Need to convert prednisone dosages? Use this simple guide for accurate calculations. Remember, always consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice; these conversions are for informational purposes only.
GlobalRPh provides a streamlined approach. We focus on clear, practical data. Our conversion tool allows for quick adjustments between different prednisone formulations, helping you avoid potential errors. Accurate calculations are critical for patient safety.
Example: Converting from methylprednisolone to prednisone? GlobalRPh’s resources offer precise conversion factors. Understanding these ratios ensures you administer the correct equivalent dose, minimizing risks. Specific instructions and examples are available on our website.
Key considerations: Patient-specific factors influence dosage. Age, weight, and underlying health conditions significantly impact response to prednisone. Our resources detail these variables, ensuring safe and accurate conversions. Always prioritize patient safety and individual needs.
- Prednisone Conversion: A GlobalRPh Guide
- Understanding Prednisone’s Dosage Forms
- Other Prednisone Forms
- Converting Prednisone to Methylprednisolone
- Converting Prednisone to Hydrocortisone
- Converting Prednisone to Dexamethasone
- Example Conversions
- Important Considerations
- Calculating Equivalent Doses for Different Prednisone Administrations
- Oral to Intravenous Conversion
- Oral Prednisone to Prednisolone Conversion
- Different Oral Dosing Schedules
- Important Considerations
- Disclaimer:
- Considering Patient-Specific Factors in Conversions
- Age and Body Weight
- Concurrent Medications
- Disease Severity and Response
- Individualized Approach
- Specific Considerations for Certain Populations
- Addressing Potential Side Effects and Monitoring
- Important Considerations for Global Prescribing Practices
- Patient-Specific Factors
- Regulatory Compliance
- Resources for Accurate Prednisone Conversion
- Reliable Online Calculators
- Pharmaceutical Reference Books
Prednisone Conversion: A GlobalRPh Guide
Use this table for quick Prednisone equivalent conversions. Remember to always consult a physician before making any medication changes.
| Medication | Conversion to Prednisone (mg) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Methylprednisolone | 5:1 ratio (e.g., 5mg methylprednisolone = 1mg prednisone) | Adjust based on specific formulation and route of administration. |
| Dexamethasone | 20:1 ratio (e.g., 20mg dexamethasone = 1mg prednisone) | Significant individual variation in response exists. |
| Triamcinolone | 4:1 ratio (e.g., 4mg triamcinolone = 1mg prednisone) | Consider individual patient factors. |
| Hydrocortisone | 4:1 ratio (e.g., 4mg hydrocortisone = 1mg prednisone) | Dosage adjustments often required. |
These are general guidelines. Accurate conversion requires considering factors like individual patient response, duration of treatment, and specific medication formulation. Always check your institution’s formulary and consult appropriate literature.
For complex cases or atypical situations, consult a specialist. These conversions are for educational purposes only and should not substitute professional medical advice.
Understanding Prednisone’s Dosage Forms
Prednisone comes in several forms, each with its own advantages and considerations. Oral tablets are the most common, available in various strengths from 1mg to 50mg. These offer straightforward administration. Liquid formulations, often suspensions, provide flexibility for patients who have difficulty swallowing pills, particularly children. They generally contain a specific amount of prednisone per milliliter. Remember to carefully check the concentration before administering.
Other Prednisone Forms
While less frequent, other delivery methods exist. Intravenous (IV) prednisone is used in severe cases requiring rapid systemic absorption. This route bypasses the digestive system, delivering the medication directly into the bloodstream. Intramuscular (IM) injections offer another option, though less common than oral or IV administration. Finally, some specialized preparations might be available; consult a pharmacist for specifics on less common dosage forms. Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding the correct dosage and administration method for your specific needs.
Converting Prednisone to Methylprednisolone
Generally, use a 5:4 ratio. This means for every 5mg of prednisone, prescribe 4mg of methylprednisolone.
For example, a patient on 20mg of prednisone daily would receive 16mg of methylprednisolone daily (20mg Prednisone x (4mg Methylprednisolone/5mg Prednisone) = 16mg Methylprednisolone).
However, individual patient responses vary. Closely monitor the patient for symptom control and potential side effects. Adjust the dosage as needed based on clinical response. Consider the patient’s specific health conditions and other medications when adjusting the dose.
Remember, this conversion is an approximation. Precise dosage adjustments should be made by a healthcare professional familiar with the patient’s medical history and current condition.
Always consult a physician or pharmacist before making any changes to medication regimens.
Converting Prednisone to Hydrocortisone
To convert Prednisone to Hydrocortisone, use a ratio of 4:5. This means 4 mg of Prednisone is roughly equivalent to 5 mg of Hydrocortisone.
