Need fast answers about Prednisone? This steroid medication powerfully reduces inflammation, but understanding its effects is key. We’ll cover common uses, potential side effects, and crucial safety information. Remember, this isn’t a substitute for professional medical advice; always consult your doctor before starting any medication.
Prednisone treats various conditions, including allergies, autoimmune diseases like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, and certain cancers. It works by suppressing the immune system, diminishing inflammation. This reduces symptoms like swelling, pain, and skin irritation. However, this immune suppression creates risks, making careful monitoring necessary.
Side effects vary depending on dosage and treatment duration. Common ones include weight gain, mood changes, increased appetite, and difficulty sleeping. More serious side effects, such as increased blood sugar, high blood pressure, and weakened bones, require immediate medical attention. Your doctor will adjust your dosage and closely monitor you for any adverse reactions.
Important considerations: Dosage is strictly individualized. Never adjust your Prednisone dosage without consulting your physician. Abruptly stopping the medication can lead to serious withdrawal symptoms. Always inform your doctor about other medications you’re taking, as interactions can occur. Open communication with your healthcare provider ensures safe and effective treatment.
- Prednisone for Humans: A Detailed Guide
- Understanding Prednisone
- Potential Side Effects
- Managing Prednisone Treatment
- Drug Interactions
- When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
- What is Prednisone and How Does it Work?
- How Prednisone Reduces Inflammation
- How Prednisone Suppresses the Immune System
- Types of Conditions Prednisone Treats
- Common Uses and Conditions Treated with Prednisone
- Potential Side Effects and Risks of Prednisone Use
- Common Side Effects
- Serious Side Effects: Seek Immediate Medical Attention
- Prednisone Dosage, Administration, and Important Considerations
Prednisone for Humans: A Detailed Guide
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Prednisone dosage and duration depend entirely on your individual condition and response to treatment. Never adjust your dosage without consulting your physician.
Understanding Prednisone
Prednisone is a corticosteroid, a powerful anti-inflammatory drug. It reduces swelling, redness, and itching. It’s used to treat various conditions, including:
- Autoimmune diseases (like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus)
- Allergic reactions
- Asthma
- Certain cancers
- Inflammation
It works by suppressing the immune system.
Potential Side Effects
Prednisone can cause side effects, their severity varies depending on dosage and duration of use. Common side effects include:
- Weight gain
- Increased appetite
- Mood changes (irritability, anxiety, depression)
- Insomnia
- High blood sugar
- Increased risk of infection
Less common, but serious, side effects can occur. These require immediate medical attention.
- Severe allergic reactions
- Muscle weakness
- Fluid retention
- Osteoporosis
- Cataracts
- Glaucoma
Regular check-ups with your doctor are crucial to monitor your health and manage potential side effects.
Managing Prednisone Treatment
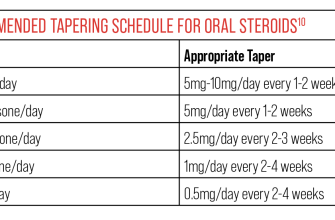
To minimize side effects, your doctor may prescribe the lowest effective dose for the shortest possible time. Gradual tapering off the medication, as directed, is essential to prevent withdrawal symptoms. Maintain a healthy diet and exercise routine. Report any new or worsening symptoms to your doctor promptly.
Drug Interactions
Prednisone interacts with many medications. Always inform your doctor and pharmacist of all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, you’re currently taking. This prevents potential dangerous interactions.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
- Difficulty breathing
- Severe swelling
- Chest pain
- Sudden weight gain
- Severe abdominal pain
This information is for general knowledge and should not replace professional medical advice. Consult your doctor for any health concerns.
What is Prednisone and How Does it Work?
Prednisone is a corticosteroid medication, a synthetic version of a hormone your body naturally produces. It powerfully reduces inflammation and suppresses your immune system.
How Prednisone Reduces Inflammation
Prednisone works by binding to specific receptors inside your cells. This binding triggers a cascade of events that ultimately lessen inflammation. It affects various processes involved in the inflammatory response, reducing swelling, redness, and pain.
How Prednisone Suppresses the Immune System
By interfering with immune cell activity, Prednisone dampens the immune response. This is helpful in treating autoimmune disorders where your immune system mistakenly attacks your own body. However, this immune suppression makes you more susceptible to infections.
Important Note: Prednisone is a powerful drug with potential side effects. Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. Never stop taking Prednisone abruptly without consulting your physician.
