High-dose prednisone, often used as a stress dose, requires careful management. We recommend consulting your doctor immediately if you experience any side effects, even seemingly minor ones. Close monitoring of blood pressure, blood sugar, and potassium levels is paramount during treatment.
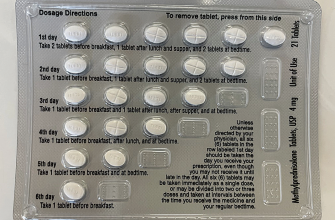
Typical stress doses range from 40-60mg daily, adjusted based on individual needs and the severity of the situation. This is not a self-treatment strategy; a physician must determine the appropriate dosage and duration. Remember, exceeding the prescribed amount can lead to severe adverse reactions.
Beyond dosage, tapering off prednisone is critical to prevent rebound effects and minimize withdrawal symptoms. Your doctor will provide a specific tapering schedule, usually a gradual reduction over several weeks or months, to allow your body to adjust naturally. Sudden cessation can be dangerous.
Potential side effects include increased blood sugar, fluid retention, insomnia, and mood swings. Promptly report any concerning symptoms to your healthcare provider. Managing these side effects may involve lifestyle adjustments, dietary changes, or additional medication. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely.
This guide offers practical information, but it’s not a substitute for professional medical advice. Your physician possesses the expertise to tailor a prednisone regimen to your unique health circumstances and monitor your progress closely.
- Prednisone Stress Dose: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding Prednisone Stress Doses: When and Why They’re Used
- Situations Requiring Prednisone Stress Doses
- Dosage and Administration
- Important Considerations
- Potential Side Effects and Risks of Prednisone Stress Doses: A Patient’s Perspective
- Common Side Effects
- Less Common, but Serious, Risks
- Managing Side Effects
- Managing Prednisone Stress Doses: Tips for Patients and Caregivers
Prednisone Stress Dose: A Comprehensive Guide
Consult your doctor before starting any Prednisone regimen, especially stress doses. They will determine the appropriate dosage based on your individual needs and medical history.
Stress doses typically involve higher-than-usual Prednisone amounts for a short period. This is often used in acute situations like severe allergic reactions or organ transplant rejection, to quickly reduce inflammation.
Common dosages range from 60 to 100mg daily, adjusted based on the severity of the condition. The duration of treatment is usually short – perhaps a few days to a week – followed by a gradual tapering of the dose to minimize side effects.
Potential side effects include increased blood sugar, weight gain, mood changes, and increased risk of infections. Regular monitoring by your physician is therefore crucial.
Closely follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and duration. Never alter your Prednisone regimen without consulting them. Sudden cessation can lead to withdrawal symptoms.
Expect regular blood tests to monitor your blood sugar, electrolytes, and other vital signs. This close monitoring allows for timely adjustments to your treatment plan.
Report any unusual symptoms, such as severe headaches, blurred vision, or rapid heartbeat, to your healthcare provider immediately. Prompt action can mitigate potential complications.
Lifestyle adjustments such as a balanced diet and regular exercise can help manage some side effects. Discuss these strategies with your physician or a registered dietician.
Remember that Prednisone is a powerful medication. Adherence to the prescribed regimen and regular medical check-ups are key to ensuring safe and effective treatment.
Understanding Prednisone Stress Doses: When and Why They’re Used
Prednisone stress doses are significantly higher than standard maintenance doses and are used to manage severe inflammation or immune system suppression during times of increased physiological stress.
Situations Requiring Prednisone Stress Doses
- Severe Infections: Sepsis, pneumonia, or other life-threatening infections often necessitate a stress dose to counteract the body’s overwhelming inflammatory response.
- Surgery: Major surgical procedures can trigger a significant inflammatory cascade. A stress dose helps mitigate this response and improve recovery.
- Trauma: Serious injury, like a severe burn or multiple fractures, warrants a stress dose to reduce the inflammatory response and promote healing.
- Organ Transplant Rejection: High doses of Prednisone can help prevent or treat organ rejection, suppressing the immune system’s attack on the new organ.
