Prednisone often helps manage pleurisy symptoms. Its anti-inflammatory properties reduce pain and swelling caused by the inflamed pleural lining. However, remember Prednisone isn’t a cure; it targets symptoms. Doctors usually prescribe it alongside other treatments to address the underlying cause of pleurisy–such as infection or autoimmune disease.
Dosage varies greatly depending on the severity of your pleurisy and your overall health. Your physician will determine the appropriate amount and duration of treatment. Common side effects include weight gain, increased appetite, and mood changes. Open communication with your doctor about any side effects is crucial for adjusting treatment accordingly.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Never alter your dosage without consulting them. Long-term Prednisone use carries risks, including weakened immunity and bone thinning. Your doctor will carefully monitor your progress and adjust the treatment plan to minimize these risks. Regular blood tests are often part of this monitoring process. The goal is to manage your pleurisy effectively while minimizing potential adverse effects.
Disclaimer: This information is for general knowledge only and does not constitute medical advice. Consult your physician for diagnosis and treatment of pleurisy.
- Prednisone and Pleurisy: A Detailed Overview
- Understanding Pleurisy and its Causes
- Infections: A Common Culprit
- Non-Infectious Causes
- Understanding the Symptoms
- Causes Summarized
- Seeking Medical Attention
- How Prednisone Works to Reduce Inflammation
- Impact on Inflammatory Molecules
- Effects on Immune Cells
- Stabilizing Blood Vessels
- Important Note:
- Dosage and Duration:
- Prednisone Dosage and Administration in Pleurisy
- Potential Benefits of Prednisone for Pleurisy
- Reducing Pleural Effusion
- Faster Symptom Resolution
- Common Side Effects of Prednisone Treatment
- When Prednisone Might Not Be the Right Choice
- Contraindications and Precautions
- Alternative Treatments
- Open Communication with Your Doctor
- Monitoring Your Condition During Prednisone Treatment
- Tracking Your Symptoms
- Managing Side Effects
- Recognizing Warning Signs
- Communication is Key
- Blood Work and Imaging
- Alternative Treatments and Management Strategies for Pleurisy
Prednisone and Pleurisy: A Detailed Overview
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, often treats pleurisy symptoms by reducing inflammation. Doctors prescribe it to alleviate pain and improve breathing. However, it’s not a cure for the underlying cause of pleurisy.
Dosage and Duration: The prescribed dose varies depending on the severity of your pleurisy and your overall health. Your doctor will determine the appropriate amount and length of treatment. Typical treatment lasts several weeks, but this can change.
Potential Side Effects: While prednisone provides significant relief, be aware of potential side effects including weight gain, increased blood sugar, mood changes, and increased risk of infection. These are often manageable with careful monitoring and adjustments to the treatment plan.
When to Contact Your Doctor: Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe breathing difficulties, worsening chest pain, or signs of infection such as fever or chills. Regular communication with your physician throughout your treatment is crucial.
Alternative Treatments: Depending on the cause of your pleurisy, other treatments might include antibiotics (for infections), pain relievers (like ibuprofen or acetaminophen), and fluid drainage procedures. Your doctor will create a treatment plan specifically for your needs.
Underlying Causes: Pleurisy is a symptom, not a disease. Pinpointing the root cause–such as pneumonia, lung cancer, or autoimmune disorders–is key to successful long-term management. Your doctor will conduct appropriate tests to determine the cause.
Long-term Management: Once the underlying cause is addressed and your pleurisy resolves, your doctor will gradually reduce your prednisone dosage to minimize side effects. They’ll also discuss long-term management strategies based on the cause of your pleurisy.
Understanding Pleurisy and its Causes
Pleurisy, or pleuritis, is inflammation of the pleura, the thin membrane lining your lungs and chest cavity. This inflammation causes sharp chest pain, usually worsened by breathing or coughing. Several conditions can trigger pleurisy; identifying the cause is critical for effective treatment.
