Yes, prednisone can significantly reduce seasonal allergy symptoms. It’s a potent corticosteroid that quickly tackles inflammation, offering relief from sneezing, congestion, and itchy eyes. However, it’s not a first-line treatment; consider it a powerful tool for managing severe symptoms that don’t respond to other therapies.
Your doctor might prescribe a short course of prednisone, typically for a week or less, to curb a severe allergy flare-up. This approach minimizes potential side effects. Remember, prolonged use carries risks, including increased blood sugar and weakened immunity. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely regarding dosage and duration.
Before starting prednisone, discuss potential interactions with other medications you’re taking. Certain drugs can interact negatively. Also, mention any existing health conditions, particularly diabetes, high blood pressure, or osteoporosis, as prednisone can exacerbate these issues. Your physician will help you weigh the benefits against the risks, ensuring safe and effective allergy management.
Important Note: Prednisone is a prescription medication. Never self-medicate. Always consult your doctor or allergist before using prednisone for allergies or any other health concern. They will create a personalized treatment plan considering your specific needs and medical history. They can guide you towards the safest and most effective approach for your situation.
- Prednisone for Seasonal Allergies: A Detailed Guide
- Understanding Prednisone’s Role
- Potential Side Effects
- Dosage and Administration
- Comparison with Other Allergy Medications
- When to Consult a Doctor
- Alternative Treatments
- Understanding Prednisone’s Role in Allergy Relief
- How Prednisone Works
- Important Considerations
- When is Prednisone Necessary for Seasonal Allergies?
- Severe Symptoms Requiring Prednisone
- When to Consult a Doctor
- Potential Side Effects and Risks of Prednisone Use
- Gastrointestinal Issues
- Long-Term Risks
- Using Prednisone Safely and Effectively: Dosage and Administration
- Alternatives to Prednisone for Seasonal Allergies
- Nasal Corticosteroids
- Other Options
- Lifestyle Changes
Prednisone for Seasonal Allergies: A Detailed Guide
Prednisone effectively reduces allergy symptoms by suppressing your immune system’s inflammatory response. However, it’s a steroid, so understand its limitations and potential side effects before use.
Understanding Prednisone’s Role
Prednisone offers rapid relief from severe allergy symptoms like nasal congestion, sneezing, and itchy eyes. It’s typically a short-term solution for allergy flares, not a long-term management strategy. Your doctor will prescribe a specific dosage and duration based on your needs.
Potential Side Effects
Common side effects include increased appetite, weight gain, mood changes, insomnia, and stomach upset. Less frequent, but more serious side effects, include increased blood sugar, high blood pressure, and weakened immunity. Report any concerning symptoms to your doctor immediately.
Dosage and Administration
Follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Prednisone dosages vary greatly depending on the severity of your allergies and your individual health. Never adjust your dosage without consulting your doctor. They’ll advise you on the optimal course of treatment, including tapering off the medication to minimize withdrawal symptoms.
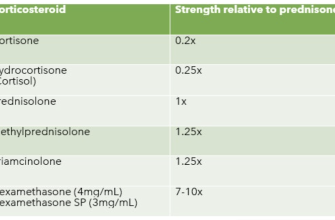
Comparison with Other Allergy Medications
| Medication Type | Onset of Action | Duration of Effect | Common Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prednisone | Rapid (hours) | Short-term (days to weeks) | Increased appetite, weight gain, mood changes |
| Antihistamines | Moderate (30-60 minutes) | Long-term (daily use) | Drowsiness, dry mouth |
| Decongestants | Fast (minutes) | Short-term (hours) | Increased heart rate, nervousness |
When to Consult a Doctor
Contact your doctor if your allergy symptoms don’t improve with Prednisone or if you experience any significant side effects. They can assess your situation and adjust your treatment plan accordingly. Remember, self-treating can be risky.
Alternative Treatments
Explore non-medication approaches such as allergy shots (immunotherapy) or nasal saline sprays to manage your seasonal allergies long-term. Your doctor can help you find the best treatment plan for you, considering your specific needs and health history.
Understanding Prednisone’s Role in Allergy Relief
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, powerfully reduces allergy symptoms by suppressing the body’s inflammatory response. This means it tackles the underlying cause of your discomfort, not just the symptoms themselves.
How Prednisone Works
Prednisone diminishes the production of inflammatory chemicals like histamines, responsible for runny noses, itchy eyes, and congestion. It also constricts blood vessels, reducing swelling in nasal passages and airways. This leads to quicker symptom relief compared to many other allergy medications.
Important Considerations
While effective, Prednisone is a prescription medication requiring doctor supervision. Long-term use carries potential side effects, so it’s typically reserved for severe allergies or short-term symptom control. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage and duration of treatment based on your individual needs and health status. They will also discuss potential side effects and how to manage them. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely.
When is Prednisone Necessary for Seasonal Allergies?
Prednisone is usually reserved for severe allergy symptoms unresponsive to other treatments. Consider it if your allergy symptoms significantly impact your daily life, causing debilitating fatigue, sleep disruption, or difficulty breathing.