- Autoimmune Flare-Ups: In cases of lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, or other autoimmune diseases, stress doses can control severe flare-ups.
Dosage and Administration
Dosage varies widely depending on the patient’s condition, severity of illness, and individual response. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dose and duration of treatment. The medication is typically administered orally, intravenously, or intramuscularly.
Important Considerations
- Close Monitoring: Regular blood tests and monitoring of vital signs are crucial during stress-dose treatment to detect and manage potential side effects.
- Potential Side Effects: Higher doses of Prednisone increase the risk of side effects, such as increased blood sugar, high blood pressure, mood changes, and increased susceptibility to infections. Your doctor will discuss these risks with you.
- Gradual Tapering: After the acute phase has passed, Prednisone dosage should be gradually reduced to minimize withdrawal symptoms and prevent a relapse of the underlying condition.
Remember, Prednisone stress doses are a powerful tool used in specific medical situations. Always discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor before beginning any treatment involving Prednisone.
Potential Side Effects and Risks of Prednisone Stress Doses: A Patient’s Perspective
Talk openly with your doctor about your concerns. They can help you weigh the benefits against potential risks specific to your health. Remember, everyone reacts differently.
Common Side Effects
Increased blood sugar: Monitor your blood sugar levels closely, especially if you have diabetes. Your doctor may adjust your diabetes medication. Weight gain: Prednisone can cause fluid retention and appetite changes. Focus on a healthy diet and regular exercise to manage this. Mood swings: Irritability, anxiety, or depression are possible. Let your doctor know if you experience significant shifts in mood. Insomnia: Take Prednisone in the morning to minimize nighttime sleep disruption. Increased risk of infection: Your immune system can be suppressed. Practice good hygiene and avoid sick people. Report any signs of infection promptly.
Less Common, but Serious, Risks
Osteoporosis: Long-term high-dose Prednisone can weaken bones. Talk to your doctor about bone density testing and preventative measures. High blood pressure: Regular monitoring is important. Your doctor might adjust your blood pressure medication. Gastrointestinal issues: Stomach upset, ulcers, and heartburn can occur. Report any severe digestive problems immediately. Cataracts or glaucoma: These eye conditions are more likely with prolonged use. Regular eye exams are recommended.
Managing Side Effects
Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water to help mitigate some side effects. Maintain a healthy diet: Focus on nutrient-rich foods. Engage in gentle exercise: As tolerated, this can improve mood and manage weight gain. Communicate openly with your doctor: Don’t hesitate to discuss any concerns or changes in your health. Your doctor’s guidance is critical to managing side effects and ensuring your safety.
Managing Prednisone Stress Doses: Tips for Patients and Caregivers
Communicate openly with your doctor. Regularly discuss any changes in your health or side effects.
Maintain a detailed medication log. Note the dosage, time of administration, and any reactions experienced. This helps you and your doctor track your progress.
Prioritize a healthy diet. Focus on fresh fruits, vegetables, and lean protein. Avoid excessive sugar and processed foods. Good nutrition supports your body during treatment.
Stay hydrated. Drink plenty of water throughout the day. Adequate hydration helps manage potential side effects.
Follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Do not alter your dosage or stop taking the medication without consulting them.
Manage stress levels. Practice relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation. Stress can influence your body’s response to prednisone.
Monitor your blood sugar levels regularly, especially if you have diabetes. Prednisone can affect blood sugar control.
Be aware of potential side effects. These can include weight gain, increased appetite, mood swings, and insomnia. Report any concerning symptoms immediately.
| Side Effect | Management Tip |
|---|---|
| Weight gain | Maintain a healthy diet and exercise regularly. |
| Increased appetite | Eat nutritious foods in moderate portions. |
| Mood swings | Practice stress-reduction techniques and seek support if needed. |
| Insomnia | Establish a regular sleep schedule and create a relaxing bedtime routine. |
Keep a list of emergency contact numbers readily accessible. This includes your doctor’s number and the number for a local emergency service.
Schedule regular check-ups with your doctor. Consistent monitoring helps ensure the treatment is progressing effectively and safely.