Prednisone isn’t typically used to treat ear fluid directly. Instead, it targets the underlying inflammation that might be contributing to the fluid buildup. Your doctor may prescribe it if they suspect an infection or allergic reaction is causing the problem.
Consider this: Prednisone is a corticosteroid, reducing swelling and inflammation. This can help alleviate pressure and discomfort associated with ear fluid, potentially speeding up the natural drainage process. However, it’s not a guaranteed solution and its effectiveness varies depending on the root cause of the fluid.
Important Note: Prednisone carries potential side effects, including increased blood sugar, mood changes, and stomach upset. Always discuss potential risks and benefits with your doctor before taking any medication, especially for ear conditions. They will assess your individual situation and determine if prednisone is the appropriate treatment.
Your doctor might recommend other treatments alongside or instead of Prednisone, such as decongestants, antibiotics (if an infection is present), or even just careful monitoring to allow natural drainage. Following your doctor’s instructions and reporting any concerns is paramount for effective treatment.
- Prednisone for Fluid in Ears: A Detailed Guide
- Understanding Middle Ear Fluid
- Prednisone Dosage and Administration
- Potential Side Effects
- When Prednisone Might Be Prescribed
- Alternatives and Complementary Treatments
- Monitoring Progress
- Disclaimer
- Understanding the Role of Prednisone in Ear Infections
- How Prednisone Helps
- Important Considerations
- Identifying Ear Infections Requiring Prednisone Treatment
- Severe Inflammation and Fluid Buildup
- Lack of Response to Antibiotics
- Severe Allergic Reaction Contributing to Ear Infection
- Chronic or Recurrent Ear Infections
- Dosage and Administration of Prednisone for Ear Fluid
- Oral Administration
- Important Considerations
- Potential Side Effects and Risks of Prednisone Use
- Alternative Treatments for Ear Fluid Buildup
- When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
- Severe Symptoms Requiring Immediate Attention
- Monitoring Progress and Follow-up Care
- Tracking Fluid Levels
- Potential Side Effects to Report
- Medication Adherence and Adjustments
- Alternative Treatments and Expectations
- When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
- Long-Term Outlook
Prednisone for Fluid in Ears: A Detailed Guide
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, can reduce inflammation, potentially helping to drain fluid from the middle ear. However, it’s crucial to understand that Prednisone doesn’t directly remove fluid; it addresses the underlying inflammation that might be contributing to fluid buildup. Your doctor will determine if Prednisone is appropriate based on your specific condition and medical history.
Understanding Middle Ear Fluid
Middle ear fluid, often associated with otitis media (ear infection), can cause hearing loss, pain, and discomfort. While antibiotics often target infection, Prednisone targets inflammation. This is key because inflammation can make it harder for the fluid to drain naturally.
Prednisone Dosage and Administration
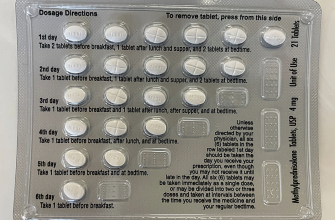
Your doctor will prescribe the correct dosage and duration of Prednisone treatment. Commonly, this involves a short course of oral medication. Strictly adhere to your doctor’s instructions. Never adjust the dosage yourself.
Potential Side Effects
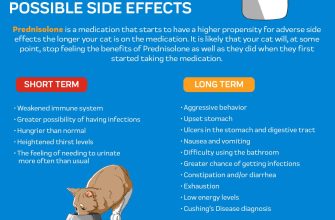
Prednisone, like all medications, carries potential side effects. These can include increased appetite, weight gain, mood changes, and insomnia. Inform your doctor immediately if you experience any concerning side effects.
When Prednisone Might Be Prescribed
| Condition | Prednisone Role |
|---|---|
| Otitis Media with Effusion (OME) | May reduce inflammation, aiding fluid drainage. Often used in conjunction with other treatments. |
| Severe Allergic Reactions Causing Ear Fluid | Can reduce inflammation caused by allergies. |
Alternatives and Complementary Treatments
Other treatments for middle ear fluid include decongestants, nasal corticosteroids, and in some cases, surgical intervention. Your doctor will help you determine the best treatment plan for your individual situation. Discuss all treatment options thoroughly.
