Prednisone, a corticosteroid, frequently plays a supporting role in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) treatment, often in combination with other therapies. It effectively reduces symptoms like fatigue and enlarged lymph nodes. However, remember Prednisone isn’t a standalone CLL cure; it’s a valuable tool within a broader treatment strategy.
Doctors typically prescribe Prednisone in specific CLL situations, such as managing symptomatic disease or as part of a chemoimmunotherapy regimen. For example, it’s commonly used in combination with fludarabine or chlorambucil. Dosage and duration vary considerably based on individual patient needs and response, and will always be determined by a qualified oncologist.
Important Note: Prednisone’s effectiveness depends on several factors, including the patient’s overall health, the stage of their CLL, and the presence of other health conditions. Potential side effects, which can include weight gain, increased blood sugar, and bone thinning, require careful monitoring by medical professionals. Always discuss any concerns or side effects with your doctor. Open communication is key to successful CLL management.
Remember: This information serves only as a general overview and should not replace personalized guidance from your healthcare provider. They will tailor a treatment plan that aligns with your specific circumstances and health status. Consult your physician or oncologist for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options.
- Prednisone for CLL Treatment
- Common Prednisone Regimens
- Potential Side Effects
- Monitoring and Follow-up
- Alternative and Adjunctive Therapies
- Long-Term Implications
- Understanding Prednisone’s Role in CLL Therapy
- Dosage and Administration
- Common Side Effects
- Prednisone in Combination Therapies
- Monitoring Treatment Response
- Specific Considerations
- Long-Term Use and Tapering
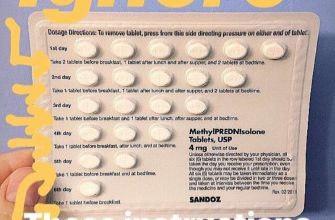
- Prednisone Dosage and Administration in CLL
- Common Side Effects and Management of Prednisone Treatment
- Weight Gain and Fluid Retention
- Increased Blood Sugar
- Mood Changes and Insomnia
- Osteoporosis Risk
- Other Potential Side Effects
- Monitoring and Support
- Long-Term Outlook and Considerations for Prednisone in CLL
- Managing Long-Term Prednisone Use
- Alternative and Combination Therapies
Prednisone for CLL Treatment
Prednisone, a glucocorticoid, often plays a supportive role in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) treatment. It’s frequently used in combination with other therapies, not as a standalone cure.
Common Prednisone Regimens
Dosage and duration vary greatly depending on the patient’s overall health, the stage of their CLL, and the specific treatment plan. Common regimens involve oral administration, often in combination with chemotherapy drugs like fludarabine or chlorambucil. Your doctor will carefully tailor the regimen to your individual needs.
Potential Side Effects
Be aware that Prednisone can cause side effects, including weight gain, increased appetite, fluid retention, high blood sugar, mood swings, and increased risk of infections. These effects are usually manageable with careful monitoring and adjustments to the treatment plan. Open communication with your doctor is key to addressing any concerns you may have.
Monitoring and Follow-up
Regular blood tests are crucial for monitoring your response to treatment and detecting any potential side effects. Your doctor will schedule these tests as needed to ensure your safety and efficacy of treatment. Don’t hesitate to contact them if you experience any unusual symptoms.
Alternative and Adjunctive Therapies
Always discuss alternative therapies with your oncologist. They can advise you on the best course of action, weighing the benefits and risks of various approaches, including potential interactions with Prednisone. Remember, this information is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Consult your physician for personalized guidance.
Long-Term Implications
Prolonged Prednisone use can lead to more pronounced side effects. Your doctor will carefully assess the risks and benefits before prescribing long-term treatment. They will strive to minimize long-term risks while maximizing treatment efficacy.
Understanding Prednisone’s Role in CLL Therapy
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, acts by suppressing the immune system and reducing the number of cancerous B-cells in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL). It’s often used in combination with other therapies, not as a standalone treatment.
Dosage and Administration
Prednisone dosage varies significantly depending on the individual’s health, CLL stage, and response to treatment. Your oncologist will determine the appropriate dose and schedule, typically involving oral administration. Regular blood tests monitor its effects and potential side effects.
Common Side Effects
Be aware that Prednisone can cause side effects like weight gain, increased blood sugar, mood changes, and fluid retention. Less common, but potentially serious, are infections due to immunosuppression. Open communication with your doctor is vital for managing these side effects.
Prednisone in Combination Therapies
Prednisone is frequently combined with other drugs like fludarabine, chlorambucil, or rituximab to enhance therapeutic efficacy. This combined approach aims for a more potent impact on CLL cells, improving remission rates and overall survival.
Monitoring Treatment Response
| Metric | Measurement Method | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Blood cell counts | Complete blood count (CBC) | Tracks changes in white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets. |
| CLL cell count | Peripheral blood smear and flow cytometry | Monitors the reduction of cancerous cells. |
| Overall health | Physical examination and patient reporting | Assesses symptom improvement and overall well-being. |
Specific Considerations
Prednisone use requires careful monitoring due to potential interactions with other medications. Your doctor should be informed about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you take. Furthermore, pre-existing conditions, such as diabetes or heart disease, may influence treatment decisions and require closer observation.
