Avoid concurrent use of Zostavax and prednisone unless absolutely necessary. Prednisone, a corticosteroid, significantly suppresses the immune system, potentially hindering Zostavax’s effectiveness in building immunity against shingles. This compromise can lead to a reduced efficacy of the vaccine.
If concurrent use is unavoidable due to a pre-existing medical condition requiring prednisone, discuss alternative vaccination schedules with your physician. Consider delaying Zostavax until your prednisone course concludes, allowing your immune system to recover its full function. Your doctor will assess your individual risk factors and health status to determine the best approach.
Close monitoring is critical if you receive both Zostavax and prednisone concurrently. Report any unusual symptoms, such as prolonged inflammation at the injection site or any signs of infection, immediately to your doctor. This proactive approach helps ensure early detection and management of potential complications.
Remember, this information serves as a general guideline, and individual circumstances dictate the optimal course of action. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice based on your specific medical history and current health status. They will help you weigh the risks and benefits of concurrent use or delayed vaccination. A transparent conversation with your physician ensures the safest and most effective treatment plan for you.
- Zostavax and Prednisone Therapy: A Detailed Look
- Understanding Zostavax (Shingles Vaccine)
- Who Should Get Zostavax?
- How Zostavax Works:
- Potential Side Effects:
- Important Considerations:
- Zostavax and Prednisone:
- Disclaimer:
- Prednisone: Its Mechanism and Uses
- Simultaneous Use: Potential Drug Interactions
- Impact on Vaccine Response
- Alternative Timing Strategies
- Monitoring for Side Effects
- Impact on Immune Response to Zostavax
- Increased Risk of Side Effects with Concurrent Use
- Recommended Timing of Zostavax and Prednisone Administration
- Monitoring Patients on Concurrent Therapy
- Assessing Immunosuppression
- Tracking Adverse Events
- Clinical Monitoring Summary
- Patient Education
- Consult Your Doctor: Importance of Personalized Advice
- Understanding Your Individual Risks
- Creating a Personalized Treatment Plan
- Questions to Ask Your Doctor
- Remember: Your health is unique. A personalized approach ensures the safest and most effective treatment.
Zostavax and Prednisone Therapy: A Detailed Look
Simultaneous use of Zostavax and prednisone requires careful consideration. Prednisone, a corticosteroid, weakens the immune system. This impacts Zostavax’s effectiveness, as the vaccine relies on a robust immune response to provide protection against shingles.
Here’s what you need to know:
- Timing is crucial: Ideally, avoid receiving Zostavax while on prednisone or within a month of stopping prednisone. This allows your immune system to recover enough to mount an adequate response to the vaccine.
- Dosage matters: The impact of prednisone depends on the dosage and duration of treatment. Higher doses and longer treatment periods carry a greater risk of interfering with Zostavax.
- Consult your doctor: Discuss your medication regimen with your physician before receiving Zostavax. They can assess your individual risk and determine the best course of action. They may recommend postponing the vaccination or suggest alternative strategies.
If you’re already taking prednisone and need the Zostavax vaccine, your doctor might:
- Suggest waiting until your prednisone course is completed and your immune system has recovered.
- Adjust your prednisone dosage if possible, aiming to minimize immune suppression.
- Monitor your response to the vaccine more closely than usual.
Remember, these are general guidelines. Your doctor will provide personalized advice based on your specific health condition and medical history. Always prioritize open communication with your healthcare provider to ensure safe and effective medical management.
Potential complications from simultaneous use include a reduced antibody response, leading to lower protection against shingles. Open communication with your doctor is key to mitigating these risks.
Understanding Zostavax (Shingles Vaccine)
Zostavax is a vaccine designed to prevent shingles, a painful rash caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), the same virus that causes chickenpox. It’s crucial to understand how it works and who should receive it.
Who Should Get Zostavax?
The CDC recommends Zostavax for adults 50 years and older, even if they’ve had chickenpox. This includes adults with weakened immune systems, although its effectiveness might be lower in this group. However, consult your doctor about vaccination if you have a compromised immune system or specific health conditions.
How Zostavax Works:
- Zostavax contains a weakened live virus. This helps your immune system build protection against the VZV.
- This protection reduces your risk of getting shingles and significantly lessens the severity of the illness if you do contract it.
- Two doses of a newer shingles vaccine, Shingrix, are now recommended over Zostavax. Talk to your doctor for advice on which vaccine best suits you.
Potential Side Effects:
- Pain at the injection site is common.
- Other possible side effects include redness, swelling, and itching at the injection site. These usually resolve on their own.
- Rarely, more serious side effects can occur. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe allergic reactions.
