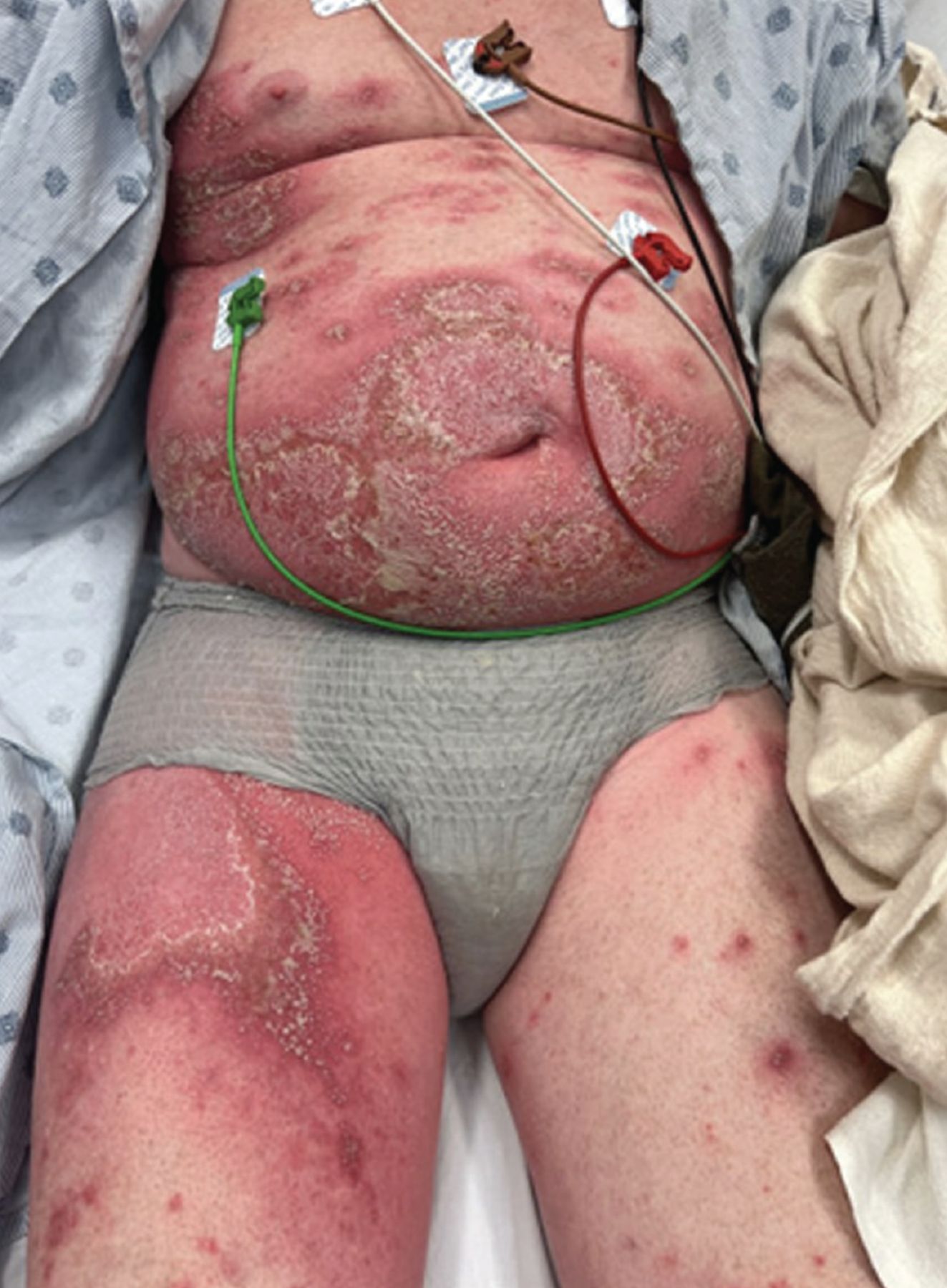
Prednisone can significantly reduce psoriasis symptoms, offering fast relief during a flare-up. However, it’s a powerful medication, and understanding its proper use is key. Always consult your dermatologist before starting any new treatment, including Prednisone.
Expect noticeable improvement within days, often seeing a reduction in redness, inflammation, and scaling. Typical dosages range from 20-60mg daily, adjusted based on your specific needs and response. Your doctor will determine the optimal dose and duration of treatment.
Remember, Prednisone isn’t a long-term solution. Prolonged use carries side effects such as weight gain, mood changes, and increased risk of infection. Your dermatologist will likely work with you on a tapering schedule to minimize withdrawal effects once your symptoms improve. They will also help you develop a maintenance plan focusing on long-term psoriasis management.
Key takeaway: Prednisone provides rapid relief, but it requires medical supervision. Discuss potential side effects and alternative treatments with your doctor to ensure you are making the best choice for your health.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment.
