Need quick access to vital Prednisone information? This sheet provides concise details on dosage, potential side effects, and precautions. Focus on understanding the medication’s purpose, specifically its anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressant properties. This knowledge empowers you to collaborate effectively with your healthcare provider.
Dosage: Carefully follow your physician’s prescription. Typical starting doses vary widely depending on the condition being treated. Never adjust your dosage without consulting your doctor. Common side effects include weight gain, fluid retention, and increased blood sugar. Monitor yourself for these and report any significant changes immediately. Regular blood pressure checks are also recommended.
Precautions: Prednisone interacts with several medications; inform your doctor about all your current medications and supplements. Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or hypertension, require close monitoring while using Prednisone. Avoid abrupt cessation of the drug; tapering off under medical supervision prevents potential complications. Remember, this sheet is for informational purposes and should not replace professional medical advice.
- Prednisone SDS Sheet: A Detailed Guide
- Understanding Prednisone’s Properties
- Safety and Handling Precautions
- Emergency Response Information
- Regulatory Compliance
- Understanding Prednisone’s Mechanism of Action
- Impact on Inflammation
- Influence on the Immune System
- Metabolic Effects
- Common Indications for Prednisone Use
- Autoimmune Diseases
- Allergic Reactions and Inflammatory Conditions
- Other Uses
- Important Note:
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- Potential Side Effects and Precautions
- Drug Interactions with Prednisone
- Storage and Disposal Recommendations
- Proper Storage
- Safe Disposal
- Additional Information
- Contact Information
- Emergency Contact Information (if applicable)
Prednisone SDS Sheet: A Detailed Guide
Always consult your Prednisone SDS sheet and your healthcare provider before starting or altering Prednisone treatment. The SDS sheet provides critical information about handling and safety precautions.
Understanding Prednisone’s Properties
The SDS sheet details Prednisone’s chemical composition, including its molecular formula and weight. It clarifies potential hazards like flammability and reactivity. Pay close attention to the recommended storage conditions to ensure the drug’s potency and stability. Improper storage can degrade the medication, rendering it ineffective.
Safety and Handling Precautions
The SDS sheet lists potential health risks associated with Prednisone exposure. This includes information on symptoms of accidental ingestion or skin contact, and the appropriate first-aid measures. Proper personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves and eye protection, are frequently recommended during handling. Understand the proper procedures for disposal to prevent environmental contamination.
Emergency Response Information
The SDS sheet provides contact information for emergency services and relevant authorities in case of accidental spills or exposure incidents. This contact information is crucial for swift and appropriate emergency response. Familiarize yourself with the emergency response protocols outlined.
Regulatory Compliance
The SDS sheet assures adherence to relevant safety regulations and standards. This section details the legal and regulatory requirements for the handling, storage, and disposal of Prednisone. Understanding these regulations ensures safe and compliant practices.
Understanding Prednisone’s Mechanism of Action
Prednisone exerts its effects by binding to glucocorticoid receptors inside cells. This interaction triggers a cascade of events impacting gene expression.
Impact on Inflammation
Prednisone significantly reduces inflammation by inhibiting the production of inflammatory mediators like cytokines and prostaglandins. This process involves suppressing the activity of immune cells, such as lymphocytes and macrophages, responsible for the inflammatory response. The result is a decrease in swelling, redness, and pain.
Influence on the Immune System
Prednisone’s impact on the immune system is multifaceted. It suppresses both the innate and adaptive immune responses, reducing the body’s overall immune activity. This effect is useful in managing autoimmune diseases but also increases susceptibility to infections.
Metabolic Effects
Prednisone affects carbohydrate, protein, and fat metabolism. It increases blood glucose levels by promoting gluconeogenesis and reducing insulin sensitivity. It can also cause changes in protein metabolism, leading to muscle wasting, and alterations in fat distribution.
Common Indications for Prednisone Use
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, treats various inflammatory and autoimmune conditions. Its use depends heavily on the specific diagnosis and severity.
Autoimmune Diseases
- Rheumatoid arthritis: Prednisone reduces joint inflammation and pain, improving mobility.
- Lupus: It manages symptoms like joint pain, fatigue, and skin rashes.
- Multiple sclerosis: Prednisone may reduce the frequency and severity of relapses.
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): It helps control inflammation in Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
Allergic Reactions and Inflammatory Conditions
- Severe allergies: It can manage severe allergic reactions that don’t respond to other treatments.
- Asthma: Prednisone reduces airway inflammation, improving breathing.
- Eczema: It helps control severe inflammation and itching.
Other Uses
- Certain cancers: Prednisone is sometimes used in combination with chemotherapy to treat some cancers.
- Organ transplantation: It helps prevent organ rejection.
- Treatment of swelling (edema): It can reduce fluid retention.
Important Note:
This information is for general knowledge only. Always consult a physician for diagnosis and treatment. Prednisone has significant side effects; long-term use requires close monitoring.
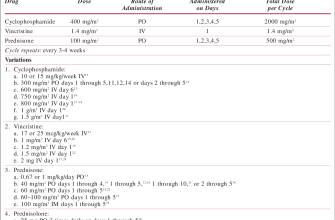
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Prednisone dosage depends heavily on the specific condition being treated and the patient’s individual response. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Typical starting doses range from 5 to 60 mg daily, often administered in a single dose. However, higher doses may be necessary for severe conditions.