Monitoring Progress
Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor your progress and adjust treatment if necessary. Your doctor will likely perform ear examinations and hearing tests to assess the effectiveness of the Prednisone and overall treatment strategy.
Disclaimer
This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting any new medication or treatment.
Understanding the Role of Prednisone in Ear Infections
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, doesn’t directly kill bacteria or viruses causing ear infections. Instead, it reduces inflammation and swelling. This can alleviate pain and pressure associated with middle ear infections (otitis media) or other ear conditions involving fluid buildup. Doctors may prescribe it alongside antibiotics, especially when severe inflammation is present.
How Prednisone Helps
The anti-inflammatory properties of prednisone target the swelling within the middle ear. This helps to drain fluid more effectively, thus speeding up recovery. It’s important to understand that prednisone doesn’t treat the underlying infection itself; it manages the symptoms.
Important Considerations
Prednisone use should always be guided by a physician. It’s not suitable for all ear infections and carries potential side effects, including increased blood sugar, stomach upset, and weakened immunity. Your doctor will assess your condition and determine if prednisone is the right treatment option for you. Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and duration of treatment. Never self-medicate.
Identifying Ear Infections Requiring Prednisone Treatment
Prednisone isn’t a first-line treatment for all ear infections. Doctors typically prescribe it for specific situations. Look for these key indicators:
Severe Inflammation and Fluid Buildup
Significant swelling and substantial fluid collection behind the eardrum (otitis media with effusion) often warrant prednisone. This is especially true if the fluid is impacting hearing or causing significant discomfort. Your doctor will assess the severity through examination and potentially audiometry.
Lack of Response to Antibiotics
If a bacterial infection isn’t responding adequately to antibiotics, prednisone may be added to reduce inflammation and improve the effectiveness of the antibiotics. This combined approach tackles both the infection and the inflammatory response.
Severe Allergic Reaction Contributing to Ear Infection
Prednisone’s anti-inflammatory properties can help manage ear infections stemming from severe allergic reactions. If allergies are suspected as a primary cause of the fluid buildup or infection, your doctor may include prednisone in the treatment plan.
Chronic or Recurrent Ear Infections
For individuals experiencing frequent or persistent ear infections, prednisone can help control inflammation and prevent further episodes, although it’s not a long-term solution. Your doctor will discuss the overall management strategy.
Remember, a doctor’s diagnosis is crucial. These indicators suggest the *potential* need for prednisone, but a professional evaluation is necessary to determine the appropriate course of treatment.
Dosage and Administration of Prednisone for Ear Fluid
Prednisone dosage for ear fluid depends entirely on your individual circumstances, including age, overall health, and the severity of your condition. A doctor will determine the appropriate dose and duration. Typical adult dosages range from 20 to 60 milligrams daily, often divided into multiple doses. Children receive much lower doses, calculated based on their weight and age. Your doctor might prescribe a higher dose initially, then gradually reduce it over several weeks.
Oral Administration
Prednisone is usually taken orally, as a tablet or liquid. Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully regarding the timing of your doses. Taking the medication with food can minimize stomach upset. Never alter your prescribed dosage or discontinue the medication without consulting your doctor, even if you feel better. Sudden cessation can lead to withdrawal symptoms.
Important Considerations
Prednisone can cause side effects, including increased appetite, weight gain, mood changes, and sleep disturbances. Inform your doctor about any side effects you experience. Regular blood tests may be needed to monitor your response to the medication and assess potential side effects. Always carry your medication information and inform other healthcare providers about your Prednisone use.
Potential Side Effects and Risks of Prednisone Use
Prednisone, while effective for some ear conditions, carries potential side effects. These vary depending on dosage and duration of treatment. Common side effects include increased appetite and weight gain, mood swings, insomnia, and increased blood sugar.
More serious, though less common, side effects can include increased risk of infection, weakened bones (osteoporosis), high blood pressure, and stomach ulcers. Rarely, prednisone can cause cataracts or glaucoma.
Individuals with diabetes, high blood pressure, osteoporosis, or a history of ulcers should discuss these risks with their doctor before starting prednisone. Regular monitoring of blood pressure and blood sugar levels may be necessary during treatment.
