Need to understand Prednisone tablets quickly? Start with dosage: Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Typical adult dosages range from 5mg to 60mg daily, adjusted based on your specific condition and response to treatment. Never alter your dosage without consulting your physician.
Prednisone is a powerful corticosteroid, reducing inflammation and suppressing the immune system. Common uses include treating allergies, asthma, autoimmune diseases, and certain cancers. However, be aware of potential side effects, such as weight gain, increased blood sugar, and mood changes. These effects vary greatly depending on dosage and duration of use.
Long-term use carries a higher risk of side effects. Your doctor will monitor you closely and adjust the dosage or duration as needed, aiming for the lowest effective dose. Remember to report any unusual symptoms promptly to your healthcare provider. Proper understanding of your treatment plan significantly improves outcomes.
Important Note: This information is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always discuss Prednisone use with your doctor before starting or stopping treatment. They can tailor a plan to your individual needs.
- Prednisone Tab: A Comprehensive Overview
- Dosage and Administration
- Potential Side Effects
- Precautions and Interactions
- Withdrawal
- When to Seek Medical Attention
- What is Prednisone and How Does it Work?
- How Prednisone Reduces Inflammation
- How Prednisone Suppresses the Immune System
- Important Considerations
- Potential Side Effects
- Common Uses and Medical Conditions Treated with Prednisone
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Prednisone Tablets
- Adjusting Your Prednisone Dose
- Timing and Administration
- Potential Side Effects
- Storage
- Potential Side Effects and Risks Associated with Prednisone
- Precautions and Interactions: Medications and Conditions to Consider
- Conditions Requiring Special Caution
- Other Important Considerations
- Withdrawal from Prednisone: A Gradual Approach
- When to Consult a Doctor Regarding Prednisone Use
Prednisone Tab: A Comprehensive Overview
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, reduces inflammation and suppresses the immune system. Doctors prescribe it for various conditions, including allergies, asthma, and autoimmune diseases. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely; never adjust your dosage without their guidance.
Dosage and Administration
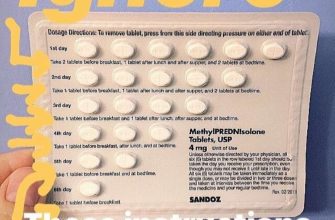
Your doctor determines the appropriate prednisone dose based on your specific needs and condition. Typical dosages range from 5mg to 60mg daily, often divided into multiple doses. Swallow tablets whole with water; avoid crushing or chewing them. The duration of treatment varies significantly depending on the condition being treated. Some treatments last days, while others may last for months. Your physician will provide a detailed treatment plan.
Potential Side Effects
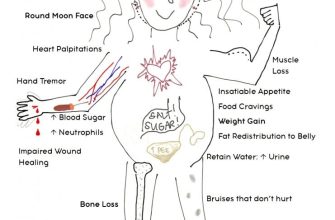
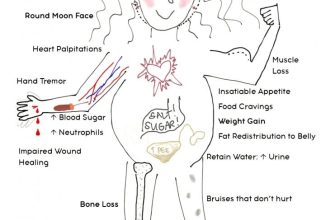
Prednisone can cause side effects, ranging in severity. Common side effects include weight gain, increased appetite, mood changes, insomnia, and increased blood sugar. More serious, though less common, side effects include increased risk of infection, osteoporosis, and high blood pressure. Report any unusual symptoms to your doctor immediately. They can help manage side effects and adjust your treatment plan.
Precautions and Interactions
Prednisone interacts with various medications. Inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you’re taking before starting prednisone. If you have diabetes, liver disease, or heart problems, discuss this with your doctor beforehand, as it impacts prednisone use. Pregnancy and breastfeeding should also be discussed with your healthcare provider. Alcohol consumption while on prednisone may exacerbate some side effects. Proper monitoring is crucial.
Withdrawal
Never stop taking prednisone suddenly. Abrupt cessation can lead to adrenal insufficiency, a serious medical condition. Your doctor will gradually reduce your dosage over time to minimize withdrawal symptoms. This process is crucial for safe discontinuation.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe side effects such as severe allergic reactions (rash, hives, difficulty breathing), severe stomach pain, or worsening of your condition. Regular check-ups with your physician are crucial for monitoring your progress and managing any potential issues. Your doctor will provide specific guidance tailored to your situation.
