Prednisone, a corticosteroid, can significantly reduce allergy symptoms. It’s a powerful anti-inflammatory medication, effectively targeting the underlying inflammation driving allergic reactions. However, it’s crucial to understand its use is typically short-term, addressing severe symptoms rather than acting as a long-term allergy management solution.
Doctors often prescribe Prednisone for severe allergic reactions like anaphylaxis or to manage flare-ups of conditions such as allergic asthma or severe hives. This medication works quickly, providing noticeable relief within hours. Expect improvements in swelling, itching, and breathing difficulties. Remember to discuss dosages and treatment duration directly with your physician.
Important Considerations: Prednisone carries potential side effects, including weight gain, increased blood sugar, and mood changes. Long-term use can weaken the immune system. Always follow your doctor’s instructions meticulously, and report any unusual symptoms promptly. This medication should only be used under the guidance of a medical professional. They’ll determine the appropriate dosage and treatment plan based on your specific needs and medical history.
- Prednisone for Allergy Relief: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding Prednisone’s Role in Treating Allergic Reactions
- How Prednisone Works in Allergic Reactions
- Important Considerations
- Dosage and Administration of Prednisone for Allergies
- Adjusting Dosage and Treatment Duration
- Administration Methods
- Potential Side Effects and Precautions When Using Prednisone for Allergies
- Gastrointestinal Issues
- Other Potential Side Effects
- Precautions
- Long-Term Use Considerations
Prednisone for Allergy Relief: A Comprehensive Guide
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, powerfully reduces allergy symptoms. It’s a prescription medication, so always consult your doctor before use.
Prednisone works by suppressing your immune system’s inflammatory response, thus relieving symptoms like:
- Sneezing
- Itchy, watery eyes
- Runny nose
- Itchy skin
- Swelling
- Difficulty breathing (in severe cases)
Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage and duration of treatment based on your specific allergy and its severity. Typical dosages range from 5mg to 60mg daily, usually in divided doses. The treatment course is usually short-term, often a few days to a couple of weeks, to minimize side effects.
Common side effects include:
- Increased appetite and weight gain
- Mood changes
- Insomnia
- Increased blood sugar
- Fluid retention
- High blood pressure
Serious side effects are less frequent but require immediate medical attention. These can include:
- Severe allergic reactions
- Muscle weakness
- Easy bruising or bleeding
- Vision problems
- Signs of infection
To reduce side effects, your doctor might prescribe a tapered dose, gradually decreasing the amount of Prednisone over time. Never stop taking Prednisone suddenly without consulting your physician; this could lead to withdrawal symptoms.
Prednisone isn’t a long-term solution for allergies. Your doctor may recommend it for severe flare-ups or when other treatments aren’t sufficient. Long-term allergy management usually involves preventative measures like allergen avoidance and other medications such as antihistamines or immunotherapy.
Remember, this information is for educational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or allergist to discuss the risks and benefits of Prednisone for your specific allergy situation.
Understanding Prednisone’s Role in Treating Allergic Reactions
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, powerfully reduces inflammation. For allergies, this means it tackles the swelling, redness, and itching associated with allergic responses. It doesn’t directly stop allergens from triggering a reaction; instead, it dampens the body’s inflammatory response to those allergens. Think of it as a volume control for your immune system’s reaction to allergens – turning the inflammation down.
How Prednisone Works in Allergic Reactions
Prednisone achieves this by influencing various immune cells, specifically reducing the release of inflammatory chemicals like histamine. This leads to faster symptom relief compared to many other allergy medications. It’s particularly effective for severe allergic reactions like anaphylaxis or severe asthma exacerbations, where quick reduction of inflammation is critical. Doctors often prescribe prednisone for short-term management of severe allergy symptoms or during acute phases of an allergic condition.
Important Considerations
While very effective, prednisone’s use isn’t without potential side effects. These can include increased appetite, weight gain, mood changes, and increased blood sugar levels. Long-term use carries additional risks; therefore, it’s usually prescribed for short bursts to manage severe flares rather than for ongoing allergy control. Always follow your doctor’s instructions meticulously regarding dosage and duration. Discuss any concerns or side effects with your doctor or pharmacist immediately. Prednisone should not be abruptly stopped, always taper down the dosage as directed by your physician to prevent withdrawal symptoms.
Dosage and Administration of Prednisone for Allergies
Your doctor will determine the correct Prednisone dosage based on your specific allergy symptoms and overall health. Typical starting dosages for allergic reactions range from 20 to 60 milligrams daily, often administered in a single dose. This is usually a short course, lasting only a few days to a week. However, some chronic allergic conditions may require longer treatment periods, potentially weeks or months under close medical supervision.
Adjusting Dosage and Treatment Duration
Prednisone dosages are gradually tapered down, not stopped abruptly, to minimize withdrawal symptoms. Your doctor will provide a detailed tapering schedule, commonly reducing the dose by 5-10 milligrams every few days. Never alter your prescribed dosage or discontinue the medication without consulting your physician. Failing to follow the prescribed tapering schedule can lead to unpleasant side effects.
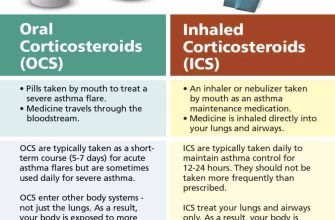
Administration Methods
Prednisone is usually administered orally, as a tablet. Swallow the tablet whole with a full glass of water. Avoid crushing or chewing the tablets. Take the medication at the same time each day, to maintain consistent blood levels. Your doctor will advise you on the best time of day to take your Prednisone, often with food to reduce stomach upset. Remember to store the medication according to the label instructions.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions When Using Prednisone for Allergies
Prednisone, while effective for allergy symptoms, carries potential side effects. Increased appetite and weight gain are common. You might also experience fluid retention, leading to swelling in your face, ankles, or feet. Mood changes, including irritability or anxiety, are possible.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Prednisone can irritate your stomach lining, potentially causing heartburn, nausea, or ulcers. To mitigate this, take it with food. If you experience persistent stomach upset, contact your doctor.
Other Potential Side Effects
Increased blood sugar: Monitor your blood sugar regularly, especially if you have diabetes. Increased blood pressure: Regular monitoring is recommended. Weakened immune system: Be mindful of infection risks; report any signs of illness immediately. Sleep disturbances: Insomnia or difficulty sleeping might occur. Muscle weakness: This is relatively uncommon but should be reported to your physician.
Precautions
Inform your doctor: about all medications you take, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, as interactions can occur. Avoid alcohol: It can exacerbate side effects. Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully: Never abruptly stop taking prednisone; gradually reduce dosage as directed to avoid withdrawal symptoms. Report any unusual symptoms: Promptly seek medical attention if you experience severe side effects.
Long-Term Use Considerations
Long-term prednisone use increases the risk of more serious side effects, including osteoporosis, cataracts, and glaucoma. Your doctor will carefully monitor you and may prescribe additional medication to mitigate these risks. Regular checkups are crucial.