Need reliable information on Prednisone? WebMD offers a wealth of resources, but navigating them efficiently requires a clear strategy. Focus your search on specific aspects: dosage, side effects, interactions with other medications, and potential long-term implications. Don’t hesitate to use WebMD’s search function with precise keywords for targeted results.
Remember to always verify information found online with your doctor or pharmacist. While WebMD provides valuable patient information, it’s not a substitute for professional medical advice. Pay close attention to the detailed descriptions of potential side effects, particularly those pertaining to your individual health history and other medications you’re currently taking. WebMD’s drug interaction checker is particularly helpful in this regard.
Specifically, look for sections on potential complications of prolonged use. Understand the tapering process is crucial to avoid withdrawal symptoms. WebMD’s articles often include patient testimonials that may provide additional context and perspective on managing the medication. Use this supplementary information judiciously; individual experiences can vary significantly.
Finally, bookmark relevant WebMD pages for easy access to the information you need. Regularly review this information to ensure you stay informed and empowered in your healthcare decisions. Always prioritize communication with your healthcare provider about any questions or concerns regarding Prednisone.
- WebMD Prednisone: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding Prednisone
- Managing Side Effects
- Dosage and Duration
- Interactions and Precautions
- WebMD’s Role
- Finding Reliable Information
- Understanding Prednisone: Uses and Indications
- Prednisone Dosage: What WebMD Recommends
- Factors Influencing Prednisone Dosage
- Typical Prednisone Regimen Examples (Illustrative, Not a Recommendation)
- Common Side Effects of Prednisone as Detailed on WebMD
- Gastrointestinal Issues
- Metabolic Changes
- Other Potential Side Effects
- Important Note:
- Serious Side Effects: When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
- Severe Allergic Reactions
- Signs of Infection
- Severe Stomach Pain
- Mental Health Changes
- Muscle Weakness or Severe Pain
- Prednisone and Interactions with Other Medications (WebMD)
- How to Safely Stop Prednisone: WebMD’s Advice
- Prednisone and Pregnancy/Breastfeeding: WebMD Insights
- Pregnancy
- Breastfeeding
- Important Note
- WebMD’s Resources for Patient Support and Further Information
- Connecting with Healthcare Professionals
- Patient Forums and Communities
- Finding Reliable Information on WebMD about Prednisone
WebMD Prednisone: A Comprehensive Guide
Always consult your doctor before starting or stopping Prednisone. WebMD provides information, not medical advice.
Understanding Prednisone
Prednisone is a corticosteroid, reducing inflammation and suppressing the immune system. Doctors prescribe it for various conditions, including allergies, asthma, autoimmune diseases, and certain cancers. It’s crucial to understand its effects and potential side effects.
Managing Side Effects
Common side effects include weight gain, increased appetite, mood changes, and increased blood sugar. To mitigate these, maintain a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and monitor your blood sugar. Discuss any concerning side effects immediately with your physician. They can adjust your dosage or recommend strategies to manage symptoms.
Dosage and Duration
Dosage depends on your specific condition and response to treatment. Your doctor determines the appropriate dose and duration. Never adjust your dosage without consulting them. Abruptly stopping Prednisone can lead to withdrawal symptoms.
Interactions and Precautions
Prednisone can interact with other medications. Inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you’re taking. Individuals with certain conditions, such as diabetes or glaucoma, may require close monitoring while on Prednisone.
WebMD’s Role
WebMD offers detailed information on Prednisone, including its uses, side effects, and potential interactions. This information complements, but doesn’t replace, medical advice from your doctor. Use WebMD as a resource, but always prioritize professional medical guidance.
Finding Reliable Information
Always verify information found on WebMD with your doctor or pharmacist. They can provide personalized advice based on your individual health needs and medical history. Remember, responsible self-care involves collaboration with your healthcare team.
Understanding Prednisone: Uses and Indications
Prednisone, a corticosteroid medication, effectively reduces inflammation and suppresses the immune system. Doctors prescribe it for various conditions requiring these actions.
Autoimmune diseases like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis benefit significantly from prednisone’s anti-inflammatory properties, helping manage symptoms and slow disease progression. This reduces joint pain, swelling, and stiffness.
Allergic reactions, including severe cases like anaphylaxis, respond well to prednisone’s ability to quell the immune response. It quickly reduces symptoms such as swelling and breathing difficulties.
