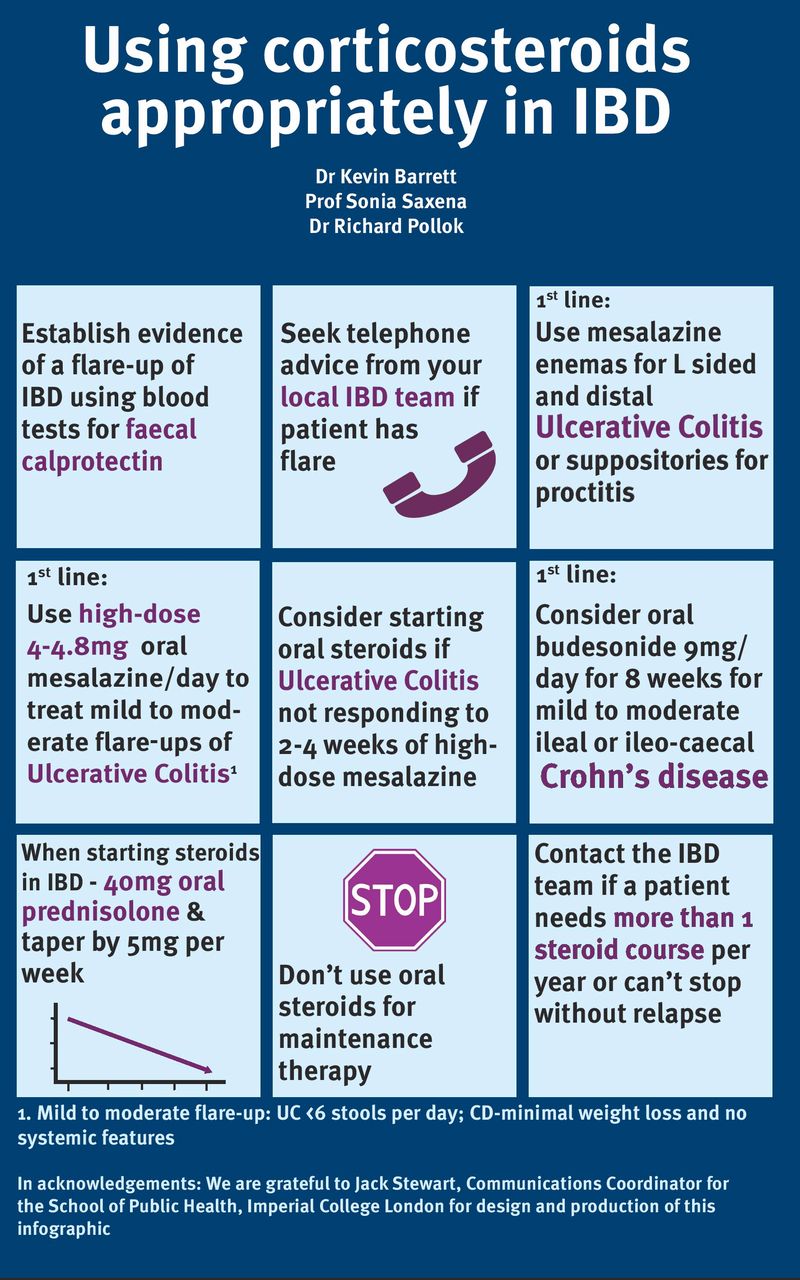
Gradually reducing your prednisone dosage is key to minimizing withdrawal symptoms. A common tapering schedule involves decreasing your daily dose by 5-10mg every few days to a week, depending on your individual response and your doctor’s guidance. Always follow your physician’s prescribed plan; there’s no one-size-fits-all approach.
Monitor for signs of relapse, such as increased bowel movements, abdominal pain, or rectal bleeding. These symptoms warrant immediate contact with your gastroenterologist. They might adjust your tapering schedule or prescribe additional medications to manage the flare-up.
Besides the medication itself, lifestyle adjustments play a significant role. A balanced diet rich in fiber, regular exercise, and stress management techniques can positively influence your condition. Adequate rest is also critical for recovery. Your healthcare provider can provide tailored recommendations based on your specific needs.
Remember: Prednisone withdrawal can cause side effects like fatigue, joint pain, and mood changes. Open communication with your doctor is paramount. They can address any concerns and help you manage these potential side effects, ensuring a smooth and safe tapering process. Don’t hesitate to reach out if you experience any difficulties.
- Prednisone Taper for Ulcerative Colitis: A Detailed Guide
- Factors Influencing Your Taper
- Managing Withdrawal Symptoms
- Alternative and Supplemental Therapies
- Monitoring for Relapse
- Understanding Prednisone’s Role in Ulcerative Colitis Treatment
- How Prednisone Works
- Important Considerations
- Prednisone and Long-Term Management
- Creating a Safe and Effective Prednisone Taper Schedule
- Monitoring Your Body During the Taper Process
- Managing Potential Side Effects of Prednisone Withdrawal
- Alternative Medications and Therapies During and After Taper
- Maintaining Remission and Preventing Relapse of Ulcerative Colitis
Prednisone Taper for Ulcerative Colitis: A Detailed Guide
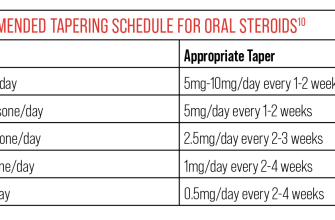
Your doctor will create a personalized prednisone tapering schedule, typically decreasing the dose gradually over several weeks or months. A common approach involves reducing the dose by 5-10 mg every few days or weeks, depending on your response. Close monitoring is key; your doctor will adjust the schedule based on your symptoms and blood tests.
