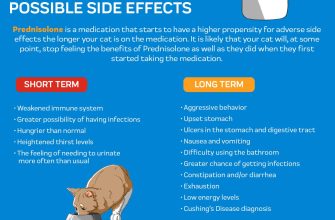
Prednisone can reduce the effectiveness of many birth control pills. This means an increased risk of pregnancy. If you’re taking prednisone and relying on hormonal birth control, consider using a backup method, such as condoms or a diaphragm, especially during treatment and for a few weeks after you finish the course.
The impact varies depending on the dosage and duration of prednisone use, as well as the type of birth control pill. Higher doses and longer treatment periods generally lead to a greater decrease in contraceptive effectiveness. This interaction occurs because prednisone can affect your liver’s metabolism of hormones, lowering the levels of active ingredients in your birth control.
Always discuss your medication regimen with your doctor or pharmacist. They can provide personalized advice based on your specific circumstances, including alternative birth control options if needed. Open communication is key to ensuring your reproductive health remains protected throughout your treatment with prednisone.
Remember to be proactive. Don’t assume your birth control is sufficient; taking proactive steps to protect yourself is always the best approach. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are also recommended to monitor your health during and after prednisone treatment.
- Prednisone and Birth Control: A Comprehensive Overview
- Impact on Different Birth Control Methods
- Recommendations and Further Actions
- Choosing Alternative Contraception
- How Prednisone Affects Hormone Levels
- Reduced Effectiveness of Hormonal Birth Control While on Prednisone
- Factors Affecting Birth Control Effectiveness
- Recommended Actions
- Types of Hormonal Birth Control and Prednisone
- Increased Risk of Breakthrough Bleeding
- Understanding the Mechanism
- Managing Breakthrough Bleeding
- Additional Precautions
- Alternative Contraception Methods During Prednisone Use
- Barrier Methods: Your Best Bet
- Beyond Barriers: Additional Options
- Contraception Summary Table
- Consult Your Doctor
- Consulting Your Doctor: Importance of Open Communication
- When to Resume Your Usual Birth Control
Prednisone and Birth Control: A Comprehensive Overview
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, can reduce the effectiveness of many birth control pills. This happens because it alters liver enzyme activity, affecting how your body processes hormones. The degree of interaction varies depending on the prednisone dosage and the type of birth control you use.
Impact on Different Birth Control Methods
Combined oral contraceptives (COCs), which contain both estrogen and progestin, are most susceptible to this interaction. Higher prednisone doses, especially those taken for extended periods, significantly increase the risk of pregnancy when using COCs. Consider using barrier methods (condoms) concurrently when taking prednisone alongside COCs.
Progestin-only pills (POPs), also known as mini-pills, are less affected by prednisone. However, any medication affecting hormone metabolism still poses some risk. Consult your doctor to discuss alternative contraception strategies while on prednisone, even with POPs.
Other hormonal methods, like patches, implants, or injections, may also experience reduced effectiveness. Discuss these interactions individually with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate course of action. The risk of reduced effectiveness depends heavily on factors such as the duration and dosage of prednisone. Long-term, high-dose prednisone use requires the strongest consideration for alternative contraception.
Recommendations and Further Actions
Always inform your doctor and pharmacist about all medications you are taking, including birth control. They can assess your specific situation and provide personalized advice. Regular checkups are crucial when combining prednisone with hormonal birth control to ensure continued protection against pregnancy. Barrier methods offer additional protection, minimizing risks during prednisone treatment.
Choosing Alternative Contraception
If you’re concerned about the interaction between prednisone and your current birth control, your doctor might suggest alternative contraceptive options during your prednisone treatment. These could include barrier methods, like condoms, or non-hormonal intrauterine devices (IUDs). The best alternative depends on your individual needs and health status.
How Prednisone Affects Hormone Levels
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, significantly impacts hormone production. It suppresses the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, reducing your body’s natural cortisol production. This decrease can disrupt the balance of other hormones, including sex hormones like estrogen and testosterone.
Specifically, prolonged or high-dose prednisone use often leads to lower levels of sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG). Reduced SHBG increases the levels of free testosterone and estrogen circulating in your blood. The effect varies depending on factors such as dosage, duration of treatment, and individual metabolism.
For women, this hormonal shift might cause irregular periods, changes in menstrual flow, or even amenorrhea (absence of menstruation). Men might experience decreased libido or erectile dysfunction. Both genders can potentially experience changes in mood, weight gain, and acne.
It’s crucial to discuss potential hormonal side effects with your doctor. They can monitor your hormone levels, adjust your prednisone dosage if necessary, and discuss management strategies for any side effects you experience. They may also advise on birth control options if necessary due to the alteration in your hormonal balance.
Remember, individual responses to prednisone vary greatly. Open communication with your healthcare provider is key to managing both your condition and the potential hormonal consequences of prednisone treatment.
Reduced Effectiveness of Hormonal Birth Control While on Prednisone
Prednisone, a corticosteroid medication, can decrease the effectiveness of hormonal birth control, increasing your risk of pregnancy. This happens because prednisone can affect your liver’s metabolism of hormones, leading to lower levels of the active hormones in your birth control. The impact varies depending on the dosage and duration of prednisone treatment and the type of birth control used.
Factors Affecting Birth Control Effectiveness
- Prednisone Dosage: Higher doses of prednisone generally lead to a greater reduction in birth control effectiveness.
- Duration of Treatment: Longer treatment periods with prednisone increase the risk of contraceptive failure.
- Type of Birth Control: The impact varies; some hormonal methods are more susceptible than others. Consult your doctor for personalized guidance.