Certain cancers respond favorably to prednisone when used in conjunction with other cancer therapies. It helps shrink tumors and improve overall treatment outcomes in specific cancer types.
Inflammatory bowel diseases, such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, frequently see improvement with prednisone’s anti-inflammatory effects, reducing inflammation in the digestive tract.
Conditions like asthma and other respiratory illnesses often benefit from prednisone’s ability to reduce airway inflammation and improve breathing. It offers relief from symptoms like wheezing and shortness of breath.
It’s crucial to remember that prednisone has potential side effects. Discuss these risks and benefits with your doctor before starting treatment. They will carefully consider your medical history and current health to determine the appropriate dosage and duration of treatment. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely.
Prednisone Dosage: What WebMD Recommends
WebMD doesn’t recommend specific dosages; it emphasizes that dosage is strictly determined by your doctor based on your individual needs and health condition. This means you should never self-medicate with Prednisone. Always follow your physician’s instructions.
Factors Influencing Prednisone Dosage
- Your specific condition: Dosage varies widely depending on whether you’re treating allergies, inflammation, or an autoimmune disease.
- Severity of your condition: A more severe condition might necessitate a higher dose.
- Your age and weight: Dosage is often adjusted based on these factors.
- Your overall health: Pre-existing conditions can influence the prescribed dose.
- Your response to treatment: Your doctor might adjust the dosage depending on how well you respond.
WebMD provides information on Prednisone’s potential side effects and interactions, highlighting the importance of open communication with your healthcare provider. This ensures your safety and optimal treatment.
Typical Prednisone Regimen Examples (Illustrative, Not a Recommendation)
It’s crucial to remember that these are examples only, and your actual dosage will differ:
- For allergic reactions, a short course of low-dose Prednisone might suffice.
- For severe inflammatory conditions, a higher dose may be prescribed for a longer duration, potentially tapered gradually.
- For autoimmune diseases, long-term, low-dose Prednisone could be part of a comprehensive management plan.
Remember: Always consult your doctor or pharmacist for any questions regarding your Prednisone prescription. They can provide personalized guidance based on your specific situation.
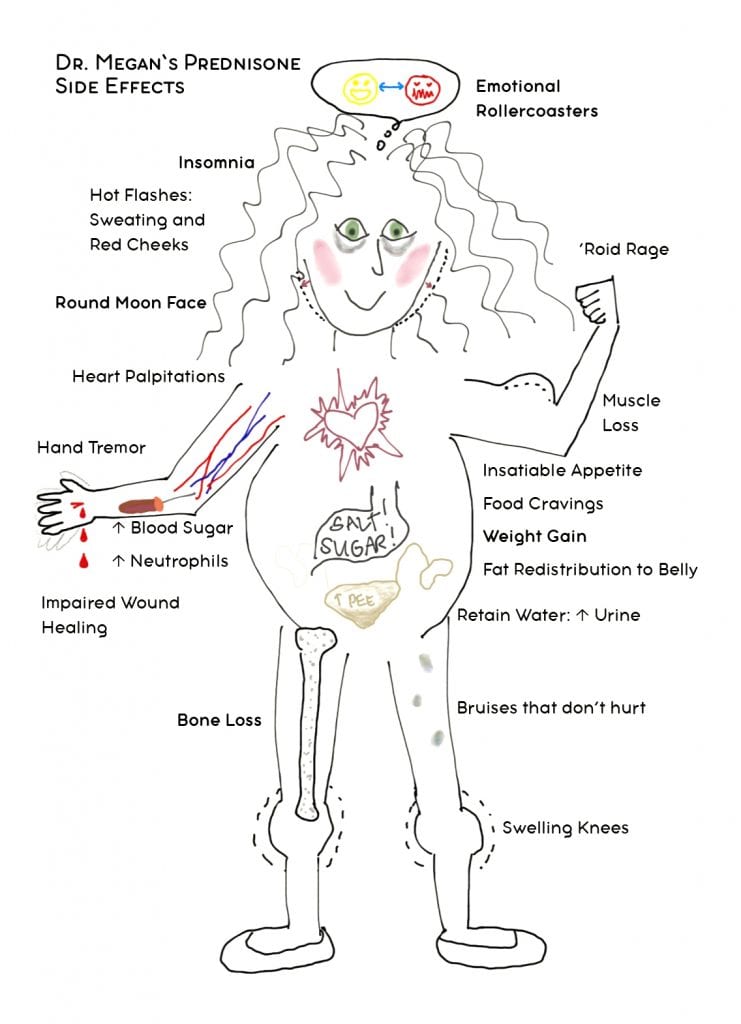
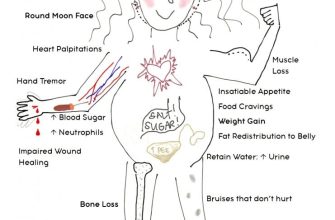
Common Side Effects of Prednisone as Detailed on WebMD
WebMD highlights several common side effects associated with Prednisone use. Understanding these potential effects allows you to better manage your treatment and discuss any concerns with your doctor.