Factors Influencing Your Taper
Several factors determine the speed of your taper. These include the severity of your ulcerative colitis, your overall health, and your response to prednisone. A slower taper is usually recommended for individuals with severe disease or a history of frequent relapses. Regular monitoring through blood tests, including a complete blood count (CBC) and inflammatory markers, helps guide the tapering process and detects any potential complications.
Managing Withdrawal Symptoms
Reducing prednisone too quickly can trigger withdrawal symptoms. These may include fatigue, muscle weakness, joint pain, nausea, and low blood sugar. To minimize these, maintain close communication with your healthcare provider. They may adjust your schedule or prescribe additional medications to help manage these side effects. Maintaining a healthy diet and incorporating regular exercise can also aid in managing withdrawal.
Alternative and Supplemental Therapies
Alongside prednisone tapering, your doctor may recommend other treatments to maintain remission. This might include aminosalicylates (like mesalamine), immunomodulators (like azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine), or biologics (like infliximab or adalimumab). These medications aim to reduce inflammation and prevent disease flares. The goal is to transition you from prednisone to a maintenance medication plan.
Monitoring for Relapse
Regular follow-up appointments with your gastroenterologist are crucial during and after the taper. Report any worsening symptoms immediately. Early detection of a relapse allows for prompt intervention, preventing the need for a higher dose of prednisone or a longer tapering period. Staying proactive and closely collaborating with your healthcare team maximizes your chances of achieving long-term remission.
Understanding Prednisone’s Role in Ulcerative Colitis Treatment
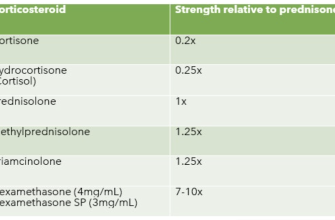
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, acts quickly to reduce inflammation in your gut, offering significant relief from ulcerative colitis symptoms like diarrhea, abdominal pain, and rectal bleeding. It’s a powerful medication, but it’s typically used for short-term symptom management, not as a long-term solution.
How Prednisone Works
Prednisone works by suppressing your immune system’s response, thereby decreasing the inflammation that characterizes ulcerative colitis. This allows your body to heal.
Important Considerations
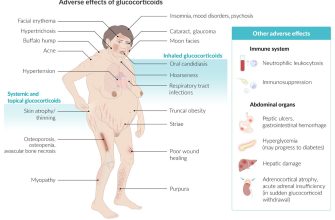
While effective, prednisone carries potential side effects. These can include weight gain, increased blood sugar, mood changes, and weakened bones. Your doctor will carefully monitor you for these and adjust your dosage accordingly. A gradual tapering schedule is always necessary to avoid withdrawal symptoms and allow your body to readjust.
| Side Effect | Possible Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|
| Weight gain | Maintain a healthy diet and regular exercise. |
| Increased blood sugar | Regular blood sugar monitoring and possible dietary adjustments. |
| Mood changes | Open communication with your doctor and support system. |
| Weakened bones (osteoporosis) | Calcium and Vitamin D supplementation may be recommended. |
Prednisone and Long-Term Management
Prednisone isn’t a cure for ulcerative colitis. Its primary role is to manage flares and allow other treatments, such as aminosalicylates, immunomodulators, or biologics, to take effect. Your gastroenterologist will develop a personalized treatment plan incorporating various therapies to achieve remission and maintain long-term control of your condition.
Creating a Safe and Effective Prednisone Taper Schedule
Your gastroenterologist will personalize your prednisone taper, considering your disease severity and response to treatment. Typical schedules involve gradual reductions, often by 5-10mg every few days or weeks. Never adjust your dosage without consulting your doctor.
Slow and steady wins the race. Rapid tapering increases relapse risk. A common schedule might look like this: If you’re on 60mg, decrease to 55mg for a week, then 50mg, and so on. However, this is just an example; your doctor will tailor a plan for you.
Monitor your symptoms closely during the taper. Increased bowel movements, abdominal pain, or rectal bleeding signal potential relapse. Report these immediately to your healthcare provider. They may need to adjust your taper or add other medications.
Maintaining regular communication with your doctor is vital. Schedule follow-up appointments to track your progress and address any concerns. Regular blood tests may also be necessary to monitor your overall health.
Support your body throughout this process. Eat a balanced diet, stay hydrated, manage stress, and get adequate rest. These factors support healing and reduce your risk of complications.
Remember, every patient is unique. A schedule that works for one person might not work for another. Trust your doctor’s expertise and actively participate in managing your condition.