What is Prednisone and How Does it Work?
Prednisone is a corticosteroid medication, a synthetic version of a hormone your body naturally produces. It powerfully reduces inflammation and suppresses your immune system.
How Prednisone Reduces Inflammation
Prednisone works by binding to receptor sites within your cells. This triggers a cascade of events, ultimately decreasing the production of inflammatory substances like prostaglandins and leukotrienes. This leads to reduced swelling, redness, and pain.
How Prednisone Suppresses the Immune System
Prednisone’s immune-suppressing effects are also a consequence of its interaction with cellular receptors. It interferes with several immune processes:
- It reduces the number of white blood cells, key players in immune responses.
- It inhibits the release of inflammatory mediators.
- It affects the production of antibodies.
This makes it effective in treating conditions involving overactive immune systems, such as autoimmune diseases.
Important Considerations
Remember, Prednisone is a powerful drug with potential side effects. These vary depending on the dosage and duration of treatment. Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully.
- Dosage: Your doctor will determine the appropriate dose based on your specific condition and response to treatment.
- Duration: Prednisone is generally prescribed for short-term use, as long-term use increases the risk of side effects.
- Tapering: Never stop taking Prednisone abruptly. Your doctor will likely prescribe a gradual tapering schedule to minimize withdrawal symptoms.
- Monitoring: Regular check-ups allow your doctor to monitor your progress and adjust your treatment as needed.
Potential Side Effects
Common side effects can include weight gain, increased appetite, mood changes, insomnia, and increased blood sugar. More serious side effects are possible and warrant immediate medical attention. Discuss any concerns with your doctor.
Common Uses and Medical Conditions Treated with Prednisone
Prednisone effectively treats various inflammatory and autoimmune conditions. Doctors frequently prescribe it for allergies, causing significant swelling and inflammation.
Autoimmune diseases like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis benefit from Prednisone’s anti-inflammatory properties, reducing joint pain and swelling. It also helps manage inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, easing symptoms like abdominal pain and diarrhea.
Certain cancers respond well to Prednisone, often used in combination with other therapies to suppress the immune system. It’s also a valuable treatment for asthma, controlling inflammation in the airways and improving breathing. Additionally, Prednisone helps manage severe skin conditions such as psoriasis and eczema, reducing inflammation and itching.
Kidney diseases, particularly those involving inflammation, may also be treated with Prednisone. It offers relief from symptoms associated with nephritis and other related conditions. In cases of organ transplantation, Prednisone helps prevent organ rejection by suppressing the immune system’s response.
Note: Prednisone carries potential side effects. Always discuss its use with your doctor to assess risks and benefits.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Prednisone Tablets
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Dosage varies significantly depending on your specific condition, its severity, and your individual response to the medication. Typical starting doses range from 5 to 60 milligrams daily, administered once or in divided doses. Higher doses are usually used for severe inflammation, while lower doses maintain remission.
Adjusting Your Prednisone Dose
Your doctor will likely adjust your dosage over time. They might begin with a higher dose to quickly control symptoms, then gradually reduce the amount as your condition improves. This tapering process is vital to prevent withdrawal symptoms. Never stop taking prednisone abruptly without consulting your physician.
Timing and Administration
Prednisone tablets are usually taken with food or milk to minimize stomach upset. Taking them at the same time each day helps maintain consistent blood levels. Follow any instructions your doctor provides regarding specific times of day or with meals.
Potential Side Effects
Be aware of potential side effects, such as increased appetite, weight gain, mood changes, and insomnia. Inform your doctor about any unusual symptoms you experience. Long-term use carries additional risks, so regular monitoring is crucial.
Storage
Store prednisone tablets in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture. Keep them out of reach of children and pets.
Potential Side Effects and Risks Associated with Prednisone
Prednisone, while effective, carries potential side effects. Understanding these risks helps you partner with your doctor for safe and effective treatment.
Common side effects often resolve once you stop taking Prednisone. These include:
- Increased appetite and weight gain
- Mood changes, including irritability or anxiety
- Difficulty sleeping (insomnia)
- Increased blood sugar levels
- Fluid retention (swelling)
- Increased risk of infections
- High blood pressure
Less common, but more serious side effects require immediate medical attention. These include:
- Severe allergic reactions (rash, swelling, difficulty breathing)
- Muscle weakness
- Thinning of the bones (osteoporosis)
- Increased risk of cataracts or glaucoma
- Stomach ulcers
- Changes in menstrual cycles
- Slow wound healing
Long-term use increases the likelihood of these serious side effects. Your doctor will carefully monitor your health and adjust your dosage as needed to minimize risk.