For example, if a patient is taking 20 mg of Prednisone daily, you would calculate the equivalent Hydrocortisone dose as follows: (20 mg Prednisone) x (5 mg Hydrocortisone / 4 mg Prednisone) = 25 mg Hydrocortisone.
Always consult a physician or pharmacist before making any medication changes. This conversion is an approximation; individual patient responses may vary. Precise conversion may require adjustments based on clinical response and patient factors.
Remember, this conversion is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always follow your doctor’s instructions.
Converting Prednisone to Dexamethasone
To convert Prednisone to Dexamethasone, use a ratio of 5:1. This means 5mg of Prednisone is roughly equivalent to 1mg of Dexamethasone.
Example Conversions
- 20mg Prednisone daily converts to 4mg Dexamethasone daily.
- 10mg Prednisone daily converts to 2mg Dexamethasone daily.
- 5mg Prednisone daily converts to 1mg Dexamethasone daily.
Remember, this is an approximate conversion. Individual patient responses vary, and a physician should always supervise this transition.
Important Considerations
- Dosage Form: Ensure you are comparing equivalent dosage forms (e.g., oral tablets to oral tablets).
- Frequency: The conversion applies to the total daily dose. Adjust the frequency (e.g., from twice daily to once daily) according to your doctor’s instructions.
- Patient Factors: Age, liver and kidney function, and other health conditions affect how individuals metabolize these medications. A doctor should adjust the dose based on these factors.
- Tapering: Sudden cessation of either steroid can cause withdrawal symptoms. Always follow a physician-prescribed tapering schedule.
This information is for educational purposes only and should not be interpreted as medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before making any changes to your medication regimen.
Calculating Equivalent Doses for Different Prednisone Administrations
Accurate dose conversion is critical for safe and effective Prednisone therapy. Remember that these are estimates, and individual patient response varies. Always consult a physician or pharmacist for personalized guidance.
Oral to Intravenous Conversion
Direct conversion from oral to intravenous Prednisone isn’t straightforward due to differing bioavailability. Generally, intravenous administration yields a higher plasma concentration. Therefore, a lower IV dose might achieve equivalent effects. A 1:1 ratio is not recommended. Consult reputable clinical guidelines or your local formulary for precise IV-to-oral equivalent dosing ratios.
Oral Prednisone to Prednisolone Conversion
Prednisolone is a metabolite of Prednisone. Approximately 5mg of Prednisolone is equivalent to 5mg of Prednisone. This means a 1:1 ratio is typically used for conversion. However, individual patient factors may influence this equivalence.
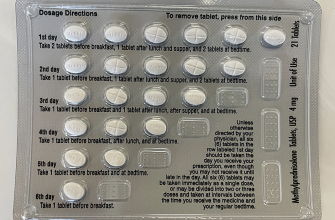
Different Oral Dosing Schedules
- Once-daily dosing: This is the most common schedule. The total daily dose is given in a single administration.
- Twice-daily dosing: The total daily dose is split into two equal doses, given 12 hours apart. This approach might be used to achieve more consistent plasma levels.
- Three-times-daily dosing: Less frequent than the previous two, this option further subdivides the daily dose to improve plasma level consistency. Specific ratios for different schedules are usually determined on a case-by-case basis.
Important Considerations
- Patient-specific factors: Age, weight, liver and kidney function, and concurrent medications significantly impact Prednisone’s pharmacokinetics.
- Disease state: The severity and type of illness influence the required Prednisone dose and the choice of administration route.
- Clinical response: Close monitoring of the patient’s response to treatment is crucial for dose adjustment.
Disclaimer:
This information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of any medical condition.
Considering Patient-Specific Factors in Conversions
Accurately converting prednisone doses requires individual assessment. Begin by reviewing the patient’s medical history, focusing on current health status, other medications, and any pre-existing conditions like liver or kidney disease. These factors significantly influence drug metabolism and clearance.
Age and Body Weight
Adjust dosages based on age and body weight. Elderly patients and those with lower body weight might require lower prednisone equivalent doses to avoid adverse effects. Use appropriate pediatric dosing guidelines for children. Consult recognized conversion charts, but always prioritize clinical judgment.
Concurrent Medications
Certain medications interact with prednisone or its equivalents. CYP3A4 enzyme inhibitors, for instance, can increase prednisone levels, potentially requiring dose reduction. Conversely, inducers might lower levels, necessitating higher doses. Review the patient’s complete medication list carefully for potential interactions.
Disease Severity and Response
The severity of the condition being treated heavily influences the conversion. Patients with severe disease may require higher doses than those with milder presentations. Monitor the patient’s response closely, adjusting the equivalent dosage as needed to achieve the desired therapeutic effect while minimizing side effects. Regular monitoring of blood levels might be necessary for some patients, particularly those with severe illness or altered metabolism.
