Combining prednisone and Benadryl can offer significant allergy relief, but requires careful consideration. Prednisone, a corticosteroid, powerfully reduces inflammation, tackling severe allergy symptoms like breathing difficulties or widespread hives. Benadryl, an antihistamine, directly counteracts histamine, the chemical responsible for many allergic reactions, providing relief from itching, sneezing, and runny nose.
However, this combination isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. Prednisone’s potent anti-inflammatory action carries potential side effects including increased blood sugar, insomnia, and mood changes. It’s crucial to use it only as prescribed by a doctor, and for the shortest duration necessary. Benadryl, while generally safe for short-term use, can cause drowsiness and shouldn’t be combined with activities requiring alertness. Always discuss the risks and benefits with your physician before starting this medication regimen.
Consider your allergy symptoms’ severity. For mild allergic reactions like mild itching or sneezing, Benadryl alone may suffice. If you experience severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing or swelling, immediately seek medical attention, as this combination may not be sufficient and may require epinephrine treatment.
Remember, this information serves as guidance, not a replacement for professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or allergist before using prednisone and Benadryl together, or changing your allergy treatment plan. They can assess your specific situation, determine the appropriate dosage, and monitor for any adverse effects.
Prednisone and Benadryl for Allergies: A Detailed Guide
Doctors often prescribe Prednisone and Benadryl together to manage severe allergic reactions. Prednisone, a corticosteroid, reduces inflammation, while Benadryl, an antihistamine, blocks histamine release, a key player in allergic responses. This combination tackles allergy symptoms from different angles.
Prednisone provides faster, more potent relief than Benadryl alone, especially for severe symptoms like breathing difficulties or swelling. However, it’s a stronger medication with potential side effects, requiring careful monitoring by your doctor.
Benadryl helps control milder symptoms like itching, sneezing, and runny nose. It acts more slowly than Prednisone, offering longer-lasting relief but with less dramatic impact on inflammation.
This combination isn’t suitable for everyone. Consider these points:
| Medication | Benefits | Side Effects | Precautions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prednisone | Rapid, powerful anti-inflammatory action. Effective for severe allergies. | Weight gain, increased blood sugar, insomnia, mood changes, increased risk of infection. | Not for long-term use. Requires doctor’s supervision. |
| Benadryl | Relieves itching, sneezing, runny nose. Relatively safe for short-term use. | Drowsiness, dry mouth, blurred vision, constipation. | May impair alertness; avoid driving or operating machinery. Not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women without consulting a doctor. |
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Never adjust dosages without consulting them. Report any adverse reactions immediately. Remember, this combination treats symptoms; it doesn’t address the underlying cause of your allergies.
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or a severe rash. These could indicate a life-threatening allergic reaction.
When to Consider Prednisone for Allergies
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, offers potent allergy relief, but isn’t a first-line treatment. Consider it when over-the-counter medications, like antihistamines and decongestants, provide insufficient relief.
Severe allergic reactions warrant immediate medical attention and often include prednisone. Symptoms like difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or a rapid, weak pulse require urgent care.
Moderate to severe allergic rhinitis (hay fever) that significantly impacts daily life–causing sleep disruption, persistent sneezing, and debilitating congestion–could benefit from a short course of prednisone. Your doctor can determine the appropriate dosage and duration.
Severe allergic reactions to insect stings or bites may require prednisone to manage inflammation and prevent potentially life-threatening complications. Seek medical advice immediately after a severe reaction.
Prednisone can also help manage allergic reactions causing severe skin conditions like eczema or hives that don’t respond to other therapies. Discuss this with your doctor or dermatologist.
Remember, prednisone has potential side effects, so your doctor will carefully assess your condition and weigh the benefits against the risks before prescribing it. Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and duration of treatment.
Benadryl’s Role in Allergy Management
Benadryl, containing diphenhydramine, acts as a first-generation antihistamine. It directly blocks histamine receptors, reducing allergy symptoms like sneezing, itching, and runny nose. This makes it a helpful short-term solution for managing mild to moderate allergy symptoms.
