Finding the right Prednisone dosage for your asthma requires close collaboration with your doctor. A typical starting dose for adults experiencing an acute asthma exacerbation might range from 30 to 60 milligrams daily, taken orally. This dose often helps quickly reduce inflammation and improve breathing.
However, the specific dosage will depend heavily on the severity of your asthma, your response to treatment, and other health conditions. Your physician will carefully assess your individual needs and adjust the dosage accordingly, possibly tapering it down gradually once your symptoms improve to prevent relapse. Never adjust your Prednisone dosage without consulting your doctor.
Long-term use of Prednisone carries potential side effects, so short courses are usually preferred. Your doctor might prescribe a lower maintenance dose if continuous treatment is necessary, carefully monitoring for side effects and adjusting the medication as needed. This approach balances symptom control with minimizing potential adverse effects.
Remember, this information serves as a general guideline, not medical advice. Always follow your doctor’s instructions and discuss any concerns regarding your Prednisone treatment. Regular check-ups and open communication with your healthcare provider are vital for successful asthma management.
- Prednisone Dosage for Asthma in Adults: A Detailed Guide
- Understanding Prednisone’s Role in Asthma Treatment
- Short-Term Use for Flare-Ups
- Long-Term Use: A Different Approach
- Working with Your Doctor
- Typical Prednisone Dosage for Asthma Exacerbations
- Factors Influencing Prednisone Dosage
- Potential Side Effects and Precautions
- When to Consult a Doctor
- Seek Immediate Medical Attention
- Reasons to Schedule a Doctor’s Appointment
Prednisone Dosage for Asthma in Adults: A Detailed Guide
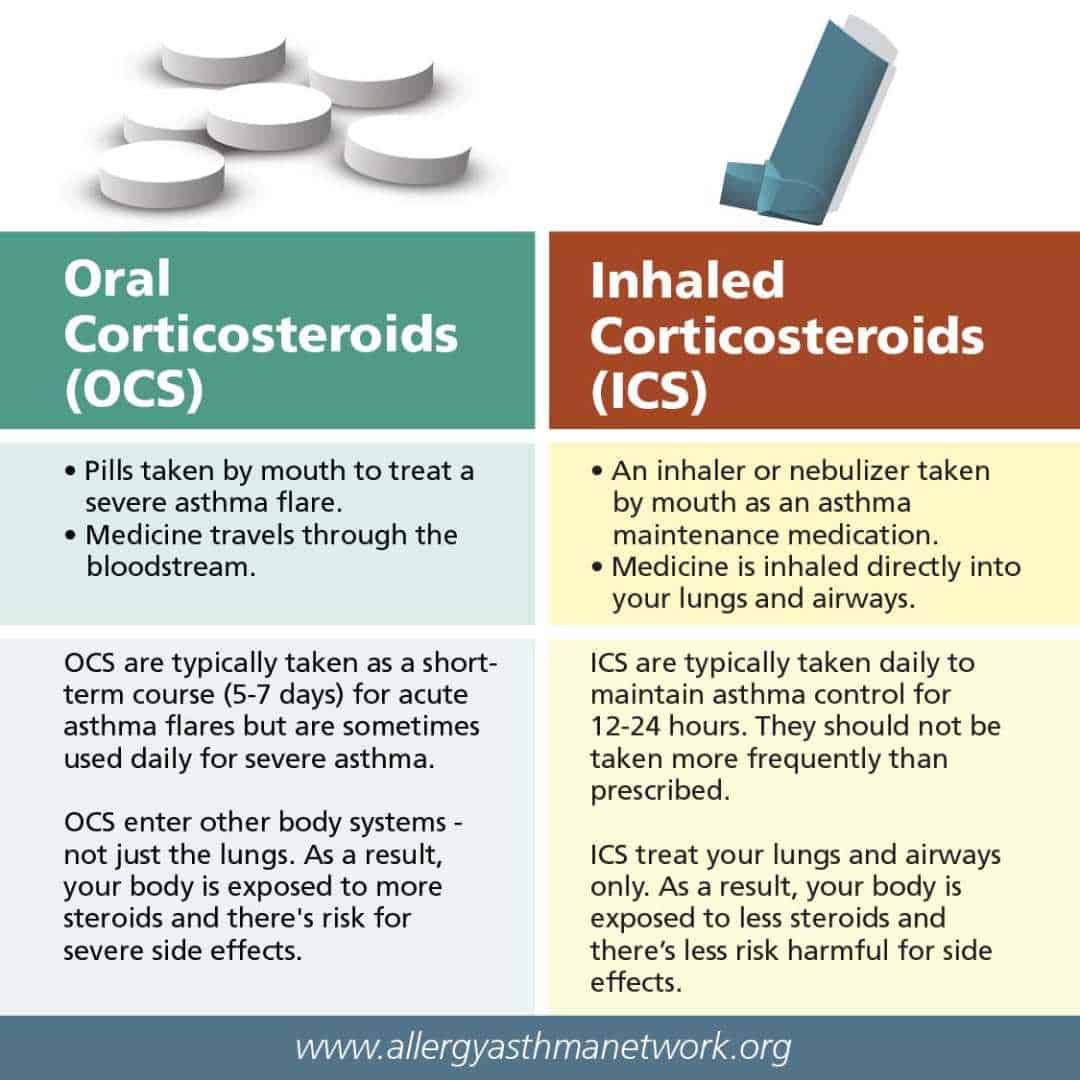
Prednisone’s role in asthma treatment is primarily for managing severe exacerbations. Doctors typically prescribe a short course, usually 5-10 days, to quickly reduce inflammation and improve breathing. The specific dosage depends on the severity of the attack and your individual response. Common starting doses range from 20-60mg daily, taken as a single dose in the morning with food.
Important Note: Always follow your doctor’s instructions exactly. Never adjust your dosage without consulting your physician. Improper use can lead to side effects.
Higher doses (over 60mg) are usually reserved for severe cases. Your doctor will monitor your progress closely and may adjust the dose based on your response to treatment and potential side effects. Gradual tapering of the dose is standard practice upon improvement to minimize withdrawal symptoms.
Potential Side Effects: While Prednisone is effective, it can cause side effects, including weight gain, increased appetite, mood changes, insomnia, and increased blood sugar. Your doctor will discuss these risks and the importance of monitoring for them.