Types of Conditions Prednisone Treats
Prednisone treats a wide range of conditions, including allergic reactions, autoimmune diseases like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, and certain cancers. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage and duration of treatment based on your specific needs.
Common Uses and Conditions Treated with Prednisone
Prednisone effectively treats various inflammatory and autoimmune conditions. Doctors frequently prescribe it for allergies, asthma, and autoimmune diseases like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis.
It also helps manage symptoms of certain cancers and blood disorders. For example, Prednisone can reduce swelling and inflammation associated with leukemia or lymphoma.
Beyond these, Prednisone finds application in treating:
| Condition | How Prednisone Helps |
|---|---|
| Severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis) | Reduces inflammation and swelling. |
| Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) | Decreases inflammation in the digestive tract. |
| Multiple sclerosis (MS) | Manages relapses by reducing inflammation in the nervous system. |
| Skin conditions (e.g., eczema, psoriasis) | Reduces skin inflammation and itching. |
| Eye inflammation (uveitis) | Reduces swelling and inflammation in the eye. |
Remember, Prednisone is a powerful medication with potential side effects. Always consult a doctor before using it, and follow their instructions carefully.
Potential Side Effects and Risks of Prednisone Use
Prednisone, while highly effective, carries potential side effects. These vary depending on dosage and duration of treatment. Higher doses and longer treatment periods increase the risk.
Common Side Effects
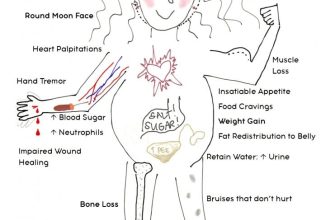
Expect some common side effects like weight gain, especially in the face and abdomen (moon face, buffalo hump), increased appetite, fluid retention (swelling), and mood changes, including irritability and insomnia. You might also experience increased blood sugar, impacting diabetics more significantly. Some individuals experience acne or increased bruising.
Serious Side Effects: Seek Immediate Medical Attention
While less frequent, serious side effects necessitate immediate medical attention. These include severe allergic reactions (difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips, or tongue), high blood pressure, vision problems, muscle weakness, and increased risk of infections. Bone loss (osteoporosis) is a long-term concern, particularly with prolonged use. Prednisone can also suppress the immune system, making you more susceptible to infections.
Your doctor will carefully weigh the benefits against these potential risks. Open communication with your physician is crucial for managing these risks and tailoring your treatment plan effectively. Regular monitoring of blood pressure, blood sugar, and bone density may be recommended.
Prednisone Dosage, Administration, and Important Considerations
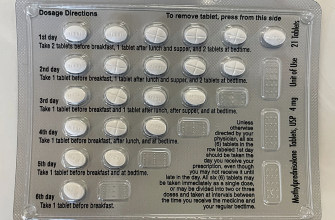
Your doctor determines the correct Prednisone dosage based on your specific condition and health. Typical starting doses range from 5 to 60 milligrams daily, adjusted according to your response. The medication comes in various forms: tablets, liquid, and injectable solutions. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely regarding the amount and frequency of intake.
Oral Prednisone tablets should be swallowed whole with water, preferably with food to minimize stomach upset. Liquid Prednisone should be measured accurately using a marked measuring device, not a household spoon. Injectable Prednisone is administered by a healthcare professional.
Never adjust your dosage without consulting your physician. Sudden changes can have serious consequences. Your doctor will likely recommend a gradual tapering schedule when it’s time to stop Prednisone to avoid withdrawal symptoms, such as fatigue and joint pain.
Monitoring is critical. Your doctor will schedule regular checkups to monitor your blood pressure, blood sugar, and other vital signs, as Prednisone can affect these measurements. Report any side effects immediately, such as mood swings, weight gain, increased thirst, or blurred vision.
Interactions are possible. Inform your doctor of all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking, as Prednisone can interact with other drugs. Some medications may increase the risk of side effects or reduce Prednisone’s efficacy.
Specific conditions require specific attention. Dosage and treatment plans vary based on conditions like asthma, lupus, or rheumatoid arthritis. Your doctor tailors the treatment to your unique situation.
Long-term use carries risks. Prolonged Prednisone use increases the chance of developing cataracts, osteoporosis, and increased susceptibility to infections. Your doctor will weigh the benefits against potential long-term risks.
This information is for general knowledge and should not substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized guidance regarding Prednisone usage.