Here’s what you can do to mitigate some risks:
- Maintain a healthy diet and exercise regularly to manage weight gain and blood sugar.
- Report any unusual symptoms to your doctor immediately.
- Follow your doctor’s instructions meticulously regarding dosage and duration of treatment.
- Discuss potential drug interactions with your physician before starting Prednisone.
- Consider bone density testing if prescribed long-term therapy.
Remember, this information is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist with any questions or concerns regarding Prednisone or any other medication.
Precautions and Interactions: Medications and Conditions to Consider
Always inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs, herbal supplements, and vitamins. Prednisone can interact negatively with many medications. For example, it can increase the risk of bleeding with blood thinners like warfarin. Simultaneous use with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may heighten the risk of stomach ulcers and bleeding. Avoid alcohol consumption while on prednisone, as it increases the risk of stomach upset and ulcers.
Conditions Requiring Special Caution
Prednisone can worsen existing conditions. People with diabetes should monitor their blood sugar closely as prednisone can raise glucose levels. Individuals with glaucoma or cataracts need careful monitoring, as prednisone can exacerbate these conditions. Those with heart problems, high blood pressure, or osteoporosis should discuss the risks with their doctor before starting prednisone. Prednisone may also increase the risk of infections; therefore, avoid contact with sick individuals if possible.
Other Important Considerations
Sudden cessation of prednisone can lead to withdrawal symptoms. Your doctor will usually recommend a gradual tapering of the dose to minimize these effects. Long-term use of prednisone may have several potential side effects including weight gain, increased risk of infections, and weakened bones (osteoporosis). Regular monitoring by your doctor is vital for detecting and managing these potential issues. Remember to report any new or worsening symptoms to your healthcare provider immediately.
Withdrawal from Prednisone: A Gradual Approach
Never stop Prednisone abruptly. Your doctor will create a tapering schedule, gradually reducing your dose. This prevents adrenal insufficiency, a serious complication.
Typical tapering involves decreasing the dose by a small amount, perhaps 5-10mg, every few days or weeks. The exact schedule depends on your individual dosage and treatment duration. Follow your physician’s instructions precisely.
Expect some withdrawal symptoms. These might include fatigue, muscle weakness, joint pain, nausea, or mood changes. These are usually manageable and lessen as your body adjusts.
Stay hydrated. Drink plenty of water to help your body cope with the changes. A healthy diet, rich in fruits and vegetables, also supports your system during this period.
Monitor your symptoms closely. Report any unusual or worsening symptoms to your doctor immediately. They may need to adjust your tapering schedule.
Regular check-ups are crucial. Your doctor will monitor your adrenal function and overall health during the withdrawal process.
Patience is key. The withdrawal process takes time. Be patient with yourself, and trust the process guided by your healthcare provider.
When to Consult a Doctor Regarding Prednisone Use
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience any severe side effects. This includes, but isn’t limited to, severe allergic reactions (rash, hives, swelling, difficulty breathing), worsening of existing conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure, significant mood changes (irritability, depression, anxiety), severe muscle weakness, vision problems, or persistent stomach upset.
Schedule a follow-up appointment as directed by your physician. Regular checkups allow your doctor to monitor your progress, assess your response to the medication, and adjust the dosage as needed. This is especially important for long-term prednisone use.
Discuss any new symptoms or health concerns with your doctor, even if they seem unrelated to prednisone. Your doctor needs a complete picture of your health to provide the best care.
Inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking. Prednisone can interact with other drugs, potentially causing harmful effects. Accurate information is critical for safe medication management.
| Symptom | Action |
|---|---|
| Sudden weight gain | Contact your doctor immediately |
| Increased thirst or urination | Contact your doctor immediately |
| Difficulty sleeping | Discuss with your doctor at your next appointment |
| Increased bruising or bleeding | Contact your doctor immediately |
Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully regarding dosage and duration of prednisone treatment. Never stop taking prednisone abruptly without consulting your physician; this can have serious consequences. Understanding your medication and actively participating in your treatment plan promotes better health outcomes.