Gastrointestinal Issues
- Heartburn: Prednisone can increase stomach acid production, leading to frequent heartburn.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Some individuals experience nausea or vomiting, often manageable with adjustments to food intake.
- Ulcers: In some cases, Prednisone can increase the risk of stomach ulcers. Your doctor might recommend protective measures.
Metabolic Changes
- Increased Blood Sugar: Prednisone can elevate blood sugar levels, posing a risk for those with diabetes or prediabetes. Regular monitoring is vital.
- Weight Gain: Fluid retention and altered metabolism can contribute to weight gain. A balanced diet and exercise help mitigate this.
- Increased Appetite: Many users experience increased hunger. Careful portion control is recommended.
Other Potential Side Effects
- Mood Changes: Irritability, anxiety, or depression can occur. Open communication with your healthcare provider is crucial.
- Insomnia: Difficulty sleeping is a common side effect. Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule might help.
- Muscle Weakness: Prednisone can weaken muscles, potentially increasing the risk of falls. Exercise caution.
- Increased Risk of Infection: Prednisone suppresses the immune system, making you more susceptible to infections. Practice good hygiene.
- High Blood Pressure: Prednisone may contribute to elevated blood pressure. Regular monitoring is recommended.
Important Note:
This information is for general knowledge and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your physician before starting or stopping Prednisone, reporting any new or worsening symptoms.
Serious Side Effects: When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Prednisone, while effective, carries risks. Contact your doctor immediately if you experience any of the following:
Severe Allergic Reactions
Signs include difficulty breathing, swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat, hives, and severe itching. These are life-threatening and require immediate emergency care.
Signs of Infection
Prednisone weakens your immune system, making you more vulnerable. Watch for high fever, chills, persistent cough, or any signs of infection. Report these promptly to avoid complications.
Severe Stomach Pain
Intense abdominal pain, especially with vomiting or bloody stools, could indicate serious gastrointestinal issues. This requires immediate medical attention.
Mental Health Changes
Prednisone can affect mood. If you experience severe anxiety, depression, hallucinations, or unusual behavior changes, seek immediate medical help. These symptoms can be serious.
Muscle Weakness or Severe Pain
Unusual muscle weakness, pain, or tenderness, especially accompanied by dark urine, might indicate muscle breakdown (rhabdomyolysis). This is a medical emergency.
This information does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your physician regarding Prednisone use and any health concerns.
Prednisone and Interactions with Other Medications (WebMD)
Always inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies, before starting prednisone. This includes prescription medications, especially those for diabetes, blood pressure, osteoporosis, or heart conditions. Prednisone can significantly alter how these medications work, sometimes leading to adverse effects.
Certain combinations demand extra caution. For example, prednisone and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen can increase your risk of stomach ulcers and bleeding. Combining prednisone with blood thinners like warfarin requires close monitoring to prevent excessive bleeding.
The interactions are complex, varying depending on dosage and individual factors. This is why open communication with your doctor is paramount. They can assess your specific situation and recommend adjustments to avoid complications. Never stop taking any medication without consulting your physician.
| Medication Class | Potential Interaction | Possible Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| NSAIDs (Ibuprofen, Naproxen) | Increased risk of gastrointestinal bleeding and ulcers | Monitor for stomach pain, black stools, or vomiting blood. |
| Anticoagulants (Warfarin) | Increased bleeding risk | Regular blood tests to monitor clotting time. |
| Insulin or Oral Hypoglycemics | Increased blood sugar | Monitor blood sugar levels closely; adjust diabetes medication as needed. |
| Digoxin | Increased digoxin levels | Monitor heart rhythm and digoxin levels. |
This table provides a few examples; many other drug interactions are possible. Your doctor will provide personalized advice based on your medical history and current medications. Remember to keep a detailed record of all medications you consume and share it with your healthcare provider during each appointment.
