Need to choose between Prednisone and Medrol? Medrol (methylprednisolone) generally offers a longer duration of action than Prednisone, meaning you may need fewer doses. This can be a significant advantage for managing chronic conditions requiring consistent medication.
However, Prednisone’s shorter half-life allows for quicker adjustments to dosage if needed. This flexibility can be beneficial during acute flare-ups or when precise control of inflammation is paramount. Your physician will consider your specific health needs and condition severity when making a recommendation.
Both medications are corticosteroids, managing inflammation effectively. They share similar side effects, including weight gain, mood changes, and increased blood sugar. Your doctor will carefully weigh the potential benefits against these risks, tailoring treatment to your individual circumstances.
Remember: Never adjust your medication dosage without consulting your doctor. Both Prednisone and Medrol require careful monitoring to manage potential side effects and ensure optimal treatment efficacy. Open communication with your healthcare provider is crucial for successful management of your condition.
- Prednisone vs. Medrol: A Detailed Comparison
- Understanding Prednisone’s Mechanism of Action and Common Side Effects
- How Prednisone Impacts the Body
- Common Side Effects: Be Aware
- Managing Side Effects
- Understanding Medrol’s Mechanism of Action and Common Side Effects
- Prednisone vs. Medrol: Dosage and Administration Differences
- Oral Administration
- Intravenous and Intramuscular Administration
- Dosage Adjustments
- Prednisone vs. Medrol: Choosing the Right Medication for Specific Conditions
- Prednisone vs. Medrol: Potential Drug Interactions and Precautions
Prednisone vs. Medrol: A Detailed Comparison
Medrol (methylprednisolone) and Prednisone are both corticosteroids, but differ slightly in their metabolic pathways. Medrol is metabolized more quickly than Prednisone, potentially resulting in a shorter duration of action. This means you might need more frequent dosing with Medrol to achieve the same effect as Prednisone.
Dosage: Your doctor will tailor the dosage to your specific needs and condition. Generally, Medrol’s initial dose might be slightly lower than Prednisone’s equivalent for similar therapeutic effects because of its faster metabolism. Close monitoring of your response is always necessary.
Side Effects: Both medications carry similar side effect profiles, including increased appetite, weight gain, mood changes, and fluid retention. The severity and frequency vary among individuals. Open communication with your physician about any concerning side effects is key.
Drug Interactions: Both drugs can interact with other medications, notably those affecting the liver or kidneys. Always inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking. This allows them to assess potential conflicts and adjust treatment appropriately.
Which is right for you? The choice between Medrol and Prednisone depends on various factors, including your specific health condition, other medications, and your doctor’s assessment of your individual needs. It is not a simple matter of one being inherently “better” than the other.
Conclusion: Both Medrol and Prednisone are powerful medications. Regular check-ups with your physician are necessary to monitor your progress and adjust the dosage as needed. Never change your dosage or stop taking the medication without first consulting your doctor.
Understanding Prednisone’s Mechanism of Action and Common Side Effects
Prednisone mimics the action of cortisol, a natural steroid hormone your body produces. It works by binding to receptors inside your cells, influencing gene expression and affecting many bodily functions. This leads to reduced inflammation and suppresses your immune system.
How Prednisone Impacts the Body
Specifically, prednisone reduces the production of inflammatory chemicals, easing swelling, pain, and other symptoms of various conditions, from allergies to autoimmune diseases. It also affects the number and activity of immune cells, reducing their ability to attack your own body’s tissues.
Common Side Effects: Be Aware
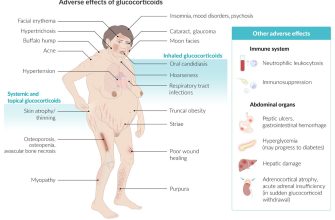
While effective, prednisone can cause side effects. Weight gain, increased appetite, and fluid retention are common. Others include mood changes (irritability, anxiety, depression), increased blood sugar, high blood pressure, and thinning of the skin. Long-term use can increase your risk of osteoporosis and infections.
Managing Side Effects
Your doctor will monitor you closely for side effects. Lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes and regular exercise, can mitigate some issues. Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and duration of treatment. Open communication with your physician is crucial for addressing any concerns you have.
Understanding Medrol’s Mechanism of Action and Common Side Effects
Medrol, or methylprednisolone, is a corticosteroid that mimics the effects of cortisol, a hormone your body naturally produces. It works by reducing inflammation and suppressing your immune system.
This mechanism involves binding to specific receptors within your cells, altering gene expression and thus impacting various bodily processes. This powerful action is what makes it effective in treating numerous inflammatory conditions, but it also means potential side effects are significant.
- Increased blood sugar: Medrol can raise your blood glucose levels, especially with prolonged use. Regular monitoring is advised, particularly for those with diabetes.
- Fluid retention: You might experience swelling in your ankles, feet, or face. Reducing sodium intake can help.
- Increased appetite and weight gain: Medrol’s impact on metabolism frequently leads to increased appetite and weight gain. A balanced diet and exercise are recommended.
- Mood changes: Some individuals experience irritability, anxiety, or even depression while taking Medrol. Open communication with your doctor is crucial.