- Prednisone for Psoriasis Outbreak: A Detailed Guide
- Understanding Prednisone’s Role
- Potential Side Effects and Precautions
- Alternative and Complementary Treatments
- Understanding Prednisone’s Role in Psoriasis Treatment
- When to Consider Prednisone for a Psoriasis Flare
- Severe Symptoms Warranting Prednisone
- When Prednisone Might Not Be The Best Option
- Potential Side Effects and Risks of Prednisone Use
- Common Side Effects
- Less Common, but Serious Side Effects
- Managing Side Effects
- Alternative Treatments and Complementary Approaches
- Long-Term Management and Tapering Off Prednisone
- Monitoring for Withdrawal Symptoms
- Alternative Therapies
- Maintaining Healthy Habits
- Regular Follow-Ups
- Remember:
Prednisone for Psoriasis Outbreak: A Detailed Guide
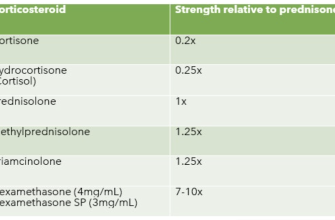
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, effectively reduces psoriasis inflammation, offering quick relief during flare-ups. However, it’s crucial to understand its limitations and potential side effects.
Understanding Prednisone’s Role
Prednisone works by suppressing the immune system, thus reducing the inflammation causing your psoriasis symptoms. It’s typically prescribed for severe outbreaks or when other treatments prove insufficient. Expect noticeable improvement within days, but remember it’s a short-term solution. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage and duration, generally avoiding long-term use due to potential side effects.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Common side effects include weight gain, mood changes, increased blood sugar, and insomnia. More serious, though rare, side effects include osteoporosis and increased risk of infection. Open communication with your doctor regarding any concerning symptoms is paramount. Prednisone can interact with other medications; inform your doctor of all your current prescriptions and supplements. Gradual tapering off the medication, as directed by your physician, is necessary to prevent withdrawal symptoms.
Alternative and Complementary Treatments
While Prednisone provides rapid relief, it’s not a permanent solution. Consider combining Prednisone treatment with other long-term psoriasis management strategies, such as topical treatments (creams, ointments), phototherapy (light therapy), or biologics (injectable or infusion medications). Lifestyle adjustments, including stress management and diet modifications, can also significantly improve psoriasis symptoms. Discuss a comprehensive treatment plan with your dermatologist to find what works best for you.
Understanding Prednisone’s Role in Psoriasis Treatment
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, doesn’t cure psoriasis, but it effectively reduces inflammation and helps manage severe outbreaks. It works by suppressing the immune system, lessening the skin’s inflammatory response responsible for the characteristic plaques and scaling.
Doctors typically prescribe Prednisone for short-term use during severe flares, aiming for rapid symptom relief. Long-term use carries risks, including side effects like weight gain, mood changes, and increased blood sugar.
Your dermatologist will determine the appropriate dosage and duration, carefully balancing benefits and potential risks. They’ll likely monitor you closely for side effects and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
| Prednisone’s Impact | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Reduces inflammation and itching | Short-term use is preferred; gradual tapering is crucial. |
| Flattens psoriasis plaques | Regular blood pressure and glucose monitoring may be required. |
| Provides rapid symptom relief | Potential for side effects such as increased risk of infection. |
Prednisone is often combined with other psoriasis treatments, such as topical corticosteroids or biologics, to enhance efficacy and minimize the need for high Prednisone doses. Your doctor will create a personalized treatment plan specific to your needs and condition.
Remember to always discuss any concerns or questions with your dermatologist. They can help you understand the potential benefits and drawbacks of Prednisone and develop a safe and effective psoriasis management strategy.
When to Consider Prednisone for a Psoriasis Flare
Prednisone is a powerful steroid, often used to quickly reduce inflammation during severe psoriasis outbreaks. Consider it when your symptoms significantly impact your quality of life. This means widespread, intensely itchy, painful plaques that disrupt sleep, work, or daily activities.
Severe Symptoms Warranting Prednisone
Think Prednisone if: your psoriasis covers a large area of your body (over 10% of your skin surface), you experience severe itching causing sleep disturbance or significant discomfort, your plaques are thick, painful, or weeping, or you’ve experienced limited success with other treatments. A recent worsening of symptoms after a period of remission is also a strong consideration.
When Prednisone Might Not Be The Best Option
However, Prednisone isn’t a long-term solution. It carries potential side effects like weight gain, increased blood sugar, and mood changes. If your psoriasis is mild to moderate, topical treatments, light therapy, or biologics might be preferable. Always discuss your options with a dermatologist to determine the best course of action for your specific situation. They will assess the severity of your symptoms, your overall health, and your medical history to make informed recommendations.
