Need clear, concise information on Prednisone Acetate? Focus on managing potential side effects like increased appetite and fluid retention by adjusting your diet and monitoring your weight. Regular exercise, while consulting your doctor, can help mitigate some of these effects.
This steroid medication effectively reduces inflammation, but remember it’s not a long-term solution. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage and duration, typically prescribing the lowest effective dose for the shortest possible time. Closely follow their instructions and attend all scheduled appointments.
Important Note: Prednisone Acetate can interact with other medications. Always inform your doctor and pharmacist about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking. This includes over-the-counter drugs. Failing to disclose such information can lead to dangerous interactions.
Managing side effects requires proactive measures. Report any unusual symptoms, such as mood changes, vision problems, or increased susceptibility to infections, to your physician immediately. They can provide personalized guidance and adjust your treatment plan as needed. Early intervention is key to a positive outcome.
- Prednisone Acetate: Understanding Its Uses
- Treating Inflammatory Conditions
- Other Therapeutic Applications
- Important Note:
- Common Conditions Treated with Prednisone Acetate
- Potential Side Effects and Precautions
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- Oral Administration
- Other Administration Routes
- Important Considerations
Prednisone Acetate: Understanding Its Uses
Prednisone acetate is a corticosteroid medication doctors prescribe to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system. This makes it effective for a variety of conditions.
Treating Inflammatory Conditions
Autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus benefit significantly. Prednisone acetate reduces joint swelling and pain in rheumatoid arthritis. Similarly, it manages the inflammation and organ damage associated with lupus. Allergic reactions, such as severe asthma or allergic rhinitis, can also be treated with prednisone acetate, significantly reducing symptoms.
Other Therapeutic Applications
Certain cancers respond favorably to prednisone acetate as part of a combination therapy regimen. It’s often used in leukemia treatment. Prednisone acetate also finds use in managing eye conditions like uveitis, reducing inflammation and protecting vision. Further, it aids in controlling severe inflammatory bowel disease flares, offering symptom relief.
Important Note:
Always consult your doctor before using prednisone acetate. They will assess your specific needs and determine the appropriate dosage and treatment duration, minimizing potential side effects. This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice.
Common Conditions Treated with Prednisone Acetate
Prednisone acetate effectively treats various inflammatory and autoimmune conditions. It’s frequently used for allergic reactions, reducing swelling and inflammation. Asthma exacerbations often respond well to prednisone acetate, providing quick relief from breathing difficulties. Autoimmune diseases like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis benefit from its anti-inflammatory properties, managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
Severe inflammatory bowel diseases, such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, find relief with prednisone acetate, helping to control inflammation and reduce symptoms like abdominal pain and diarrhea. It also plays a role in managing certain types of cancer, working in conjunction with other treatments to minimize side effects and improve patient comfort.
Conditions like multiple sclerosis and certain skin diseases, such as severe eczema and psoriasis, sometimes require prednisone acetate to help control inflammation and reduce flare-ups. It’s important to note that prednisone acetate is a powerful medication, and its use should always be under the guidance of a healthcare professional, considering potential side effects and long-term implications.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Prednisone acetate, while effective, carries potential side effects. Understanding these risks helps you manage treatment effectively.
Common side effects include:
- Increased appetite and weight gain.
- Mood changes, including irritability or anxiety.
- Difficulty sleeping (insomnia).
- Increased blood sugar levels.
- Fluid retention (edema).
- High blood pressure.
Less common, but potentially serious, side effects require immediate medical attention:
- Severe allergic reactions (rash, hives, difficulty breathing).
- Muscle weakness.
- Bone thinning (osteoporosis).
- Increased risk of infections.
- Glaucoma or cataracts.
- Slow wound healing.
Precautions:
- Inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Interactions can occur.
- Regularly monitor blood pressure, blood sugar, and weight. Your doctor will provide guidelines.
- Avoid alcohol consumption as it can worsen some side effects.
- Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully regarding dosage and duration of treatment. Never abruptly stop taking prednisone.
- Report any unusual symptoms to your doctor immediately.
- Discuss vaccination plans with your doctor, as prednisone may affect your immune response.
This information should not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your physician or pharmacist for personalized guidance regarding prednisone acetate usage and potential side effects.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
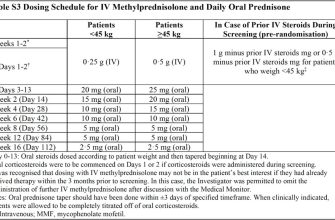
Prednisone acetate dosage depends heavily on the specific condition being treated and the patient’s individual response. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Typical adult dosages range from 5 to 60 milligrams per day, often administered in divided doses. Children’s dosages are significantly lower and are carefully calculated based on weight and condition.
Oral Administration
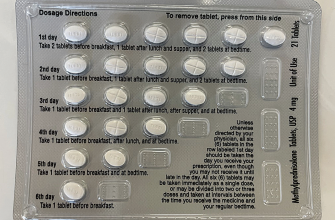
Prednisone acetate is usually taken orally, with or without food. Taking it with food can help minimize stomach upset. Maintain a consistent schedule, taking the medication at the same time each day for optimal results. Do not suddenly stop taking prednisone without consulting your doctor; tapering the dose is usually necessary to avoid withdrawal symptoms.
Other Administration Routes
While oral administration is most common, prednisone acetate can also be administered through injection (intra-articular, intramuscular, or intravenous) in certain situations. Your healthcare provider will determine the appropriate route and dosage based on your individual needs. For example, intra-articular injections target specific joints affected by inflammation.
Important Considerations
Regular blood tests may be necessary to monitor your response to prednisone and check for potential side effects. Report any unusual symptoms to your doctor immediately. This includes, but isn’t limited to, changes in mood, weight gain, increased thirst, or frequent urination. Remember, proper medication management is key to a successful treatment outcome.