Always discuss Prednisone use with your doctor before combining it with other medications. This is crucial for managing potential interactions and side effects. Specific interactions vary greatly depending on the other drugs you’re taking, so open communication is key.
For example, combining Prednisone with NSAIDs (like ibuprofen) increases the risk of stomach ulcers. Similarly, concurrent use with certain antibiotics might affect Prednisone’s effectiveness. Your doctor will assess your complete medication list, considering both prescription and over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and even herbal remedies, to create a safe and effective treatment plan.
Remember: Don’t adjust your Prednisone dosage without consulting your physician. Sudden changes can lead to serious complications. Your healthcare provider will carefully monitor your progress, potentially adjusting your medication regimen based on your response and any adverse reactions.
Key takeaway: Proactive communication with your doctor is paramount for safe and successful medication management. They can provide tailored advice based on your individual health profile and help you avoid potential medication conflicts.
Prednisone: Understanding its Interactions with Other Medications
Always inform your doctor about all medications you take, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies, before starting Prednisone. This helps prevent dangerous interactions.
Blood thinners (like Warfarin): Prednisone can reduce the effectiveness of these, increasing your risk of blood clots. Your doctor might need to adjust your blood thinner dosage.
Diabetes medications (like Insulin and Metformin): Prednisone can raise blood sugar levels, potentially requiring adjustments to your diabetes medication. Monitor your blood sugar closely.
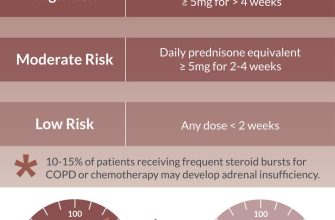
Potassium-wasting diuretics: Prednisone can increase potassium loss, potentially leading to dangerously low potassium levels. Your doctor may monitor your potassium levels and adjust your medication accordingly.
NSAIDs (like ibuprofen and naproxen): Combining these with Prednisone increases the risk of stomach ulcers and bleeding. Use with caution and only as directed by your doctor.
Vaccines: Prednisone can weaken your immune response, making vaccines less effective. Discuss the timing of vaccines with your doctor.
Antibiotics: Some interactions are possible, although not always significant. Your doctor will determine if adjustments are necessary.
Never stop or alter your medication dosage without consulting your doctor. They can provide personalized advice based on your specific health conditions and medications.
Regular check-ups with your doctor are crucial while on Prednisone to monitor for potential side effects and interactions.
Managing Prednisone Therapy: Considerations for Concurrent Medications
Always inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies. Prednisone interacts with many medications, potentially increasing or decreasing their effects.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen increase the risk of stomach ulcers and bleeding when combined with prednisone. Your doctor might suggest an alternative pain reliever.
Prednisone can reduce the effectiveness of some vaccines. Discuss your vaccination schedule with your doctor before starting or during prednisone therapy.
Drugs affecting blood sugar, such as insulin or oral diabetes medications, require careful monitoring when taking prednisone, as prednisone can raise blood glucose levels. Regular blood sugar checks are recommended.
Warfarin (Coumadin) and other anticoagulants interact significantly with prednisone. Close monitoring of blood clotting time is crucial to prevent bleeding or clotting complications.
Digoxin levels can be affected by prednisone. Your doctor may need to adjust your digoxin dose.
Some antifungal medications may interact with prednisone, potentially increasing the risk of side effects. Discuss this interaction with your doctor.
Prednisone can weaken the immune system, impacting how your body responds to other medications. This requires careful monitoring for unexpected reactions.
Regular communication with your doctor is key throughout your prednisone therapy. Report any new or worsening symptoms immediately. This proactive approach allows for prompt adjustments to your treatment plan to ensure your safety and well-being.