Long-term use of Prednisone isn’t recommended for asthma management due to the risk of significant side effects. It’s crucial to have a long-term asthma management plan focusing on preventative measures like inhalers.
Consult Your Doctor: This information is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always discuss your treatment options with your doctor to develop a personalized plan that best suits your individual needs and health status. They can guide you on the appropriate Prednisone dosage and monitor you for any adverse reactions.
Understanding Prednisone’s Role in Asthma Treatment
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, acts by reducing inflammation in your airways. This helps to relieve asthma symptoms like wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath. It’s a powerful medication, but it’s usually used for short periods to manage severe asthma attacks or exacerbations, not for daily long-term control. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage based on your individual needs and the severity of your asthma.
Short-Term Use for Flare-Ups
During an asthma flare-up, prednisone quickly reduces swelling and inflammation, providing significant symptom relief within a day or two. This allows you to breathe more easily and regain control. Your doctor might prescribe a course of prednisone for several days to a week. The exact duration depends on your response to treatment and your overall health.
Long-Term Use: A Different Approach
Prednisone is not typically recommended for long-term daily use in asthma management due to potential side effects. Long-term use can weaken your bones, increase blood sugar, and impact your immune system. For ongoing asthma control, your doctor will likely recommend inhalers or other maintenance medications.
Working with Your Doctor
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely regarding dosage and duration of prednisone treatment. Open communication with your doctor is crucial; discuss any concerns or side effects you experience. Regular monitoring of your asthma symptoms and lung function is essential for determining the need for prednisone and adjusting your treatment plan.
Typical Prednisone Dosage for Asthma Exacerbations
For adults experiencing an asthma exacerbation, the typical prednisone dose is 40-60 milligrams daily. This is usually given as a single daily dose, although some doctors may split it into two doses. The duration of treatment typically ranges from 5 to 10 days, depending on the severity of the exacerbation and your response to treatment.
Your doctor will closely monitor your condition while you’re on prednisone. They’ll assess your symptoms and lung function to determine if adjustments are needed. Improved symptoms usually appear within 24 to 48 hours.
