication with your vet ensures the best possible outcome for your dog.
Potential Side Effects and Monitoring Your Dog
Closely monitor your dog for any changes in behavior or physical condition while on Prednisone. Increased thirst and urination are common. Watch for excessive drinking and frequent urination; weigh your dog regularly to detect fluid retention.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Prednisone can cause stomach upset. Observe your dog for vomiting or diarrhea. Feed small, frequent meals of bland food if digestive issues arise. Consult your vet if these symptoms persist or worsen.
Other Potential Side Effects
Increased appetite is expected, but monitor weight gain. Observe for lethargy, weakness, or changes in coat condition. Skin infections are also possible. Report any unusual behavior, such as aggression or anxiety, to your veterinarian immediately.
Regular veterinary check-ups are vital while your dog is on Prednisone. Blood tests can help monitor organ function and detect potential problems early. Your vet will adjust the dosage as needed and provide guidance based on your dog’s individual response to the medication.
Important Note on Tapering
Never suddenly stop Prednisone. Always follow your veterinarian’s instructions for gradually reducing the dosage to prevent withdrawal symptoms. Abrupt cessation can be harmful to your dog’s health.
Long-Term Use and Tapering Off Prednisone
Never abruptly stop Prednisone. Sudden cessation can trigger serious health problems in your dog.
Long-term Prednisone use requires careful monitoring by your veterinarian. They will adjust the dosage based on your dog’s response and overall health. Regular blood tests are usually necessary to check for side effects.
Tapering off Prednisone involves gradually reducing the dosage over several weeks or months, under veterinary supervision. The specific tapering schedule depends on several factors, including your dog’s condition, the duration of treatment, and the current dosage.
Common side effects of Prednisone, such as increased thirst and urination, may worsen during tapering. Monitor your dog closely for these and other potential issues, reporting any changes immediately to your vet.
During the tapering process, your vet may recommend alternative treatments to manage your dog’s underlying condition, minimizing reliance on Prednisone. This may include different medications or lifestyle adjustments.
Patience is key. Following your veterinarian’s instructions precisely is crucial for a safe and successful weaning process. Do not adjust the dosage without consulting them.
Expect your dog to potentially exhibit some withdrawal symptoms during tapering. These can range from lethargy to increased appetite. Your vet can advise you on how to manage these symptoms. Remember consistent communication with your veterinarian is essential throughout the process.
When to Seek Veterinary Attention
Contact your vet immediately if your dog exhibits any of the following symptoms while taking Prednisone:
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased thirst or urination | Significantly more water consumption and urination than usual. |
| Increased appetite | Excessive hunger, often beyond normal variations. |
| Weight gain | Noticeable increase in body weight, potentially indicating fluid retention. |
| Vomiting or diarrhea | Persistent vomiting or diarrhea, especially if severe or bloody. |
| Lethargy or weakness | Unusual tiredness, lack of energy, or difficulty moving. |
| Muscle weakness | Difficulty standing, walking, or climbing stairs. |
| Panting | Excessive panting, even at rest. |
| Tremors or shaking | Uncontrollable shaking or tremors in the body. |
| Increased aggression or behavioral changes | Unusual aggression or marked changes in temperament. |
| Swelling | Noticeable swelling in any part of the body. |
| Skin changes | Increased skin infections, thinning of the fur, or changes in skin color. |
| Eye problems | Increased tearing, cloudy eyes, or changes in vision. |
Schedule an appointment if you notice any gradual changes in your dog’s behavior or health, even if they are subtle. Early detection helps facilitate quicker recovery.
Remember, this information is not a substitute for professional veterinary advice. Always follow your vet’s instructions regarding Prednisone dosage and monitoring. They can provide personalized guidance based on your dog’s specific needs and health condition.