- Weakened immune system: Because Medrol suppresses your immune system, you may be more susceptible to infections. Good hygiene practices are paramount.
- Osteoporosis: Long-term Medrol use can increase the risk of osteoporosis. Your doctor may recommend calcium and vitamin D supplements.
- Thinning skin: Medrol can thin your skin, making it more susceptible to bruising and injury. Gentle skincare is recommended.
- Gastrointestinal issues: Some patients experience heartburn, nausea, or ulcers. Your doctor may recommend medication to protect your stomach lining.
The severity of these side effects varies depending on the dosage, duration of treatment, and individual factors. Always discuss potential side effects and risk factors with your physician before beginning or continuing Medrol treatment. They can help you manage these risks and monitor your progress.
Remember, this information is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment.
Prednisone vs. Medrol: Dosage and Administration Differences
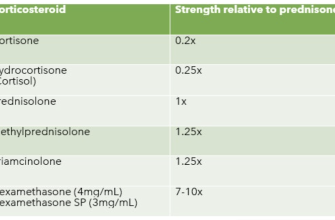
Medrol (methylprednisolone) and Prednisone are both corticosteroids, but their dosages differ. Medrol is generally administered at lower doses than Prednisone to achieve the same therapeutic effect. This is because methylprednisolone is more potent than prednisone. For example, a 4mg dose of Medrol roughly equates to a 5mg dose of Prednisone.
Oral Administration
Both medications are commonly taken orally. Follow your doctor’s prescribed dosage and schedule precisely. Never adjust your dosage without consulting your physician. Missed doses should be taken as soon as possible, unless it’s nearly time for the next dose; in this case, skip the missed dose and resume your normal schedule.
Intravenous and Intramuscular Administration
Medrol also comes in injectable forms (intravenous and intramuscular), offering a faster onset of action than oral prednisone in situations requiring rapid treatment. Prednisone, however, is primarily administered orally. Your doctor will determine the appropriate route of administration based on your individual needs and medical condition. Injectable forms require medical supervision. Always discuss potential side effects and appropriate management with your physician.
Dosage Adjustments
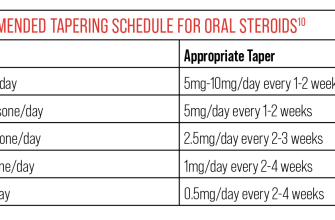
Dosage adjustments for both medications depend on your response to treatment, the severity of your condition, and potential side effects. Your doctor will monitor you closely and adjust your dosage as needed. They may gradually reduce your dosage as your condition improves to minimize withdrawal symptoms.
Prednisone vs. Medrol: Choosing the Right Medication for Specific Conditions
Both prednisone and Medrol (methylprednisolone) are corticosteroids, but their applications vary slightly. Medrol is often preferred for intravenous administration in severe inflammatory conditions like acute exacerbations of multiple sclerosis or severe allergic reactions due to its longer duration of action. Oral prednisone, conversely, suits long-term management of conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus, offering better convenience.
For inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), doctors frequently prescribe prednisone for inducing remission during flare-ups, given its rapid onset of action. However, maintaining remission often requires different medications, as prolonged prednisone use carries significant side effects. Medrol might be used intravenously in severe IBD cases requiring immediate intervention.
Asthma management frequently involves both medications. Prednisone’s oral route makes it suitable for managing acute exacerbations at home. However, Medrol, administered intravenously or intramuscularly, can be more effective for severe attacks requiring hospitalization.
Ultimately, the choice depends on several factors: the severity and type of condition, the patient’s overall health, and the preferred route of administration. Always consult with your doctor to determine the most appropriate medication for your specific needs.
Prednisone vs. Medrol: Potential Drug Interactions and Precautions
Both prednisone and Medrol (methylprednisolone) interact with numerous medications. Always inform your doctor of all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, you are taking before starting either prednisone or Medrol.
Warfarin: Prednisone and Medrol can decrease warfarin’s effectiveness, increasing your risk of blood clots. Regular blood monitoring is crucial.
NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs): Concurrent use with NSAIDs like ibuprofen or naproxen increases the risk of stomach ulcers and bleeding. Your doctor might recommend a protective medication.
Diabetes Medications: These corticosteroids can raise blood sugar levels, potentially requiring adjustments to your diabetes medication.
Potassium-Depleting Diuretics: The combination increases the risk of hypokalemia (low potassium). Your doctor may monitor your potassium levels.
Antibiotics (e.g., rifampin): Some antibiotics can speed up the breakdown of prednisone and Medrol, reducing their effectiveness. Dosage adjustments might be necessary.
Precautions: Avoid alcohol consumption, as it can increase the risk of stomach ulcers and other side effects. Report any unusual bruising, weight gain, mood changes, or vision problems to your doctor immediately. Gradual tapering of the dosage is necessary to avoid withdrawal symptoms upon stopping the medication. Regular monitoring of blood pressure and blood sugar is often advised.
Note: This information is not exhaustive. This section provides a glimpse into potential interactions and precautions. Consult your physician or pharmacist for personalized advice and a complete understanding of potential risks associated with your specific medical situation and medication interactions.