The reduction in effectiveness is not always predictable, meaning you may experience a decrease in protection even with low doses or short treatment periods. This risk persists for several days after you stop taking prednisone, as hormone levels in your body readjust.
Recommended Actions
- Talk to your doctor: Discuss your use of hormonal birth control and prednisone treatment. They can assess your individual risk and advise on the best approach.
- Consider alternative contraception: While on prednisone, your doctor might recommend using a barrier method, such as condoms, in addition to your hormonal birth control, to increase protection.
- Monitor for changes: Pay attention to your body and consult your doctor immediately if you experience any irregularities in your menstrual cycle.
- Follow your doctor’s advice: Always adhere to the prescribed dosage and duration of both your prednisone and your birth control medication.
Types of Hormonal Birth Control and Prednisone
While the interactions are complex and vary by individual, it’s critical to understand that any hormonal birth control method, including the pill, patch, ring, and implant, may have reduced efficacy while taking prednisone. Your doctor will help determine the safest course of action for your specific situation.
Increased Risk of Breakthrough Bleeding
Prednisone can interact with birth control pills, sometimes causing unexpected bleeding between periods, known as breakthrough bleeding. This occurs because prednisone alters your body’s metabolism of hormones, potentially reducing the effectiveness of the hormones in your birth control. The severity varies; some women experience light spotting, while others have heavier bleeding.
Understanding the Mechanism
Prednisone affects your liver’s enzyme activity. These enzymes help process hormones. Increased enzyme activity from prednisone can speed up the breakdown of estrogen and progestin in your birth control, leading to lower hormone levels and potential breakthrough bleeding. The extent of this effect depends on the prednisone dosage and the type of birth control you’re using.
Managing Breakthrough Bleeding
Talk to your doctor. They can assess your individual situation and recommend strategies. Options might include adjusting your birth control dosage, switching to a different birth control method, or temporarily increasing your birth control dosage while on prednisone. Never stop taking your birth control or prednisone without consulting your doctor first. They can also rule out other causes of irregular bleeding.
Additional Precautions
Remember, prednisone can also reduce the effectiveness of your birth control, increasing the risk of pregnancy. Use additional contraceptive methods, such as condoms, while taking prednisone to ensure reliable protection. Consistent communication with your doctor is key to managing both your treatment and contraception effectively.
Alternative Contraception Methods During Prednisone Use
Prednisone can interact with hormonal birth control, potentially reducing its effectiveness. Therefore, consider switching to a non-hormonal method while taking Prednisone. Barrier methods offer excellent protection.
Barrier Methods: Your Best Bet
Condoms (male and female) are readily available and highly effective at preventing pregnancy and STIs when used correctly. The diaphragm, cervical cap, and sponge are also options, though they require proper fitting and usage instructions from a healthcare provider. Remember, consistent and correct use is key.
Beyond Barriers: Additional Options
Consider the copper IUD. This is a long-acting, hormone-free intrauterine device that provides effective, long-term contraception. It’s inserted by a healthcare professional and can stay in place for several years. Another viable option is the fertility awareness method (FAM), which involves tracking your menstrual cycle to identify fertile days. However, FAM requires diligent record-keeping and might not be suitable for everyone.
Contraception Summary Table
| Method | Hormonal? | Effectiveness | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Condoms (male/female) | No | High (with correct use) | Protects against STIs |
| Diaphragm/Cervical Cap/Sponge | No | Moderate to High (with proper fit and use) | Requires professional fitting |
| Copper IUD | No | High | Long-acting, requires professional insertion |
| Fertility Awareness Method (FAM) | No | Variable (depends on accuracy) | Requires diligent tracking |
Consult Your Doctor
Before making any changes to your contraception, schedule a consultation with your doctor or gynecologist. They can help you choose the best method based on your individual health needs and preferences while taking Prednisone.
Consulting Your Doctor: Importance of Open Communication
Schedule a consultation to discuss Prednisone’s impact on your birth control. Clearly explain all medications you’re taking, including the type of birth control.
Don’t hesitate to ask detailed questions about potential interactions and alternative birth control methods if necessary. Inquire about the expected duration of Prednisone use and its influence on your birth control effectiveness during and after treatment.
Provide your doctor with a complete medical history, including any previous experiences with hormones or medications. This helps them assess individual risks accurately.
Actively listen to your doctor’s explanations. Ask for clarification if anything is unclear. Understanding the potential implications ensures informed decisions.
Discuss your concerns openly and honestly. Your doctor is there to support you, and frank communication is key to receiving the best possible care and advice.
Follow your doctor’s recommendations carefully, including any prescribed adjustments to your birth control regimen. Regular follow-up appointments facilitate ongoing monitoring and adjustments as needed.
Remember: Open communication is vital for managing your health effectively. Don’t feel shy about expressing your concerns; your doctor is your partner in healthcare.
Proactive communication contributes significantly to successful treatment and safe healthcare practices.
When to Resume Your Usual Birth Control
Generally, you can restart your usual birth control pills once your prednisone course ends and you feel well enough. However, this depends on the dosage and duration of your prednisone treatment.
For short-term, low-dose prednisone (less than 10 days of a low dose), you likely don’t need to adjust your birth control method. However, always discuss this with your doctor.
If you took prednisone for a longer period or higher dosage (more than 10 days or higher than 5mg daily), you should consider using a backup method of contraception, like condoms, for at least one to two menstrual cycles after completing your prednisone treatment.
Prednisone can affect your body’s hormone levels, potentially interfering with the effectiveness of hormonal birth control. Using a backup method mitigates this risk.
Your doctor can provide personalized advice based on your specific situation and medication. They can assess the potential impact of prednisone on your birth control and recommend the best course of action.
Always consult your healthcare provider before making changes to your birth control regimen.