Monitoring Your Body During the Taper Process
Regularly track your symptoms. Note any increases in bowel movements, changes in stool consistency (frequency, blood, mucus), and abdominal pain. Keep a detailed diary; this is invaluable for your doctor.
Weigh yourself weekly. Prednisone can cause fluid retention; weight gain might indicate this. Sudden, significant weight changes warrant a call to your doctor.
Monitor your blood pressure. Prednisone can elevate blood pressure. Check it regularly, particularly if you have a history of hypertension.
Pay close attention to your blood sugar levels, especially if you have diabetes or a family history of it. Prednisone can affect blood sugar control.
Observe your mood. Prednisone can impact mental well-being; watch for changes in mood, anxiety, or depression. Don’t hesitate to seek support if needed.
Report any skin changes, such as thinning, bruising, or infections, to your doctor promptly. These are potential side effects of the medication.
Watch for signs of infection, such as fever, chills, or persistent fatigue. Your immune system may be temporarily suppressed.
Maintain open communication with your gastroenterologist. Regular check-ups and blood tests are crucial throughout the tapering process. Describe any concerns you have, no matter how small.
Don’t adjust your medication dosage without your doctor’s explicit approval. Stopping or altering the taper schedule abruptly can lead to complications.
Managing Potential Side Effects of Prednisone Withdrawal
Reducing Prednisone gradually is key to minimizing withdrawal symptoms. Expect some discomfort; it’s a normal part of the process.
Monitor for these common issues:
- Fatigue and Weakness: Increase rest periods throughout the day. Gradually increase your activity levels as tolerated. Consider light exercise, like walking, to boost energy.
- Joint and Muscle Pain: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can provide relief. Your doctor might suggest other options.
- Mood Changes: These can range from irritability to depression. Open communication with your doctor is vital. They may recommend support groups or medication adjustments. Maintain a regular sleep schedule.
- Gastrointestinal Upset: Eat smaller, more frequent meals. Avoid foods that trigger symptoms. Consider probiotics to support gut health.
- Low Blood Pressure: Drink plenty of fluids, especially water, and avoid standing for prolonged periods. Report any dizziness or lightheadedness to your doctor immediately.
Helpful strategies for managing withdrawal:
- Follow your doctor’s prescribed tapering schedule precisely. Don’t adjust the dosage on your own.
- Maintain a healthy diet. Focus on nutritious foods to support your body during this transition.
- Prioritize sufficient sleep. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Stay hydrated. Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Communicate openly with your medical team. Report any concerns or worsening symptoms without delay.
Remember, while withdrawal symptoms are common, they are usually manageable. Consistent communication with your doctor and adherence to the tapering schedule are critical for a smoother transition.
Alternative Medications and Therapies During and After Taper
Consider adding 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) medications, like mesalamine, to maintain remission after your prednisone taper. These help reduce inflammation in the gut. Your doctor might suggest a specific 5-ASA formulation depending on your disease location (colon, rectum, or both).
Immunomodulators, such as azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine, offer long-term control by suppressing the immune system’s overreaction. These drugs often take several months to become fully effective, so they may be started while tapering prednisone. Regular blood tests monitor for side effects.
Biologics, including anti-TNF agents (infliximab, adalimumab) or integrin antagonists (vedolizumab, ustekinumab), target specific parts of the immune system more precisely than immunomodulators. These can be extremely beneficial for patients who don’t respond to other treatments. They require careful monitoring for potential side effects.
Dietary changes can support your overall health and potentially ease symptoms. A doctor or registered dietitian can advise on specific dietary adjustments. Consider working with them to create a personalized plan. Focus on easily digestible foods, limiting known trigger foods like dairy or gluten if needed.
Stress management techniques, like mindfulness meditation or yoga, may help reduce inflammation and improve your quality of life. Consider incorporating these practices into your daily routine. Explore guided meditation apps or local yoga studios.
Maintaining Remission and Preventing Relapse of Ulcerative Colitis
Closely monitor your symptoms. Report any changes to your doctor immediately.
Adhere strictly to your prescribed medication regimen. This includes completing your prednisone taper as directed and continuing any maintenance medications, like immunomodulators or biologics, as your doctor recommends.
- Missed doses can increase the risk of relapse; don’t skip doses.
- Understand potential side effects of your medication and report any concerning issues to your physician.
Maintain a healthy diet. This often involves avoiding known triggers, which may include dairy, caffeine, alcohol, or spicy foods. Keep a food diary to identify personal triggers.
Manage stress effectively. Stress can exacerbate ulcerative colitis. Consider techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises. Discuss stress management strategies with your doctor or a therapist.
- Regular exercise, even moderate activity, supports overall well-being.
- Prioritize adequate sleep. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
Attend regular follow-up appointments with your gastroenterologist. These visits allow for ongoing monitoring and adjustments to your treatment plan as needed.
Consider joining a support group. Connecting with others who understand your condition can provide emotional support and practical advice.
Smoking cessation is vital. Smoking is strongly linked to increased inflammation and disease severity. Seek support for quitting if needed.