Important Considerations:
Inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including prednisone, before receiving the Zostavax vaccine. Certain medications can affect the vaccine’s efficacy. Follow your doctor’s advice on the appropriate timing for vaccination.
Zostavax and Prednisone:
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, can weaken the immune system. Discuss the use of prednisone and the Zostavax vaccination with your physician, as the interplay between the two requires careful consideration. Your doctor can determine the optimal time for vaccination given your prednisone regimen.
Disclaimer:
This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your doctor for personalized guidance.
Prednisone: Its Mechanism and Uses
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, powerfully reduces inflammation by binding to intracellular receptors. This action suppresses the immune system, decreasing the production of inflammatory molecules like cytokines. This mechanism makes it highly effective against a wide array of inflammatory conditions.
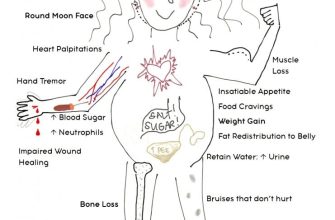
Prednisone finds application in treating various ailments. Its anti-inflammatory properties are harnessed in managing autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. It also effectively controls allergic reactions and asthma. Furthermore, it’s used to treat certain cancers and manage swelling associated with injuries or surgeries.
| Condition | Prednisone’s Role |
|---|---|
| Rheumatoid Arthritis | Reduces joint inflammation and pain. |
| Lupus | Manages inflammation and autoimmune activity. |
| Asthma | Reduces airway inflammation, improving breathing. |
| Allergic Reactions | Suppresses the immune response to allergens. |
| Certain Cancers | Used in conjunction with other cancer treatments. |
| Post-surgical Swelling | Reduces inflammation and swelling after surgery. |
Dosage and treatment duration vary significantly depending on the specific condition and patient response. Always consult a physician for proper prescription and monitoring, especially when considering concurrent medications like Zostavax. Potential side effects include increased blood sugar, weight gain, and weakened immunity. Close monitoring for these effects is vital for safe and effective use.
Simultaneous Use: Potential Drug Interactions
Avoid concurrent use of Zostavax and prednisone without consulting your doctor. Prednisone, a corticosteroid, suppresses the immune system. Zostavax, a live attenuated vaccine, requires a robust immune response for effectiveness. This combination may reduce the vaccine’s efficacy, potentially leaving you vulnerable to shingles.
Impact on Vaccine Response
Studies haven’t definitively quantified the exact reduction in Zostavax effectiveness caused by prednisone, but the immunosuppressive effect is well-documented. The higher the prednisone dosage and the longer the treatment duration, the greater the risk of impaired vaccine response. Your doctor will weigh the benefits of prednisone therapy against the potential risk of reduced Zostavax protection.
Alternative Timing Strategies
If prednisone treatment is unavoidable, delaying Zostavax administration until after the prednisone course is complete is generally recommended. Your physician can determine the appropriate waiting period depending on the prednisone dosage and your individual health status. This minimizes the risk of compromised immunity during vaccination. Always discuss your medication schedule with your doctor before getting any vaccines.
Monitoring for Side Effects
Even with careful timing, monitor yourself closely for any unusual symptoms after receiving the Zostavax vaccine while taking or having recently taken prednisone. Report any concerning signs to your healthcare provider immediately. This may include intensified side effects from either medication or potential signs of shingles.
Impact on Immune Response to Zostavax
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, can weaken the immune system. This means it may reduce the effectiveness of Zostavax, the shingles vaccine. Studies show that higher doses of prednisone, especially those taken long-term, correlate with a diminished antibody response after Zostavax administration. This translates to a potentially lower level of protection against shingles.
Specifically, patients receiving prednisone at doses above 20mg daily for extended periods (more than two weeks) may see a significantly reduced immune response compared to those not on corticosteroids. Those on lower doses or shorter treatment courses may still experience some reduction, but the impact might be less pronounced.
Important Note: This doesn’t mean Zostavax is ineffective for everyone taking prednisone. Many factors influence vaccine response. The timing of prednisone administration relative to Zostavax vaccination is also critical. Delaying Zostavax until prednisone treatment concludes, if feasible, is generally recommended. Consult your doctor to assess your individual risk and determine the best course of action.
Always discuss your medication regimen, including prednisone and Zostavax, with your physician. They can help weigh the potential benefits and risks to personalize your healthcare plan.
Increased Risk of Side Effects with Concurrent Use
Avoid concurrent use of Zostavax and prednisone if possible. Prednisone, a corticosteroid, weakens the immune system. This suppression increases the chance of experiencing Zostavax side effects, including a higher risk of shingles.
Studies haven’t definitively quantified this increased risk, but clinical experience suggests a higher incidence of side effects among patients using both medications simultaneously. Expect more frequent and potentially severe reactions compared to Zostavax administration alone.