Potential Side Effects and Risks of Prednisone Use
Prednisone, while effective for psoriasis flares, carries potential side effects. Understanding these risks helps you make informed decisions with your doctor.
Common Side Effects
- Weight gain: Prednisone can increase appetite and cause fluid retention.
- Mood changes: Irritability, anxiety, and insomnia are possible.
- Increased blood sugar: This is particularly concerning for individuals with diabetes.
- High blood pressure: Regular monitoring is necessary.
- Increased risk of infection: Your immune system might be suppressed.
- Muscle weakness: This can range from mild discomfort to significant weakness.
- Stomach upset: Nausea, heartburn, and ulcers are potential complications.
Less Common, but Serious Side Effects
- Osteoporosis: Long-term use can weaken bones, increasing fracture risk. Calcium and Vitamin D supplementation might be recommended.
- Cataracts and glaucoma: Eye exams are important during and after treatment.
- Skin thinning: This can make skin more susceptible to bruising and injury.
- Slowed wound healing: This is another consequence of immune suppression.
- Fluid retention (edema): Swelling in the legs and ankles is possible.
The severity of side effects varies depending on dosage and duration of treatment. Always discuss potential risks and benefits with your doctor before starting prednisone. They will help you weigh the advantages against potential drawbacks and create a safe and effective treatment plan. Regular check-ups during treatment are crucial for early detection and management of any side effects.
Managing Side Effects
Your doctor can help minimize side effects by adjusting dosage, prescribing additional medications, or suggesting lifestyle changes. Open communication is key to a successful treatment experience.
Alternative Treatments and Complementary Approaches
Consider incorporating these strategies alongside, or sometimes instead of, prednisone for psoriasis management:
- Topical Treatments: Explore options like calcipotriene (vitamin D analog) or coal tar ointments. These directly target skin cells involved in psoriasis. Always follow your dermatologist’s instructions for application.
- Phototherapy (Light Therapy): UVB and narrowband UVB light therapy can significantly reduce inflammation and skin scaling. Your doctor can determine the appropriate dosage and frequency.
- Biologics: These targeted medications, administered via injection or infusion, help control the immune system’s role in psoriasis. Discuss this option with your dermatologist; they’re powerful but have potential side effects.
- Lifestyle Changes: Managing stress levels through techniques like meditation or yoga can be beneficial, as stress often exacerbates psoriasis. Maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise may also improve your skin’s condition.
Further exploration into complementary therapies can be valuable:
- Acupuncture: Some studies suggest acupuncture may help reduce pain and inflammation associated with psoriasis.
- Dietary Adjustments: While not a cure, eliminating potential food triggers like dairy or gluten, and focusing on anti-inflammatory foods like omega-3 fatty acids, may lessen symptoms for some individuals.
Remember to discuss any alternative or complementary treatments with your dermatologist or healthcare provider before starting them. They can help you determine the best course of action, ensuring it complements your overall treatment plan and doesn’t interfere with your prednisone use or other medications.
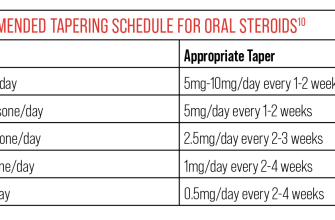
Long-Term Management and Tapering Off Prednisone
Prednisone provides quick psoriasis relief, but long-term use carries risks. Your doctor will create a tapering schedule to gradually reduce your dosage, minimizing withdrawal symptoms. This typically involves decreasing the dose by a small amount at regular intervals, for example, 5mg every few days or a week.
Monitoring for Withdrawal Symptoms
Watch for signs of relapse, like increased itching or skin inflammation. Also, monitor for potential side effects of prednisone withdrawal, such as fatigue, muscle aches, and joint pain. Report any concerning symptoms to your dermatologist immediately. They may adjust the tapering schedule accordingly.
Alternative Therapies
Prednisone isn’t a long-term solution for psoriasis. Your doctor might recommend alternative treatments alongside or after prednisone to maintain remission. These include topical corticosteroids, phototherapy, biologics, or other systemic medications. Discuss a personalized management plan with your doctor, taking into account your psoriasis severity, medical history, and preferences.
Maintaining Healthy Habits
Lifestyle factors play a crucial role in psoriasis management. Prioritize stress management techniques like regular exercise, meditation, or yoga. Maintain a balanced diet and avoid known triggers, such as alcohol or certain foods. Adequate hydration is also key for overall health and skin health. Consistent skincare routines, using gentle, fragrance-free cleansers and moisturizers are important for managing symptoms.
Regular Follow-Ups
Schedule regular check-ups with your dermatologist to monitor your psoriasis, assess the effectiveness of your treatment plan, and make necessary adjustments. Open communication with your doctor is paramount for successful long-term management. They will provide guidance and support throughout this process.
Remember:
Always follow your doctor’s instructions for tapering off prednisone. Never stop taking it abruptly.