Long-Term Use and Tapering
Prednisone is usually not administered long-term due to its potential for significant side effects. Once remission is achieved or the desired therapeutic outcome is reached, the dosage is gradually reduced (“tapered”) under your doctor’s strict supervision to minimize withdrawal symptoms.
Prednisone Dosage and Administration in CLL
Prednisone dosage in CLL varies greatly depending on factors like the patient’s overall health, disease stage, and response to treatment. Your doctor will personalize your treatment plan.
Commonly, initial dosages range from 40 to 60 milligrams daily, often given in divided doses. This might be adjusted based on your response. Some regimens involve alternating daily dosing schedules.
- Oral Administration: Prednisone is typically administered orally, usually with food, to minimize stomach upset.
- Dosage Adjustments: Your doctor will closely monitor your blood counts and overall health, adjusting the dosage as needed. They may reduce the dosage if side effects become problematic or increase it if the response isn’t sufficient.
- Treatment Duration: The length of treatment varies significantly. It can range from several weeks to months, depending on your specific circumstances and response.
Important Considerations:
- Side Effects: Prednisone can cause numerous side effects, including weight gain, increased appetite, fluid retention, mood changes, and increased risk of infection. Report any concerns to your doctor immediately.
- Monitoring: Regular blood tests are crucial to monitor your blood cell counts and assess the treatment’s efficacy and detect potential complications.
- Drug Interactions: Prednisone can interact with other medications. Always inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking.
- Tapering: When stopping Prednisone, it’s essential to gradually reduce the dosage (taper) under your doctor’s supervision to avoid withdrawal symptoms and adrenal insufficiency.
Remember, this information is for general knowledge only and should not replace advice from your healthcare provider. Always discuss your treatment plan with your doctor to ensure it’s tailored to your individual needs.
Common Side Effects and Management of Prednisone Treatment
Prednisone, while effective in managing CLL, often causes side effects. Managing these is key to a better quality of life during treatment. Let’s address some common issues.
Weight Gain and Fluid Retention
Many patients experience weight gain and fluid retention. This often stems from increased appetite and sodium retention. To mitigate this, focus on a balanced diet lower in sodium and processed foods. Regular exercise, even gentle walking, helps. Discuss these issues with your doctor; they may adjust your medication or suggest diuretics.
Increased Blood Sugar
Prednisone can elevate blood sugar levels, potentially worsening diabetes or causing it in susceptible individuals. Regular blood glucose monitoring is vital. Maintaining a healthy diet, incorporating regular exercise, and adhering to your doctor’s diabetes management plan (if applicable) are crucial. Your doctor might adjust your diabetes medications.
Mood Changes and Insomnia
Prednisone can affect mood, leading to anxiety, irritability, or even depression. Insomnia is also common. Maintaining a regular sleep schedule, practicing relaxation techniques (like meditation or deep breathing), and engaging in regular physical activity can help. If these measures are insufficient, talk to your doctor; they may prescribe medication to address these issues or adjust your prednisone dosage.
Osteoporosis Risk
Long-term prednisone use increases osteoporosis risk. This is because prednisone interferes with calcium absorption. To minimize this risk, ensure adequate calcium and vitamin D intake through diet and supplements (as advised by your doctor). Regular weight-bearing exercise is also beneficial. Your physician might also recommend medications to protect your bones.
Other Potential Side Effects
Other possible side effects include increased risk of infections, thinning skin, easy bruising, and high blood pressure. Report any concerning symptoms to your healthcare provider immediately. Prompt attention can prevent complications. Remember, open communication with your doctor is paramount for effective management of these side effects.
Monitoring and Support
Regular checkups with your doctor are crucial to monitor your progress and address any emerging side effects. Don’t hesitate to seek support from family, friends, or support groups. Managing prednisone’s side effects requires a proactive approach, and the right support system makes all the difference.
Long-Term Outlook and Considerations for Prednisone in CLL
Prednisone offers short-term benefits for many CLL patients, reducing symptoms and improving blood counts. However, long-term use presents challenges. Expect potential side effects like weight gain, increased blood sugar, osteoporosis, and mood changes. These often require careful management with lifestyle adjustments and sometimes additional medications. Regular monitoring of blood pressure and bone density is vital.
Managing Long-Term Prednisone Use
Your doctor will tailor your treatment plan, potentially adjusting dosage or adding other therapies to minimize side effects while maintaining CLL control. Regular communication with your healthcare team is key to address any concerns and proactively manage potential problems. Consider joining a support group for CLL patients; sharing experiences can be invaluable. A healthy diet and regular exercise, approved by your physician, can significantly improve your quality of life and help mitigate some side effects.
Alternative and Combination Therapies
Prednisone is frequently used in combination with other CLL treatments, such as chemotherapy or targeted therapies. These combinations often provide better disease control and minimize the duration and dosage of prednisone, reducing the risk of long-term complications. Discuss all treatment options thoroughly with your doctor to determine the best approach for your individual circumstances and health status. New therapies continually emerge, making it crucial to stay informed about the latest advancements.