Specific side effects to watch for include: more intense pain at the injection site, more widespread rash, and potentially prolonged recovery time.
Consult your doctor immediately if you experience any unusual or worsening symptoms after receiving the Zostavax vaccine while on prednisone. They can assess your individual risk and advise on the best course of action.
If prednisone is necessary, discuss alternative timing of Zostavax administration with your physician. Delaying the vaccine might be recommended, allowing for a period where prednisone’s immunosuppressive effects have lessened.
Remember, open communication with your healthcare provider is key to managing potential risks associated with concurrent medication use. They can help you make informed decisions regarding your health.
Recommended Timing of Zostavax and Prednisone Administration
Ideally, administer Zostavax before starting a course of prednisone. This minimizes potential interference with the vaccine’s effectiveness.
If prednisone treatment is unavoidable before Zostavax vaccination, consult a healthcare professional. They can assess your individual health status and determine the safest approach, potentially delaying vaccination until prednisone therapy concludes.
A gap of at least one month between the last prednisone dose and Zostavax administration is often recommended. This allows your immune system sufficient time to recover and respond optimally to the vaccine.
High-dose prednisone (greater than 20mg daily for prolonged periods) carries a higher risk of immunosuppression, making the timing of vaccination even more critical. Discuss this with your doctor.
Remember, individual circumstances vary. A physician’s assessment and guidance are necessary to make an informed decision about the optimal timing of Zostavax and prednisone administration.
Monitoring Patients on Concurrent Therapy
Closely monitor patients for adverse effects. Regular blood tests, including complete blood counts (CBCs) and liver function tests (LFTs), are crucial. Frequency depends on individual patient factors and clinical judgement, but at minimum, consider baseline testing before starting concurrent therapy and follow-up tests at 2-4 weeks, then every 3 months. Adjust intervals as needed.
Assessing Immunosuppression
Pay close attention to signs of infection. Patients should report any fever, chills, cough, or unusual fatigue immediately. Assess the patient’s overall health status considering the immunosuppressive effects of both prednisone and the potential for Zostavax to cause a weakened immune response in some individuals. Proactive communication is key.
Tracking Adverse Events
Maintain a detailed record of all medications, including dosages and administration routes. Document any adverse events experienced by the patient, no matter how minor they may seem. This detailed record enables effective monitoring and prompt adjustments to the treatment plan if necessary. Thorough documentation protects both patient and physician.
Clinical Monitoring Summary
| Parameter | Monitoring Frequency | Actionable Findings |
|---|---|---|
| CBC | Baseline, 2-4 weeks, every 3 months (adjust as needed) | Significant decreases in WBC, neutrophils, or lymphocytes |
| LFTs | Baseline, 2-4 weeks, every 3 months (adjust as needed) | Elevated liver enzymes (AST, ALT) |
| Infection signs | Continuous monitoring, patient reporting | Fever, chills, cough, unusual fatigue |
| Adverse Events | Continuous monitoring, patient reporting | Any unusual symptoms or side effects |
Patient Education
Educate patients about potential side effects of both medications and the importance of reporting any changes in their health. Provide clear instructions on medication adherence and what constitutes an urgent situation requiring immediate medical attention. Empower patients to actively participate in their care.
Consult Your Doctor: Importance of Personalized Advice
Schedule a consultation. Discuss your specific health history, including any allergies or other medications you’re taking.
Understanding Your Individual Risks
Your doctor will assess your risk factors for shingles and complications from both Zostavax and prednisone. This includes your age, overall health, and pre-existing conditions. They’ll consider potential interactions between Zostavax and your other medications, especially prednisone.
- Factors influencing Zostavax efficacy: Immune system strength, previous infections.
- Prednisone’s impact: Its dosage and duration of use will be reviewed for potential interference with Zostavax.
- Alternative vaccination options: Your doctor might explore alternatives if Zostavax is deemed unsuitable.
Creating a Personalized Treatment Plan
Based on this assessment, your doctor will create a personalized plan. This may involve adjusting your prednisone dosage, delaying the Zostavax vaccination, or choosing an alternative approach. Clear communication is key.
- Timeline for vaccination: Your doctor will determine the best time for vaccination, considering your prednisone regimen.
- Monitoring for side effects: You will discuss strategies for identifying and managing any potential side effects from either medication or the vaccine.
- Follow-up appointments: Regular check-ups help monitor your response to treatment and address any concerns.
Questions to Ask Your Doctor
- What are the specific risks of Zostavax given my current health status and prednisone use?
- Are there alternative shingles vaccines suitable for my situation?
- What are the potential side effects of Zostavax and prednisone, and how should I manage them?
- How long should I wait after completing my prednisone course before getting the Zostavax vaccine (if applicable)?