Sudden discontinuation of prednisone can cause withdrawal symptoms. Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding tapering off the medication to minimize this risk. Report any concerning side effects to your physician immediately. They can adjust your dosage or prescribe alternative treatment if needed.
Remember, this information is for general knowledge and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor before starting any medication, including prednisone, to assess the risks and benefits for your specific situation.
Alternative Treatments for Ear Fluid Buildup
Consider saline nasal sprays. These help clear nasal passages, often improving Eustachian tube function and drainage. Use as directed on the product label.
Try over-the-counter decongestants. Pseudoephedrine or phenylephrine can temporarily reduce swelling, potentially improving drainage. Always follow dosage instructions and consult a doctor if you have underlying health conditions.
Explore natural remedies. Some people find relief with warm compresses applied gently to the affected ear. Others report improvement with nasal irrigation using a neti pot (always use distilled or sterile water).
- Note: Natural remedies are not a replacement for medical advice. Consult your doctor before using them, especially if you have pre-existing conditions.
Consider allergy management. Allergies are a common cause of ear fluid. Identify and manage your allergies through medication, immunotherapy, or environmental changes.
- Identify and avoid allergens.
- Use allergy medications as prescribed by your doctor.
- Consider allergy testing and immunotherapy if appropriate.
Seek medical attention if symptoms persist. If ear fluid persists for several weeks or is accompanied by pain, fever, or hearing loss, see an ENT specialist. They may recommend other treatments such as myringotomy (a procedure to drain fluid from the middle ear).
Maintain good hygiene practices. Regular handwashing prevents infections that can contribute to ear fluid build-up.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Contact your doctor or go to the emergency room immediately if you experience sudden hearing loss, severe ear pain, dizziness, or facial weakness alongside fluid in your ears. These symptoms could indicate a serious underlying condition requiring urgent medical care.
Severe Symptoms Requiring Immediate Attention
Seek immediate medical attention if you develop a high fever (over 101°F or 38.3°C) accompanied by ear fluid, or if you notice any signs of infection, such as pus draining from your ear. Severe dizziness that impairs your balance or coordination also warrants immediate medical evaluation. If you experience any neurological symptoms such as numbness, tingling, or weakness in your face, arms, or legs, get help immediately.
Remember: While prednisone may help manage fluid in the ears, it doesn’t address the underlying cause. Prompt medical intervention is crucial for addressing serious complications.
Monitoring Progress and Follow-up Care
Schedule a follow-up appointment with your doctor within one to two weeks of starting Prednisone to assess your ear fluid reduction. This allows for timely adjustments to your treatment plan if needed.
Tracking Fluid Levels
Your doctor will likely use an otoscope to visually check your ear canals for fluid. They might also perform a hearing test to assess your hearing improvement. Keep a personal record of your symptoms, including pain levels (on a scale of 1-10), and any changes in hearing or fullness in your ears. This aids your doctor in evaluating treatment success.
Potential Side Effects to Report
- Increased thirst or urination
- Weight gain
- Mood changes, including irritability or anxiety
- Increased appetite
- Difficulty sleeping
Report any of these to your doctor immediately. They may be able to adjust your medication or suggest strategies for managing these side effects.
Medication Adherence and Adjustments
Take Prednisone exactly as prescribed. Do not stop taking it abruptly without consulting your doctor. Gradual tapering of the dosage is typically necessary to minimize withdrawal symptoms. Your doctor will provide guidance on this process.
Alternative Treatments and Expectations
Prednisone aids in reducing ear fluid, but it is not a guaranteed cure. Your doctor might discuss additional therapies, like decongestants or ear drops, to complement the Prednisone treatment. Recovery time varies; be patient and communicate openly with your doctor about your progress and any concerns.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
- Sudden worsening of hearing loss
- Severe ear pain
- Signs of infection (e.g., increased pus or drainage)
- Facial paralysis
These symptoms require immediate medical attention and may indicate a more serious condition.
Long-Term Outlook
With proper management, most individuals experience a resolution of ear fluid. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor progress and ensure optimal treatment. Discuss your long-term health goals with your doctor.