Lower doses, such as 30 milligrams daily, might suffice for milder exacerbations, while more severe cases could necessitate higher doses, possibly up to 80 milligrams daily, but this is less common and requires careful monitoring. The doctor will carefully tailor the dosage to your individual needs.
Prednisone should always be taken as prescribed. Stopping treatment prematurely could lead to a relapse. You should discuss any concerns or side effects with your physician immediately.
Remember, this information is for general understanding only and does not substitute for personalized medical advice from a doctor. Always consult your healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment of asthma.
Factors Influencing Prednisone Dosage
Your doctor determines your prednisone dosage based on several key factors. Severity of your asthma symptoms plays a crucial role; more severe symptoms generally require higher doses. The frequency and intensity of your asthma attacks directly influence the prescribed amount.
Your overall health also matters. Pre-existing conditions, such as liver or kidney disease, might necessitate lower prednisone doses to minimize potential side effects. Similarly, your age and weight are considered; children and individuals with lower body weights typically receive adjusted dosages.
Your response to treatment is continuously monitored. If your symptoms improve quickly on a lower dose, your doctor may reduce it. Conversely, if your symptoms persist, they might increase the dose. This adjustment process aims to find the lowest effective dose that controls your asthma.
Finally, remember that other medications you take may interact with prednisone. This interaction can affect both the efficacy and potential side effects of prednisone, requiring careful dosage adjustments by your doctor. Always inform your doctor about all medications you are taking.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Never adjust your prednisone dosage without consulting your physician.
This information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Consult your doctor for personalized asthma management.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Prednisone, while effective for asthma, carries potential side effects. These vary depending on dosage and duration of treatment. Higher doses and longer treatment periods increase the risk.
Common side effects include weight gain, increased appetite, mood changes (including irritability and anxiety), difficulty sleeping, and increased blood sugar. You may also experience increased blood pressure, muscle weakness, and thinning of the skin.
Less common, but more serious side effects include:
| Side Effect | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Osteoporosis | Weakening of bones, increasing fracture risk. | Discuss bone density monitoring with your doctor. |
| Cataracts/Glaucoma | Eye problems leading to vision impairment. | Regular eye exams are recommended. |
| Increased risk of infection | Your body’s ability to fight infection may decrease. | Report any signs of infection immediately. |
| Gastrointestinal issues | Such as ulcers, heartburn, and nausea. | Follow doctor’s instructions regarding taking prednisone with food. |
To minimize side effects, your doctor will prescribe the lowest effective dose for the shortest possible duration. They may also recommend gradual tapering of the medication to reduce withdrawal symptoms. Open communication with your doctor about any side effects experienced is crucial for safe and effective management of your asthma.
Before starting prednisone, inform your doctor about all other medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, as interactions can occur. Also, discuss any existing health conditions, particularly diabetes, high blood pressure, osteoporosis, or glaucoma.
When to Consult a Doctor
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience any severe symptoms, such as difficulty breathing or wheezing that doesn’t improve with your usual rescue inhaler, or if your asthma symptoms worsen significantly. This includes chest tightness, rapid heart rate, or a feeling of suffocation.
Seek Immediate Medical Attention
- Severe shortness of breath or difficulty breathing.
- Wheezing that doesn’t respond to your rescue inhaler.
- Chest tightness accompanied by intense anxiety.
- Rapid heart rate (tachycardia).
- Blue discoloration of the lips or fingertips (cyanosis).
- Inability to speak in full sentences due to breathlessness.
Schedule an appointment with your doctor if you notice any of the following:
Reasons to Schedule a Doctor’s Appointment
- Your asthma symptoms are not well controlled despite using your prescribed medications.
- You experience frequent nighttime awakenings due to asthma.
- You require your rescue inhaler more than twice a week.
- You are experiencing side effects from Prednisone, such as increased appetite, weight gain, mood changes, or insomnia.
- You need to increase your Prednisone dosage to manage your asthma symptoms.
- You have any questions or concerns about your asthma treatment plan or Prednisone use.
Regular check-ups with your doctor are vital for monitoring your asthma and adjusting your treatment as needed. Open communication with your doctor ensures the best possible management of your condition.