For most conditions, your doctor will likely start you on a higher dose then gradually reduce it over time as your condition improves. This is called a tapering schedule, minimizing potential side effects. Your doctor will guide you through the process. Never adjust your dosage without consulting your physician.
Prednisone is usually taken orally, with or without food. Follow the prescribed schedule; consistency is key. If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember unless it’s nearly time for your next dose. Never double up on doses.
Long-term use of prednisone carries potential side effects, including increased risk of infections, elevated blood sugar, bone thinning, and mood changes. Your doctor will monitor you closely for these risks, particularly if your treatment extends beyond a few weeks.
If you experience any unusual side effects, such as severe headaches, vision problems, or unexplained weight gain, contact your doctor immediately. Open communication with your doctor is crucial for safe and effective prednisone therapy.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Prednisone, while effective, carries potential side effects. Monitor yourself closely for any unusual changes. Report any concerning symptoms to your doctor immediately.
Common side effects include increased appetite and weight gain, mood changes (including irritability and anxiety), insomnia, and increased blood sugar. You might also experience fluid retention, leading to swelling in your ankles or face. Some people experience increased blood pressure and thinning of the bones (osteoporosis) with long-term use.
Serious, though less common, side effects include increased risk of infections, glaucoma, cataracts, and stomach ulcers. Prednisone can also worsen existing conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure. Sudden withdrawal can cause adrenal insufficiency, so tapering off the medication is crucial under medical supervision.
| Side Effect Category | Specific Examples | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal | Heartburn, nausea, vomiting, ulcers | Report to your doctor; consider antacids as directed. |
| Musculoskeletal | Muscle weakness, bone thinning | Consult your doctor about bone density testing and preventive measures. |
| Endocrine | Increased blood sugar, Cushing’s syndrome | Regular blood sugar monitoring and close medical follow-up are necessary. |
| Ophthalmologic | Cataracts, glaucoma | Regular eye examinations are crucial. |
| Psychological | Mood swings, anxiety, depression | Seek support from your doctor or therapist. |
Before starting Prednisone, inform your doctor about all your medical conditions, including any allergies or other medications you are taking. This includes over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements. Pregnancy and breastfeeding should also be discussed with your doctor.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely regarding dosage and duration of treatment. Do not stop taking Prednisone suddenly. Regular check-ups are important to monitor your progress and identify any potential problems early.
Drug Interactions with Prednisone
Prednisone interacts with many medications. Always inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking before starting Prednisone. This includes prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, and even vitamins.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Combining Prednisone with NSAIDs like ibuprofen or naproxen increases your risk of stomach ulcers and bleeding. Your doctor might recommend monitoring for these side effects.
Blood thinners (anticoagulants): Prednisone can interact with blood thinners like warfarin, increasing the risk of bleeding. Close monitoring of your blood clotting time is necessary.
Diabetes medications: Prednisone can raise blood sugar levels, potentially requiring adjustments to your diabetes medications. Regular blood sugar monitoring is crucial.
Drugs affecting the immune system: Combining Prednisone with other immunosuppressants, like azathioprine or cyclosporine, increases the risk of infections. Your doctor may conduct regular health checks.
Potassium-depleting diuretics: Prednisone can lower potassium levels; using potassium-depleting diuretics simultaneously worsens this effect. Potassium levels need close monitoring.
Digoxin: Prednisone may reduce digoxin levels, potentially affecting its effectiveness. Careful monitoring of digoxin levels is required.
Vaccines: Prednisone can reduce the effectiveness of live vaccines. Avoid live vaccines while taking Prednisone. Consult your doctor for safe alternatives.
This information is not exhaustive. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized advice regarding potential drug interactions with Prednisone.
Storage and Disposal Recommendations
Store Prednisone tablets at room temperature, between 68°F and 77°F (20°C and 25°C). Keep the container tightly closed to protect from moisture.
Proper Storage
- Avoid extreme temperatures – don’t freeze or expose to direct sunlight.
- Keep out of reach of children and pets.
- Check the expiration date printed on the label and discard any expired medication.
Safe Disposal
Never flush Prednisone down the toilet or pour it into a drain. Follow these steps for safe disposal:
- Mix the medication with an undesirable substance, such as used coffee grounds or kitty litter.
- Seal the mixture in a sturdy, sealed plastic bag.
- Dispose of the bag in your household trash.
- Alternatively, you can participate in local pharmaceutical take-back programs. Check with your local pharmacy or health department for details on these programs and their availability.
Additional Information
Consult your pharmacist or doctor for further guidance on specific disposal methods in your area, especially for larger quantities of leftover medication. They can provide tailored advice based on your location and circumstances.
Contact Information
For any questions regarding storage or proper disposal, contact your pharmacist or physician. Your healthcare provider can clarify any uncertainties you may have.
Emergency Contact Information (if applicable)
Always keep your doctor’s contact information readily available. Note their phone number and address. If you experience severe side effects, contact them immediately.
Consider listing emergency contacts, such as a family member or close friend, who can assist you in case of a medical emergency. Include their phone numbers and addresses in your personal medication record.
For severe allergic reactions or life-threatening symptoms, dial your local emergency number (911 in the US, 999 in the UK, etc.) immediately. Be prepared to provide your location and a brief description of your symptoms.
Maintain a readily accessible list of all relevant medical professionals and their contact details, including your pharmacist. This proactive approach ensures swift access to vital support when needed.