Severe Symptoms Requiring Prednisone
Specific scenarios where Prednisone might be necessary include: severe allergic conjunctivitis (eye inflammation) causing significant vision impairment; uncontrollable nasal congestion obstructing breathing; severe coughing or wheezing indicating bronchospasm; or hives covering a large area of your body. If your usual allergy medications provide minimal relief, a doctor may prescribe a short course of Prednisone to quickly alleviate intense symptoms.
When to Consult a Doctor
Schedule an appointment with your doctor if over-the-counter allergy medications don’t alleviate your symptoms or if your symptoms worsen rapidly. They can properly assess your condition and determine if Prednisone or other treatments are necessary. Remember, Prednisone is a powerful medication with potential side effects and should only be used under a doctor’s supervision.
Potential Side Effects and Risks of Prednisone Use
Prednisone, while effective for seasonal allergies, carries potential side effects. These vary in severity and frequency, depending on dosage and duration of treatment. Common side effects include increased appetite leading to weight gain, insomnia, mood changes (including irritability or anxiety), and increased blood sugar. You might also experience fluid retention causing swelling, particularly in the face and ankles.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Prednisone can irritate your stomach lining, potentially causing heartburn, indigestion, or nausea. In some cases, more severe stomach ulcers may develop. Always inform your doctor if you experience persistent stomach discomfort.
Long-Term Risks
Prolonged use of Prednisone increases the risk of osteoporosis (weakening of bones), cataracts (clouding of the eye lens), and glaucoma (increased pressure inside the eye). Additionally, long-term use can suppress your immune system, making you more susceptible to infections. Your doctor will carefully weigh the benefits against these risks when prescribing prednisone, and will monitor you closely if you’re on a long-term course.
Inform your doctor immediately if you experience any severe side effects, such as severe abdominal pain, vision changes, or signs of infection (fever, chills, persistent cough).
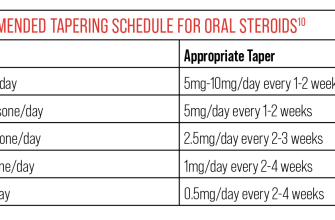
Using Prednisone Safely and Effectively: Dosage and Administration
Always follow your doctor’s prescribed dosage. Never adjust your Prednisone dose without consulting them. Typical dosages for seasonal allergies range from 5mg to 60mg daily, depending on the severity of your symptoms.
Prednisone is usually taken orally, once or twice daily, with food to minimize stomach upset.
- Never crush or chew Prednisone tablets. Swallow them whole with a full glass of water.
- Maintain a consistent schedule. Take your medication at the same time each day to ensure consistent blood levels.
- Store Prednisone properly. Keep it in a cool, dry place, away from children and pets.
Your doctor will likely recommend a specific treatment duration. Prednisone is usually not taken for extended periods due to potential side effects. They will gradually reduce your dose to minimize withdrawal symptoms, such as fatigue or joint pain. This tapering process is important to avoid potential health issues.
- Report any side effects immediately. Common side effects include increased appetite, weight gain, mood changes, and insomnia. Less common, but serious side effects require prompt medical attention.
- Discuss potential drug interactions. Inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking to avoid harmful interactions.
- Monitor your blood sugar. Prednisone can increase blood sugar levels, particularly in individuals with diabetes. Regular monitoring is advised.
Following your doctor’s instructions meticulously ensures safe and successful allergy management. Remember, open communication with your healthcare provider is crucial for optimal results and managing any potential problems.
Alternatives to Prednisone for Seasonal Allergies
Consider exploring non-prednisone options for allergy relief. First-line treatments often include over-the-counter antihistamines like cetirizine (Zyrtec) or fexofenadine (Allegra). These effectively reduce sneezing, runny nose, and itchy eyes. For more intense symptoms, your doctor might suggest a prescription antihistamine, such as levocetirizine (Xyzal) or desloratadine (Clarinex), which can provide stronger relief.
Nasal Corticosteroids
Nasal sprays containing corticosteroids, such as fluticasone (Flonase) or mometasone (Nasonex), directly target nasal inflammation, reducing congestion and other symptoms. Start using these early in the allergy season for optimal results. Remember to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully.
Other Options
Cromolyn sodium nasal spray works by preventing mast cell activation, thereby reducing allergy symptoms. It’s a good option if you’re looking for a medication with fewer side effects than other treatments. Montelukast (Singulair), a leukotriene inhibitor, is a daily oral medication that can also be helpful. Finally, immunotherapy, also known as allergy shots, can desensitize you to allergens over time, offering long-term relief. Discuss these options with your allergist to determine the best approach for your specific needs.
Lifestyle Changes
Simple changes can make a difference! Regularly washing bedding and clothing in hot water helps remove allergens. Use air filters in your home and car, and avoid exposure to known allergens, such as pollen. These steps, combined with medication, can significantly improve your quality of life during allergy season.