Diphenhydramine’s impact on histamine offers quick relief, usually within 30-60 minutes of taking a dose. However, remember its effects are temporary, typically lasting 4-6 hours. For persistent allergy relief, a longer-acting medication might be preferable.
While effective for many, Benadryl can cause drowsiness. Avoid driving or operating machinery after taking it. This side effect is a common reason some people prefer alternative antihistamines.
Always follow dosage instructions carefully. Overdosing can lead to serious side effects. Consult your doctor or pharmacist if you have questions or concerns about Benadryl’s use in your specific allergy management plan, particularly when combined with other medications such as Prednisone.
Consider Benadryl as a part of a broader allergy management strategy, not necessarily a standalone solution. Lifestyle changes, such as avoiding allergens, can significantly improve allergy control.
Combining Prednisone and Benadryl: Benefits and Risks
Doctors sometimes prescribe Prednisone and Benadryl together for severe allergies. Prednisone, a corticosteroid, powerfully reduces inflammation, while Benadryl, an antihistamine, blocks histamine release, a key player in allergic reactions. This combination offers a stronger anti-inflammatory and antihistamine effect than either drug alone.
The benefit lies in faster and more complete allergy symptom relief. This is especially helpful during severe allergic episodes like anaphylaxis or severe asthma attacks. Expect quicker reduction of swelling, itching, and breathing difficulties. However, combining these medications carries risks.
Prednisone’s side effects, including increased blood sugar, fluid retention, and insomnia, can be intensified by Benadryl, which also causes drowsiness and dry mouth. The combined sedative effects can be significant, impacting daily activities and driving ability. Long-term use of Prednisone raises the risk of osteoporosis and other health complications.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Never adjust dosages without consulting them. Open communication about any side effects is paramount. Report any unusual symptoms immediately. Consider alternatives if these medications are unsuitable, perhaps exploring different antihistamines or allergy immunotherapy.
Alternatives to Prednisone and Benadryl
Consider exploring alternative allergy treatments if Prednisone and Benadryl aren’t working for you or cause unwanted side effects. Many options exist, depending on your specific allergy triggers and symptoms.
Over-the-Counter Options
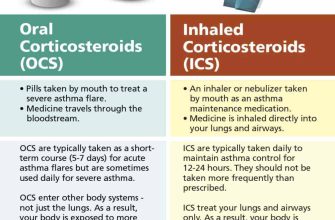
- Nasal Corticosteroids: Products like Flonase or Nasacort provide effective relief from nasal congestion and sneezing. They require daily use for best results, but generally have fewer side effects than oral steroids.
- Oral Antihistamines (non-sedating): Cetirizine (Zyrtec) and Fexofenadine (Allegra) offer similar allergy relief to Benadryl but with less drowsiness. Choose one based on your preference and potential interactions with other medications.
- Eye Drops: Antihistamine or mast cell stabilizer eye drops can alleviate itchy, watery eyes. Look for formulations containing ketotifen or olopatadine.
Prescription Medications
- Leukotriene Modifiers: Montelukast (Singulair) and Zafirlukast (Accolate) reduce inflammation in the airways and can be particularly helpful for asthma triggered by allergies. They’re generally taken daily.
- Immunotherapy (Allergy Shots): This long-term treatment involves regular injections of small amounts of allergens to gradually desensitize your immune system. It’s a good option for significant or persistent allergies, but requires commitment to a treatment schedule.
- Biologics: These newer medications target specific parts of the immune system and are effective for severe allergies that don’t respond to other treatments. Examples include omalizumab (Xolair) and dupilumab (Dupixent).
Lifestyle Changes
- Identify and Avoid Triggers: Pinpointing your allergy triggers (pollen, pet dander, dust mites, etc.) and minimizing exposure is crucial for managing symptoms. Consider air purifiers and regular cleaning.
- Saltwater Nasal Rinse: A daily rinse can help remove irritants from nasal passages, reducing congestion and inflammation.
Remember to consult your doctor or allergist before starting any new treatment, especially if you have other health conditions or are taking other medications. They can help determine the best approach for managing your allergies.