Infections: A Common Culprit
Respiratory infections, like pneumonia and bronchitis, are frequent culprits. Viral infections are more common, but bacterial and fungal infections can also cause pleurisy. Tuberculosis (TB) is another infectious disease that can lead to pleuritis. Prompt diagnosis and treatment of these underlying infections are vital.
Non-Infectious Causes
Autoimmune diseases like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis can inflame the pleura. Certain cancers, particularly lung cancer, can also cause pleuritis as cancer cells spread. Less common causes include pulmonary embolism (blood clot in the lung), asbestos exposure (leading to asbestosis), and trauma to the chest.
Understanding the Symptoms
The primary symptom is sharp, stabbing chest pain. This pain typically worsens with deep breaths or coughing. Other symptoms might include shortness of breath, fever, and a dry cough. The severity of these symptoms varies depending on the underlying cause.
Causes Summarized
| Category | Specific Causes |
|---|---|
| Infectious | Pneumonia, Bronchitis, Tuberculosis, Viral infections |
| Autoimmune | Lupus, Rheumatoid Arthritis |
| Cancer Related | Lung cancer and other cancers with pleural metastasis |
| Other | Pulmonary embolism, Asbestosis, Chest trauma |
Seeking Medical Attention
Chest pain, especially when accompanied by shortness of breath, warrants immediate medical attention. A healthcare professional will conduct a thorough evaluation, including physical examination, imaging tests (like chest X-rays or CT scans), and possibly blood tests to determine the underlying cause of your pleurisy and recommend appropriate treatment.
How Prednisone Works to Reduce Inflammation
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, tackles inflammation by binding to specific receptors inside your cells. This binding triggers a cascade of events that significantly alter how your body responds to injury or infection.
Impact on Inflammatory Molecules
- Prednisone inhibits the production of inflammatory molecules, such as cytokines (e.g., TNF-alpha, IL-1, IL-6) and prostaglandins.
- These molecules are key players in the inflammatory process, causing swelling, pain, and tissue damage. By reducing their levels, Prednisone dampens the intensity of the inflammatory response.
This reduction happens through several mechanisms. Prednisone decreases the activity of enzymes like phospholipase A2, a crucial enzyme in prostaglandin synthesis. It also influences the transcription of genes responsible for producing inflammatory proteins, effectively silencing their production.
Effects on Immune Cells
- Prednisone directly affects immune cells like lymphocytes and macrophages, reducing their activation and migration to the site of inflammation.
- Fewer activated immune cells mean less inflammation. This also helps to prevent further tissue damage caused by these cells’ activity.
- Furthermore, Prednisone stabilizes lysosomal membranes within these cells, preventing the release of destructive enzymes that contribute to tissue damage during inflammation.
Stabilizing Blood Vessels
Prednisone also helps stabilize blood vessels, reducing their permeability. Less permeable blood vessels mean less fluid leakage into the affected area, leading to decreased swelling.
Important Note:
While Prednisone is highly effective, it’s a powerful medication with potential side effects. Always discuss its use with your doctor. They will carefully weigh the benefits against the risks and help manage any side effects.
Dosage and Duration:
- Dosage varies depending on the severity of the inflammation and your individual health. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dose and duration of treatment.
- Following your doctor’s instructions is critical for successful treatment and minimizing potential side effects.
Prednisone Dosage and Administration in Pleurisy
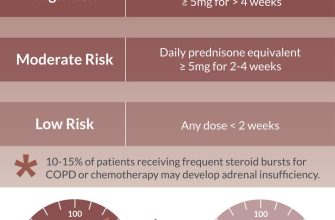
Prednisone dosage for pleurisy varies greatly depending on the underlying cause and severity of inflammation. Your doctor will personalize your treatment plan.
Typical starting doses range from 40-60 mg daily, often given in a single morning dose. This higher initial dose aims to quickly reduce inflammation.
- Important Note: Never adjust your prednisone dosage without consulting your physician.