How to Safely Stop Prednisone: WebMD’s Advice
Never stop Prednisone abruptly. A sudden halt can cause serious health problems.
Your doctor will create a tapering schedule. This involves gradually reducing your dose over time. Follow this plan precisely.
- Expect your doctor to decrease your dosage slowly, often by small increments.
- The tapering schedule varies depending on factors like your dosage, treatment duration, and overall health.
- Typical schedules might involve reducing the dose every few days or weeks.
During the tapering process, monitor yourself closely for withdrawal symptoms. Common symptoms include fatigue, muscle weakness, joint pain, and nausea.
- Report any concerning symptoms to your doctor immediately.
- They may adjust your tapering schedule based on your individual response.
Be patient. Reducing Prednisone takes time. The process may last for several weeks or months, depending on your situation.
Maintain open communication with your healthcare provider throughout the entire process. Don’t hesitate to ask questions and address any concerns you may have.
- Regular check-ups are vital to monitor your progress and ensure a safe transition.
- Openly discuss any side effects or changes in your health status.
Stopping Prednisone safely requires careful planning and monitoring. Your doctor’s guidance is paramount. Adherence to their plan is key to minimizing potential risks.
Prednisone and Pregnancy/Breastfeeding: WebMD Insights
Consult your doctor immediately if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or planning pregnancy before starting or continuing Prednisone. Prednisone can cross the placenta and enter breast milk.
Pregnancy
The potential risks to a developing fetus depend heavily on the dosage and duration of Prednisone use. High doses, especially during the first trimester, may increase the risk of cleft palate, low birth weight, and premature birth. Lower doses are generally associated with less risk, but potential risks always warrant careful monitoring by your obstetrician. They will weigh the benefits of the medication against the potential risks to your pregnancy.
Breastfeeding
Prednisone does appear in breast milk. While small amounts may not cause harm to the infant, the decision to breastfeed while on Prednisone should be carefully considered. Doctors often recommend close monitoring of the baby for potential side effects, such as irritability or weight gain issues. The doctor can help determine if the benefits of breastfeeding outweigh any potential risks to the infant. Switching to formula may be an option, discussed with your healthcare provider.
Important Note
This information is for general knowledge and does not constitute medical advice. Always seek personalized guidance from your healthcare professional regarding Prednisone use during pregnancy or breastfeeding. They can assess your specific situation and provide tailored recommendations.
WebMD’s Resources for Patient Support and Further Information
Find reliable information on Prednisone’s usage, side effects, and interactions directly on WebMD’s drug database. This database provides detailed descriptions, including potential risks and benefits. Use the search function to find the specific Prednisone information you need.
Connecting with Healthcare Professionals
WebMD offers tools to locate doctors and other healthcare providers in your area. Use their provider directory to find specialists experienced in managing Prednisone treatment. Schedule a consultation to discuss your specific health concerns and receive personalized advice.
Patient Forums and Communities
Engage with other patients taking Prednisone through WebMD’s support forums. Share experiences, ask questions, and learn from others navigating similar challenges. Remember that this is a support community, not a substitute for professional medical advice.
Finding Reliable Information on WebMD about Prednisone
Check WebMD’s drug information section directly. Search for “prednisone” to access a dedicated page. This page provides details on the medication’s uses, potential side effects, dosage information, and precautions.
Prioritize the sections on “Uses,” “Side Effects,” and “Precautions.” These areas contain vital information about the drug’s intended purposes and potential risks. Pay close attention to warnings and interactions with other medications.
Look for tables summarizing key information. WebMD frequently uses tables to organize data about medications. These help quickly compare different aspects of Prednisone use, making it easier to understand the drug’s properties.
| Section | What to Look For |
|---|---|
| Uses | Specific conditions Prednisone treats. |
| Side Effects | Common and serious side effects, including potential long-term effects. |
| Dosage | Recommended doses, frequency, and duration of treatment. |
| Warnings & Precautions | Conditions that may make Prednisone unsafe, interactions with other drugs, and important considerations before using it. |
Remember, WebMD offers information, not medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting, stopping, or changing your Prednisone dosage. They can address your specific health situation and ensure safe medication use.