Individualized Approach
Remember: Conversion charts provide estimations, not precise equivalents. Always tailor the conversion to the individual patient. Closely monitor patients for both therapeutic efficacy and adverse reactions, making adjustments accordingly. A collaborative approach with other healthcare professionals can further enhance accuracy and safety.
Specific Considerations for Certain Populations
Pregnancy and Lactation: Prednisone conversion during pregnancy and lactation demands extra caution due to potential fetal and neonatal effects. Consult specialized resources and guidelines before making any adjustments. Patients with Renal or Hepatic Impairment: Dosage adjustments are crucial in patients with compromised liver or kidney function to prevent drug accumulation and toxicity. Reduce doses and monitor closely for adverse reactions.
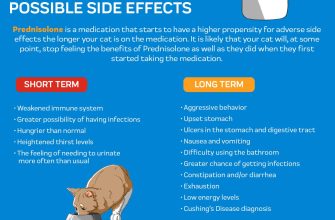
Addressing Potential Side Effects and Monitoring
Regularly monitor your blood pressure and blood glucose levels, especially if you have a history of hypertension or diabetes. Prednisone can affect both.
Report any unusual weight gain, fluid retention (swelling in your ankles or face), or increased thirst to your doctor immediately. These can be signs of serious side effects.
Pay close attention to your mood and mental state. Prednisone can cause mood swings, anxiety, or even depression. Open communication with your doctor is key.
Gastrointestinal issues, such as heartburn, nausea, or stomach upset, are possible. Your doctor might suggest over-the-counter antacids or other remedies. Severe stomach pain requires immediate medical attention.
Understand that bone thinning (osteoporosis) is a potential long-term risk with prolonged Prednisone use. Discuss bone density testing and preventative measures with your physician.
Skin changes, such as thinning skin or easy bruising, are also possible. Protect your skin from sun exposure and report any significant changes.
Children using Prednisone need close monitoring for growth and development. Regular check-ups are vital.
| Side Effect | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Blood Pressure | Elevated readings | Report to doctor; monitor regularly |
| Fluid Retention | Swelling in ankles, face | Report to doctor immediately |
| Mood Changes | Anxiety, depression, irritability | Discuss with doctor; consider support resources |
| Gastrointestinal Issues | Heartburn, nausea, stomach pain | Use antacids; report severe pain |
This information is not exhaustive; always consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized advice and to address any concerns.
Important Considerations for Global Prescribing Practices
Always confirm the specific prednisone dosage forms and strengths available in the target country. Variations exist; a formulation readily available in one region might be unavailable or differently formulated elsewhere. This necessitates careful review of local formularies and medication databases before prescribing.
Account for potential drug interactions with locally prevalent herbal remedies or over-the-counter medications. Many regions utilize traditional medicine alongside conventional treatments; understanding these interactions is critical to safe prescribing.
Patient-Specific Factors
Adapt prescribing practices to consider local socioeconomic factors. Access to healthcare, patient literacy, and affordability significantly impact medication adherence. For example, high costs might necessitate exploring alternative, cost-effective therapies where appropriate.
Recognize differing cultural perspectives on healthcare. Patient preferences and beliefs regarding medication use vary widely. Open communication and cultural sensitivity are paramount in ensuring treatment success.
Regulatory Compliance
Strictly adhere to all local regulatory requirements for prescribing and dispensing prednisone. Licensing, import/export regulations, and record-keeping practices differ globally. Non-compliance can lead to serious legal ramifications.
Continuously update knowledge on local guidelines and best practices for prednisone use. Medical knowledge and regulatory frameworks evolve. Regularly consulting reputable international sources and local health authorities ensures current, accurate information.
Resources for Accurate Prednisone Conversion
Begin with a reputable online calculator specifically designed for medication conversions. Many pharmacy websites offer these tools. Always double-check the results with a qualified healthcare professional.
Reliable Online Calculators
- Search for “prednisone equivalent dose calculator” on a reputable medical website, such as those affiliated with major universities or pharmaceutical companies. Carefully review the calculator’s methodology before using it.
- Ensure the calculator accounts for different prednisone formulations (e.g., tablets, solutions) and the specific glucocorticoid you are converting from or to.
Consult pharmaceutical reference books. These offer detailed conversion tables and explanations of the underlying pharmacology. Some examples include:
Pharmaceutical Reference Books
- The Merck Index
- Remington: The Science and Practice of Pharmacy
- Other reputable compendia available in your local pharmacy or medical library.
Directly consult your doctor or pharmacist. They possess the expertise to handle individual patient needs and potential interactions. They can provide personalized guidance and ensure accuracy.
Remember to always confirm any conversion with your prescribing physician or pharmacist before administering any medication.