The doctor will likely decrease the dosage gradually over weeks or months. This tapering process helps minimize withdrawal symptoms and allows your body to adjust naturally. A typical tapering schedule might involve reducing the dose by 5-10 mg every few days or weeks, depending on your response. For example:
- Week 1-4: 60mg daily
- Week 5-8: 50mg daily
- Week 9-12: 40mg daily
- etc.
Prednisone is usually administered orally, as a tablet. It’s crucial to take it with food to reduce stomach upset.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of fluids while taking prednisone.
- Diet: Maintain a healthy diet rich in calcium and potassium to counteract potential side effects.
- Monitoring: Regular blood tests may be required to monitor your blood sugar, potassium levels, and other vital signs.
Remember, this information is for general knowledge only and doesn’t replace professional medical advice. Always discuss your specific case and medication plan with your doctor or other qualified healthcare provider. They will assess your individual needs and create the safest and most effective treatment strategy.
Potential Benefits of Prednisone for Pleurisy
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, can significantly reduce inflammation in the pleural space, a key symptom of pleurisy. This leads to pain relief, often allowing for quicker recovery and improved comfort. The anti-inflammatory effects help manage the underlying cause of the pain, reducing the need for strong painkillers.
Reducing Pleural Effusion
In cases of pleural effusion (fluid buildup around the lungs), Prednisone can help reduce the amount of fluid. This lessens pressure on the lungs and improves breathing capacity. The extent of fluid reduction depends on the underlying cause of the effusion and individual response to the medication. Doctors usually monitor fluid levels regularly during treatment.
Faster Symptom Resolution
Many patients experience a noticeable improvement in their symptoms within a few days of starting Prednisone. This rapid response is a significant benefit, enabling them to return to normal activities sooner. However, the duration of Prednisone treatment varies depending on the severity and cause of the pleurisy. Close monitoring by a healthcare professional is essential.
Common Side Effects of Prednisone Treatment
Prednisone, while effective, can cause various side effects. Weight gain is common, often appearing as fluid retention. Monitor your weight and diet accordingly.
Increased appetite frequently accompanies prednisone use. Plan balanced meals to manage weight and avoid excessive calorie consumption.
Mood changes, including irritability and anxiety, are possible. Open communication with your doctor is vital should you experience significant emotional shifts.
Insomnia can occur. Maintaining a regular sleep schedule and avoiding caffeine before bed may help.
High blood sugar is a risk, especially in individuals with diabetes. Regular blood sugar monitoring is crucial. Your doctor might adjust your diabetes medication.
Increased blood pressure is another possibility. Regular blood pressure checks are necessary. Your doctor can adjust your treatment plan as needed.
Muscle weakness and thinning bones (osteoporosis) can develop with prolonged use. Regular exercise and a calcium-rich diet can help mitigate these risks. Discuss bone density testing with your physician.
Increased risk of infections is a concern. Practice good hygiene and report any signs of infection promptly to your doctor.
These are some of the most frequent side effects. Others are possible. Always report any new or worsening symptoms to your doctor immediately. They can help manage these side effects and adjust your medication if needed.
When Prednisone Might Not Be the Right Choice
Prednisone, while often helpful for pleurisy, isn’t always the best solution. Consider alternatives if you experience specific issues.
Contraindications and Precautions
- Active Infections: Prednisone weakens your immune system, making you more susceptible to infections. Avoid it if you have a current infection. Your doctor will need to treat the infection first.
- Diabetes: Prednisone can raise blood sugar levels, posing risks for those with diabetes. Close blood sugar monitoring is vital, and alternative treatments might be preferred.
- High Blood Pressure: Prednisone can increase blood pressure. If you already have hypertension, your doctor may opt for a different approach to manage your pleurisy.
- Osteoporosis: Long-term prednisone use increases the risk of bone thinning. Alternatives should be considered, especially in patients with pre-existing osteoporosis or risk factors.
- Glaucoma or Cataracts: Prednisone can worsen these conditions. Careful monitoring and alternative therapies might be necessary.
- Mental Health Concerns: Prednisone can cause mood swings, anxiety, and even psychosis in some individuals. This risk needs careful consideration, especially in those with a history of mental illness.
Alternative Treatments
If prednisone isn’t suitable, your doctor might suggest:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): These can help reduce pain and inflammation. Ibuprofen or naproxen are common examples.
- Other medications: Depending on the underlying cause of your pleurisy, your doctor may prescribe other medications, such as antibiotics (for infections) or antiviral drugs.
- Thoracentesis: This procedure involves removing excess fluid from the pleural space using a needle, providing immediate relief.
- Lifestyle changes: Rest, avoiding irritants, and adopting good posture can significantly help manage pleurisy symptoms.
Open Communication with Your Doctor
Always discuss your medical history and concerns with your doctor before starting any medication, including prednisone. They will assess your individual situation and recommend the best course of action.
Monitoring Your Condition During Prednisone Treatment
Schedule regular check-ups with your doctor. These visits allow for close monitoring of your pleurisy and your response to Prednisone. Your doctor will assess your symptoms and adjust your medication accordingly. Be sure to attend all scheduled appointments.
Tracking Your Symptoms
Maintain a detailed symptom diary. Record daily the severity of your chest pain, shortness of breath, and fever. Note any changes in your appetite or weight. This information helps your doctor accurately gauge the effectiveness of the treatment and identify any potential complications.
Managing Side Effects
Prednisone can cause several side effects. Watch for weight gain, increased blood sugar, increased blood pressure, mood changes, and insomnia. Report any concerning side effects to your healthcare provider immediately. They can help manage these side effects and adjust your medication plan as needed. Follow your doctor’s advice regarding diet and exercise to minimize potential issues.
Recognizing Warning Signs
Immediately contact your doctor if you experience severe chest pain, difficulty breathing, or a high fever. These could indicate serious complications that require urgent medical attention. Don’t hesitate to seek help if you are concerned about your health.
Communication is Key
Open communication with your doctor is crucial. Don’t hesitate to ask questions or express your concerns. Active participation in your treatment plan contributes to better outcomes.
Blood Work and Imaging
Your doctor might order periodic blood tests and imaging studies (like chest X-rays) to monitor your condition and the effectiveness of the Prednisone. These tests help ensure your treatment is on track and that any problems are caught early.
Alternative Treatments and Management Strategies for Pleurisy
Managing pleurisy often involves addressing the underlying cause. For viral pleurisy, rest and over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen provide significant relief. Plenty of fluids help support your body’s healing process.
If bacterial infection is the culprit, antibiotics are prescribed. Your doctor will determine the appropriate course of treatment based on the specific bacteria identified.
For pain management beyond over-the-counter options, your physician may recommend stronger analgesics or, in severe cases, nerve blocks. These targeted interventions can significantly reduce discomfort.
Lifestyle modifications can complement medical treatments. Deep breathing exercises and regular, gentle movement help prevent lung collapse and improve chest expansion. Quitting smoking, if applicable, is paramount. Avoiding triggers that worsen inflammation, such as pollutants or allergens, is also beneficial.
Complementary therapies, such as acupuncture or physical therapy, might offer additional comfort and support recovery. However, these should always be discussed with your doctor to ensure they won’t interfere with your primary treatment plan.
| Treatment Type | Description | Benefits | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rest and Hydration | Adequate rest and fluid intake | Supports the body’s natural healing | May not be sufficient for severe cases |
| Over-the-counter Pain Relievers | Ibuprofen or acetaminophen | Reduces pain and inflammation | Follow dosage instructions carefully |
| Antibiotics | For bacterial infections | Eliminates the infection | Requires prescription and diagnosis |
| Nerve Blocks | Targeted pain relief injections | Significant pain reduction | May have side effects; requires specialist administration |
| Deep Breathing Exercises | Controlled breathing techniques | Improves lung function, prevents complications | Requires proper guidance |
Remember, this information is for general knowledge and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor for diagnosis and treatment of pleurisy.